Abstract
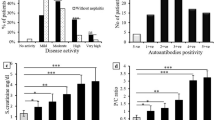
There has been a renewed interest in anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies in the last few years. To assess the prevalence of anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies in patients with systematic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to correlate serum levels of these antibodies with clinical features of the disease, the presence of anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies in 38 patients with SLE was investigated by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). To determine the specificity of these antibodies, 15 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, 15 patients with systemic sclerosis, and 15 normal controls were also tested. Sensitivity of anti-chromatin antibodies in SLE patients was 89.5% and specificity was 80.0%, while sensitivity of anti-histone antibodies was 92.1% and specificity was 82.2%. Significant associations were found between the levels of anti-chromatin antibodies and arthritis, malar rash, oral ulcer, pulmonary affection (P < 0.05) also, lupus nephritis (P < 0.01), and disease activity score as measured by SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI; P < 0.001). Significant association was found between anti-histone antibodies and fatigue (P < 0.05). The incidence of positive anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies was significantly higher than that of anti-dsDNA antibodies in early stage of the disease. We conclude that anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies are both sensitive and specific for SLE and could be a useful addition to the laboratory tests that can help in the diagnosis of SLE. Anti-chromatin antibodies seem to be a promising marker useful in early diagnosis and assessment of disease activity in SLE patients especially in patients who are negative for anti-dsDNA antibodies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherer Y, Gorstein A, Frizler MJ, Shoenfeld Y (2004) Autoantibody explosion in systemic lupus erythematosus: more than 100 different antibodies found in SLE patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34:501–537
Pisetsky DS (2000) Anti-DNA and autoantibodies. Curr Opin Rheumatol 12:364–368
Simon JA, Cabiedes J, Ortiz E, Alcocer-Varela J, Sanchez-Guerrero J (2004) Anti-nucleosome antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus of recent onset. Potential utility as a diagnostic tool and disease activity marker. Rheumatology 43:220–224
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for classification of SLE. Arthritis Rheum 25:377–382
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association (1987): revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatism 31:315–324
Masi AT, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA et al (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590
Bombardier C, Gladman DA, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang DH (1992) And the committee on prognosis studies in SLE. Derivation of the SLEDAI: a disease activity index for lupus patients. Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640
Weening JJ, D'Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB et al (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:241–250
Burlingame RW, Boey ML, Starkebaum G (1994) The central role of chromatin in the autoimmune responses to histones and DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 94:784–192
Gockel S, Binder WL (1985) Immunoglobulin class specific of antihistone. Arthritis Rheum (supple) 28:558
Cervera R, Vinas O, Ramos-Casals M et al (2003) Anti-chromatin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a useful marker for lupus nephropathy. Ann Rheum Dis 62:431–434
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB (1997) Systemic lupus erythematosus clinical and laboratory features. In: Klippel JH, Weyond CM, Wortmann RL (eds) Primer on Rheumatic Diseases, 11th edition 250-257
Kim WU, Kim SI, Yoo WH, Par JH, Min JK, Kim SC, Hong YS, Lee SH, Cho CS, Kim HY (1999) ARDS in SLE patients: Rheumatic Dis. In: Kang-Nam St Mary’s Hospital p. 552-7
Cairns AP, McMillan SA, Crockard AD et al (2003) Antinucleosome antibodies in the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 62:272–273
Moder KG, Miller TD, Tazelaer HD (1999) Cardiac involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mayo Clin Proc 74:275
Roldan CA, Shively BK, Crawford MH (1996) An echocardiographic study of valvular heart disease associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 335:1424–1430
Medina F, Ayala A, Jara LJ, Becerra M, Miranda JM, Fraga A (1997) Acute abdomen is systemic lupus eythematosus: the importance of early laparotomy. Am J Med 103:100–105
Czaja A, Homburger H (2001) Antibodies in liver disease. Gastroenterology 129:239
Cohen MG, Pollard M, Webb J (1992) Antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence, specificity, and relationship to clinical and laboratory features. Ann Rheum Dis 51:61–66
Moss KE, Loannou Y, Sutton SM, Hag I, Isenberg DA (2002) Outcome of a cohort of 300 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus attending a dedicated clinic for over two decades. Ann Rheum Dis 61:409–413
Haddouk S, Ben M, Baklouti S, Hachicha J, Bahloul Z, Masmoudi H (2005) Clinical significance of antinucleosome antibodies in Tunisian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Rheumatol 24:219–222
Chabre H, Amoura Z, Piette JC, Godeau P, Bach JF, Koutouzov S (1995) Presence of nucleosome-restricted antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 38(10):1485–1491
Sato S, Kodera M, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Takehara K (2004) Antinucleosome antibody is a major autoantibody in localized scleroderma. Br J Dermatol 151:1182–1188
Quattrocchi P, Barrile A, Bonanno D et al (2005) The role of antinucleosome antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Results of a study of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other connective tissue diseases. Reumatismo 57:109–113
Ravirajan CT, Rowse L, MacGowan JR, Isenberg DA (2001) An analysis of clinical disease activity and nephritis associated serum autoantibody profiles in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatology 40:1405–1412
Burlingame RW, Cervera R (2002) Anti-chromatin (anti-nucleosome) autoantibodies. Autoimmu Rev 1:321–328
Schett G, Smolen J, Zimmermann C et al (2002) The autoimmune response to chromatin antigens in systemic lupus erythematosus: autoantibodies against histone H1 are a highly specific marker for SLE associated with increased disease activity. Lupus 11:704–715
Ghedira I, Landolsi H, Mankai A, Fabien N, Jeddi M (2006) Antihistones antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus, comparison of three assays: ELISA, dot blot and immunoblot. Pathol Biol (Paris) 54:148–154
Amoura Z, Koutouzov S, Chabre H et al (2000) Presence of anti-nucleosome autoantibodies in a restricted set of connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum 43:76–84
Sato S, Ihr H, Kikuchi K, Takehara K (1994) Antih-histone antibodies in systemic sclerosis: association with pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 37:391–394
Hasegawa M, Sato S, Kikuchi K, Takehara K (1998) Antigen specificity of anti-histone antibodies in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 57:470–475
Gomez-Puerta JA, Molina JF, Anaya JM, Molina J (2001) Clinical significance anti-chromatin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 10(supp1):S73
Hmida Y, Schmit P, Gilson G, Humbel RL (2002) Failure to detect antinucleosome antibodies in scleroderma: comment on the article by Amoura et al. Arthritis Rheum 46:280–282
Ghirardello A, Doria A, Zampieri S et al (2004) Antinucleosome antibodies in SLE: a two-year follow-up study of 101 patients. J Autoimm 22:235–240
Gomez-Puerta JA, Burlingame RW, Cervera R (2006) Anti-chromatin (anti-nucleosome) antibodies. Lupus 15:408–411
Wallace DJ, Lin HC, Shen GQ (1994) Antibodies to histone (H2A–H2B) DNA complexes in the absence of antibodies to double-strand DNA or to (H2A–H2B) complexes are more sensitive and specific for scleroderma–related disorders than for lupus. Arthritis Rheum 37:1795–1797
Gonzalez C, Garcia-Berrocal B, Herraez O, Navajo AJ, Gonzalez-Buitrago J (2004) Antinucleosome, antichromatin, anti-ds DNA and anti-histone antibody reactivity in systemic lupus erythematsus. Clin Chem Lab Med 42:266–272
Fritzler M, Salazar M (1991) Diversity and origin of rheumatology autoantibodies. Clin Microbial Rev 4:256–269
Gompertz NR, Isenberg DA, Turner BM (1990) Correlation between clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus and levels of antihistone antibodies of the IgG, IgA and IgM isotypes. Ann Rheum Dis 49:524–527
Min DJ, Kim SJ, Park SH et al (2002) Anti-nucleosome antibody: significance in lupus patients lacking anti-double stranded DNA antibody. Clin Exp Rheum 20:13–18
Siegert CE, Daha M, Westedt ML (1991) IgG autoantibodies against CIq are correlated with nephritis, hypocomplementaemia, and ds DNA antibodies in systemic lupus disease. J Rheumatol 18:230–234
Siegert CE, Daha MR, Tseng CM (1993) Predictive value of IgG autoantibodies against CIq for nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 52:851–856
Cortés-Hernández J, Ordi-Ros J, Labrador M (2004) Predictors of poor renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis treated with combined pulses of cyclophosphamide and methyl prednisolone. Lupus 12:287–298
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table (1) Suppl.:
Prevalence of SLE Clinical manifestation in various populations. (DOC 173 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabana, A.A., El-Ghawet, A.E., Machaly, S.A. et al. Anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies in Egyptian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 28, 673–678 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1130-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1130-2