Abstract
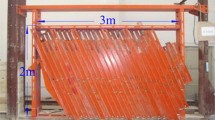
Field examples of fast exploitation from underground coal seams in Bulianta mines, China, show that unexpected developmental rules of settlement and cracks can occur. In situ observation and a physical model consisting of sand, plaster, mica, and calcium carbonate were jointly employed to study the movement of strata, as well as the developmental characteristics of surface cracks. The physical model was observed with a high-precision industrial photogrammetric system. The results indicate that ground cracks are caused by strata deformation, but the formation of ground cracks can, in turn, promote the deformation of strata. Moreover, by contrast with coal mining at a speed of about 2 m/day, we found that the ground does not achieve full subsidence until the advancing distance exceeds 2.2 times the mining depth under rapid excavation (approximately 12 m/day), which would cause large errors for surface settlement prediction. OCF (opening and closing fractures) above gobs are self-closing, but the duration of the closing phase is 3.6 times that of the opening phase, different from the symmetric distribution caused by mining with slower speed. The whole developmental cycle is inversely proportional to mining speed, and fast excavation can shorten development time of OCF. However, the horizontal tension deformation is the most stable factor for predicting ground cracks regardless of excavation speed. The research results can provide theoretical basis for dynamic prediction of ground subsidence and cracks development caused by underground coal mining.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Specifications for the first and second order leveling in China, 2006.
References
Cui X, Miao X, Zhao Y, Jin R (1999) Discussion on the time function of time dependent surface movement. J China Coal Soc 5:453–456
Dai H, Lian X, Liu J, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Deng W, Cai Y (2010) Model study of deformation induced by fully mechanized caving below a thick loess layer. Int J Rock Mech Min 47:1027–1033
Deng K, Tan Z, Jiang Y, Dai H, Shi Y, Xu L (2014) Deformation monitoring and subsidence engineering. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Fan L, Zhang X, Xiang M, Zhang H, Shen T, Lin P (2015) Characteristics of ground fissure development in high intensity mining area of shallow seam in Yushenfu coal field. J China Coal Soc:1442–1447
Ghabraie B, Ren G, Zhang X, Smith J (2015) Physical modelling of subsidence from sequential extraction of partially overlapping longwall panels and study of substrata movement characteristics. Int J Coal Geol 140:71–83
He G, Yang L, Ling G, Jia C, Hong D (1991) Mining subsidence theory. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Hu Z, Wang X, He A (2014) Distribution characteristic and development rules of ground fissures due to coal mining in windy and sandy region. J China Coal Soc:11–18
Huang F, Zhu H, Xu Q, Cai Y, Zhuang X (2013) The effect of weak interlayer on the failure pattern of rock mass around tunnel - scaled model tests and numerical analysis. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 35:207–218
Lee Y, Bassett RH (2007) Influence zones for 2D pile-soil-tunnelling interaction based on model test and numerical analysis. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 22:325–342
Li G, Li Z (2011) The principles and applications of industrial measuring systems. Surveying and Mapping Press, Beijing
Li L, Wu K, Zhou D (2014) AutoCAD-based prediction of 3D dynamic ground movement for underground coal mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci:194–203
Liu P (1986) Model test study on double lining of tunnels. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 1:53–58
Liu Y, Zhou F, Liu L, Liu C, Hu S (2011) An experimental and numerical investigation on the deformation of overlying coal seams above double-seam extraction for controlling coal mine methane emissions. Int J Coal Geol 87:139–149
Ni X, Wang F (2014) Technical study and practice of thick coal mining under watercourse in Yanzhou mining area. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Shi X, Xu J, Zhu W (2008) Site measurement on surface subsidence occurred by coal mining with high cutting height under complicated conditions in Bulianta Mine. Coal Sci Technol:80–83
Thongprapha T, Fuenkajorn K, Daemen JJK (2015) Study of surface subsidence above an underground opening using a trap door apparatus. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 46:94–103
Wang X (2014) Monitoring, evolution and self-healing characteristic of land damage due to high tension coal mining in windy and sandy area. China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, p 136
Wang L, Chu Y, Zhao N (2010) Numerical simulation study on ground fissures induced by mining. J Shenyang Jianzhu Univ (Nat Sci):1138–1141.
Whittaker BN, Reddish DJ (1989) Subsidence Occurrence. Elsevier, Prediction and Control
Whittaker BN, Reddish DJ, Fitzpatrick DJ (1985) Ground fractures due to longwall mining subsidence. In: International Mine Water Association: Granada, Spain. pp 1057–1072.
Wu K, Hu Z, Chang J, Ge J (1997) Distribution law of ground crack induced by coal mining. J China Univ Min Technol:56–59.
Wu K, Cheng G, Zhou D (2015) Experimental research on dynamic movement in strata overlying coal mines using similar material modeling. Arab J Geosci 8:6521–6534
Zhang D, Liang J, Guo C, Liu J, Zhang X, Chen Z (2010) Exploitation of photogrammetry measurement system. Opt Eng 49
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China and Shenhua Group Co., Ltd. (Grant number U1361203). The authors would like to thank the editor and reviewers for their contributions on the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wu, K., Li, L. et al. Ground cracks development and characteristics of strata movement under fast excavation: a case study at Bulianta coal mine, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78, 325–340 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1047-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1047-y