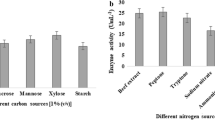
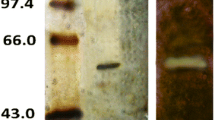
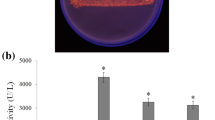
Abstract
A haloalkaliphilic solvent-tolerant lipase was produced from Alkalibacillus salilacus within 48 h of growth in liquid medium. An overall 4.9-fold enhanced production was achieved over unoptimized media after medium optimization by statistical approaches. Plackett–Burman screening suggested lipase production maximally influenced by olive oil, KH2PO4, NaCl, and glucose; and response surface methodology predicted the appropriate levels of each parameter. Produced lipase was highly active and stable over broad ranges of temperature (15–65 °C), pH (4.0–11.0), and NaCl concentration (0–30 %) showing excellent thermostable, pH-stable, and halophilic properties. The enzyme was optimally active at pH 8.0 and 40 °C. Majority of cations, except some like Co2+ and Al3+ were positive signals for lipase activity. In addition, the presence of chemical agents and organic solvents with different log P ow was well tolerated by the enzyme. Finally, efficacy of lipase-mediated esterification of various alcohols with oleic acid in organic solvents was studied.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlercreutz P (2013) Immobilisation and application of lipases in organic media. Chem Soc Rev 42:6406–6436
Aghaie-Khouzani M, Forootanfar H, Moshfegh M, Khoshayand MR, Faramarzi MA (2012) Decolorization of some synthetic dyes using optimized culture broth of laccase producing ascomycete Paraconiothyrium variabile. Biochem Eng J 60:9–15
Ahmed EH, Raghavendra T, Madamwar D (2010) An alkaline lipase from organic solvent tolerant Acinetobacter sp. EH28: application for ethyl caprylate synthesis. Bioresour Technol 101:3628–3634
Balan A, Ibrahim D, Abdul-Rahim R (2013) Organic-solvent and surfactant tolerant thermostable lipase, isolated from a thermophilic bacterium, Geobacillus thermodenitrificans IBRL-nra. Adv Stud Biol 5:389–401
Boran R, Ugur A (2010) Partial purification and characterization of the organic solvent-tolerant lipase produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens RB02-3 isolated from milk. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 40:229–241
Box GEP, Wilson KB (1951) On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol 13:1–45
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burkert JFM, Maugeri F, Rodrigues MI (2004) Optimization of extracellular lipase production by Geotrichum sp. using factorial design. Bioresour Technol 91:77–84
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2002) Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 6th edn. Benjamin Cummings, Menlo Park, pp 133–198
Cheng SW, Wang YF, Liu FF (2011) Optimization of medium compositions using statistical experimental design to produce lipase by Bacillus subtilis. Chem Biochem Eng Q 25:377–383
Dandavate V, Jinjala J, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2009) Production, partial purification and characterization of organic solvent tolerant lipase from Burkholderia multivorans V2 and its application for ester synthesis. Bioresour Technol 100:3374–3381
de Lourdes Moreno M, Pérez D, García MT, Mellado E (2013) Halophilic bacteria as a source of novel hydrolytic enzymes. Life 3:38–51
Dheeman DS, Frias JM, Henehan GT (2010) Influence of cultivation conditions on the production of a thermostable extracellular lipase from Amycolatopsis mediterranei DSM 43304. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:1–17
Dheeman DS, Henehan GTM, Frías JM (2011) Purification and properties of Amycolatopsis mediterranei DSM 43304 lipase and its potential in flavour ester synthesis. Bioresour Technol 102:3373–3379
Ebrahimpour A, Zaliha Abd Rahman RN, Ean Ch’ng DH, Basri M, Salleh AB (2008) A modeling study by response surface methodology and artificial neural network on culture parameters optimization for thermostable lipase production from a newly isolated thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. BMC Biotechnol 8:15
Enache M, Kamekura M (2010) Hydrolytic enzymes of halophilic microorganisms and their economic values. Rom J Biochem 47:47–59
Esakkiraj P, Prabakaran G, Maruthiah T, Immanuel G, Palavesam A (2014) Purification and characterization of halophilic alkaline lipase from Halobacillus sp. DOI, Proc Natl Acad Sci India, Sect B. doi:10.1007/s40011-014-0437-1
Essamri M, Deyris V, Comeau L (1998) Optimization of lipase production by Rhizopus oryzae and study on the stability of lipase activity in organic solvents. J Biotechnol 60:97–103
Gupta N, Sahai V, Gupta R (2007) Alkaline lipase from a novel strain Burkholderia multivorans: statistical medium optimization and production in a bioreactor. Process Biochem 42:518–526
Haaland PD (1989) Experimental design in biotechnology. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 1–18
Hasan-Beikdashti M, Forootanfar H, Safiarian MS, Ameri A, Ghahremani MH, Khoshayand MR, Faramarzi MA (2012) Optimization of culture conditions for production of lipase by a newly isolated bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43:670–677
Hun CJ, Abd Rahman RNZ, Salleh AB, Basri M (2003) A newly isolated organic solvent tolerant Bacillus sphaericus 205y producing organic solvent-stable lipase. Biochem Eng J 15:147–151
Jaeger K-E, Dijkstra BW, Reetz MT (1999) Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:315–351
Ji Q, Xiao S, He B, Liu X (2010) Purification and characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa LX1 and its application for biodiesel production. J Mol Catal B Enzym 66:264–269
Khunt M, Pandhi N (2012) Purification and characterization of lipase from extreme halophiles isolated from little rann of Kutch, Gujarat, India. Int J Life Sci Pharma Res 2:L55–L61
Kouker G, Jaeger KE (1987) Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:211–213
Laane C, Boeren S, Vos K, Veeger C (1987) Rules for optimization of biocatalysis in organic solvents. Biotechnol Bioeng 30:81–87
Li X, Qian P, Wu SG, Yu HY (2014) Characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Idiomarina sp. W33 and its application for biodiesel production using Jatropha oil. Extremophiles 18:171–178
Mahanta N, Gupta A, Khare SK (2008) Production of protease and lipase by solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PseA in solid-state fermentation using Jatropha curcas seed cake as substrate. Bioresour Technol 99:1729–1735
Marques TA, Baldo C, Borsato D, Buzato JB, Celligoi MAPC (2014) Production and partial characterization of a thermostable, alkaline and organic solvent tolerant lipase from Trichoderma atroviride 676. Int J Sci Technol Res 3:77–83
Mehta A, Kumar R, Gupta R (2012) Isolation of lipase producing thermophilic bacteria: optimization of production and reaction conditions for lipase from Geobacillus sp. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 59:435–450
Mevarech M, Frolow F, Gloss LM (2000) Halophilic enzymes: proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys Chem 86:155–164
Meyer RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-Cook CM (2009) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. Wiley, Canada
Moshfegh M, Shahverdi AR, Zarrini G, Faramarzi MA (2013) Biochemical characterization of an extracellular polyextremophilic a-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Halorubrum xinjiangense. Extremophiles 17:677–687
Pérez D, Martín S, Fernández-Lorente G, Filice M, Guisán JM, Ventosa A, García MT, Mellado E (2011) A novel halophilic lipase, LipBL, showing high efficiency in the production of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). PLoS One 6:1–11
Rao P, Divakar S (2001) Lipase catalyzed esterification of α-terpineol with various organic acids: application of the Plackett–Burman design. Process Biochem 36:1125–1128
Rao PV, Jayaraman K, Lakshmanan CM (1993) Production of lipase by Candida rugosa in solid state fermentation. 2: medium optimization and effect of aeration. Process Biochem 28:391–395
Reis P, Holmberg K, Watzke H, Leser ME, Miller R (2009) Lipases at interfaces: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 147–148:237–250
Schmid RD, Verger R (1998) Lipases: interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 37:1608–1633
Sharma D, Sharma B, Shukla AK (2011) Biotechnological approach of microbial lipases: a review. Biotechnol 10:23–40
Sinha R, Khare SK (2014) Effect of organic solvents on the structure and activity of moderately halophilic Bacillus sp. EMB9 protease. Extremophiles. doi:10.1007/s00792-014-0683-4
Treichel H, de Oliveira D, Mazutti MA, Di Luccio M, Oliveira JV (2010) A review on microbial lipases production. Food Bioprocess Technol 3:182–196
Verger R (1997) Interfacial activation of lipases: facts and artifacts. Trends Biotechnol 15:32–38
Volpato G, Rodrigues RC, Heck JX, Ayub MAZ (2008) Production of organic solvent tolerant lipase by Staphylococcus caseolyticus EX17 using raw glycerol as substrate. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:821–828
Wu G, Wu G, Zhan T, Shao Z, Liu Z (2013) Characterization of a cold-adapted and salt-tolerant esterase from a psychrotrophic bacterium Psychrobacter pacificensis. Extremophiles. doi:10.1007/s00792-013-0562-4
Yoo HY, Simkhada JR, Cho SS, Park DH, Kim SW, Seong CN, Yoo JC (2011) A novel alkaline lipase from Ralstonia with potential application in biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 102:6104–6111
Zaks A, Klibanov AM (1988) The Effect of water on enzyme action in organic media. Biol Chem 263:8017–8021
Zaliha RN, Rahman RA, Baharum SN, Salleh AB, Basri M (2006) S5 lipase: an organic solvent tolerant enzyme. J Microbiol 44:583–590
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the Grant No. 93-01-90-25247 from Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran to M.A.F.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Driessen.
M. R. Khoshayand is the correspondence for the section of statistical experimental design.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samaei-Nouroozi, A., Rezaei, S., Khoshnevis, N. et al. Medium-based optimization of an organic solvent-tolerant extracellular lipase from the isolated halophilic Alkalibacillus salilacus . Extremophiles 19, 933–947 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0769-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0769-7