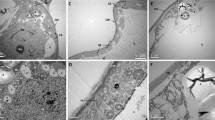
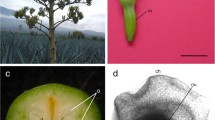
Abstract
Somatic embryogenesis is a morphogenetic route useful for the study of embryonic development, as well as the large-scale propagation of endangered species, such as the Brazilian pine (Araucaria angustifolia). In the present study, we investigated the morphological and ultrastructural organization of A. angustifolia somatic embryo development by means of optical and electron microscopy. The proembryogenic stage was characterized by the proliferation of proembryogenic masses (PEMs), which are cellular aggregates composed of embryogenic cells (ECs) attached to suspensor-like cells (SCs). PEMs proliferate through three developmental stages, PEM I, II, and III, by changes in the number of ECs and SCs. PEM III-to-early somatic embryo (SE) transition was characterized by compact clusters of ECs growing out of PEM III, albeit still connected to it by SCs. Early SEs showed a dense globular embryonic mass (EM) and suspensor region (SR) connected by embryonic tube cells (TCs). By comparison, early somatic and zygotic embryos showed similar morphology. ECs are round with a large nucleus, nucleoli, and many cytoplasmic organelles. In contrast, TCs and SCs are elongated and vacuolated with cellular dismantling which is associated with programmed cell death of SCs. Abundant starch grains were observed in the TCs and SCs, while proteins were more abundant in the ECs. Based on the results of this study, a fate map of SE development in A. angustifolia is, for the first time, proposed. Additionally, this study shows the cell biology of SE development of this primitive gymnosperm which may be useful in evolutionary studies in this area.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- CA:
-
Cytochemical analysis
- CBB:
-
Coomassie Brilliant Blue
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
- ECs:
-
Embryogenic cells
- EM:
-
Embryonic mass
- FLD:
-
Fluridone
- LM:
-
Light microscopy
- PAS:
-
Periodic acid-Schiff
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol 3350
- PEM:
-
Proembryogenic mass
- PEMs:
-
Proembryogenic masses
- PGRs:
-
Plant growth regulators
- SCs:
-
Suspensor-like cells
- SR:
-
Suspensor region
- SE:
-
Somatic embryo
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TB-O:
-
Toluidine blue
- TCs:
-
Embryonic tube cells
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
References
Abrahamsson M, Valadares S, Larsson E, Clapham D, von Arnold S (2012) Patterning during somatic embryogenesis in Scots pine in relation to polar auxin transport and programmed cell death. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109:391–400
Astarita LV, Guerra MP (1998) Early somatic embryogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia —induction and maintenance of embryonal-suspensor mass cultures. Braz J Plant Physiol 10:113–118
Baker CN, Banerjee SN, Tenover FC (1994) Evaluation of alamar colorimetric MIC method for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol 32:1261–1267
Balbuena TS, Silveira V, Junqueira M, Dias LLC, Santa-Catarina C, Shevchenko A, Floh EIS (2009) Changes in the 2-DE protein profile during zygotic embryogenesis in Brazilian Pine (Araucaria angustifolia). J Proteome 72:337–352
Dodeman VL, Ducreux G, Kreis M (1997) Zygotic embryogenesis versus somatic embryogenesis. J Exp Bot 48:1493–1509
Dogra PD (1978) Morphology, development and nomenclature of conifer embryo. Phytomorphology 28:307–322
Domínguez F, Cejudo FJ (2012) A comparison between nuclear dismantling during plant and animal programmed cell death. Plant Sci 197:114–121
Durzan DJ (2008) Monozygotic cleavage polyembryogenesis. Cytol Genet 42:159–173
Dutra NT, Silveira V, de Azevedo IG, Gomes-Neto LR, Façanha AR, Steiner N, Guerra MP, Floh EIS, Santa-Catarina C (2013) Polyamines affect the cellular growth and structure of pro- embryogenic masses in Araucaria angustifolia embryogenic cultures through the modulation of proton pump activities and endogenous levels of polyamines. Physiol Plant 148:121–132
Elbl PM, Lira BS, Andrade SCS, Jo L, Santos ALW, Coutinho LL, Floh EIS, Rossi MM (2015) Comparative transcriptome analysis of early somatic embryo formation and seed development in Brazilian pine Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:903–915
Farias-Soares FL, Burrieza HP, Steiner N, Maldonado S, Guerra MP (2013) Immunoanalysis of dehydrins in Araucaria angustifolia embryos. Protoplasma 250:911–918
Farias-Soares FL, Steiner N, Schmidt EC, Pereira MLT, Rogge-Renner GD, Bouzon ZL, Floh EIS, Guerra MP (2014) The transition of proembryogenic masses to somatic embryos in Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze is related to the endogenous contents of IAA, ABA and polyamines. Acta Physiol Plant 36:1853–1865
Filonova LH, Bozhkov PV, von Arnold S (2000a) Developmental pathway of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies as revealed by time-lapse tracking. J Exp Bot 51:249–264
Filonova LH, Bozhkov PV, Brukhin VB, Daniel G, Zhivotovsky B, von Arnold S (2000b) Two waves of programmed cell death occur during formation and development of somatic embryos in the gymnosperm, Norway spruce. J Cell Sci 113:4399–4411
Filonova LH, Von Arnold S, Daniel G, Bozhkov PV (2002) Programmed cell death eliminates all but one embryo in a polyembryonic plant seed. Cell Death Differ 9:1057–1062
Gahan PB (1984) Plant histochemistry and cytochemistry: an introduction. Academic, London
Gärtner PJ, Nagl W (1980) Acid phosphatase activity in plastids (plastolysomes) of senescing embryo-suspensor cells. Planta 149:341–349
Geburek T, Konrad H (2008) Why the conservation of forest genetic resources has not worked. Conserv Biol 22:267–274
Global Strategy for Plant Conservation. The targets 2011–2020 https://www.cbd.int/gspc/targets.shtml. Accessed 01 Oct 2014
Gordon EM, McCandless EL (1973) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of Chondrus crispus Stack. Proc Nova Scotian Inst Sci 27:111–133
Grigová M, Kubeš M, Drážná N, Øezanka T, Lipavská H (2007) Storage lipid dynamics in somatic embryos of Norway spruce (Picea abies): histochemical and quantitative analyses. Tree Physiol 27:1533–1540
Guerra MP, Silveira V, Santos ALW, Astarita LV, Nodari RO (2000) Somatic embryogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia (Bert) O. Ktze. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht, pp 457–478
Guerra MP, Steiner N, Mantovani A, Nodari RO, Reis MS, dos Santos KL (2008) Evolução, ontogênese e diversidade genética em Araucaria angustifolia. In: Barbieri RL, Stumpf ERT (eds) Origem e evolução de plantas cultivadas. Embrapa Inf Tecnol, Brasilia, DF, pp 149–184
Gupta PK, Durzan DJ (1987) Somatic embryos from protoplasts of loblolly pine proembryonal cells. Nat Biotechnol 5:710–712
Gupta PK, Pullman GS (1991) Method for reproducing coniferous plants by somatic embryogenesis using abscisic acid and osmotic potential variation. US Patent 5:36–37
Hayat MA (1978) Introduction to biological scanning electron microscopy. University Park Press, Baltimore
Haywood V, Kragler F, Lucas WJ (2002) Plasmodesmata: pathways for protein and ribonucleoprotein signaling. The Plant Cell S303–S325
Helmersson A, von Arnold S (2009) Embryogenic cultures of Juniperus communis; easy establishment and embryo maturation, limited germination. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 96:211–217
Helmersson A, von Arnold S, Bozhkov PV (2008) The level of free intracellular zinc mediates programmed cell death/cell survival decisions in plant embryos. Plant Physiol 147:1159–1167
International Union of Conservation of Nature Red List of Threatened Species (2013) http://www.iucnredlist.org/search. Accessed 02 Oct 2013
Jaskowiak MA (2014) Reviews of science for science librarians: the conservation of endangered plants using micropropagation. Sci Technol Libr 33:1
Jo L, Dos Santos ALW, Bueno CA, Barbosa HR, Floh EIS (2013) Proteomic analysis and polyamines, ethylene and reactive oxygen species levels of Araucaria angustifolia (Brazilian pine) embryogenic cultures with different embryogenic potential. Tree Physiol 34:94–104
Joy RW, Yeung EC, Kong L, Thorpe TA (1991) Development of white spruce somatic embryos: I. Storage product deposition. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 27:32–41
Khuri S, Shmoury MR, Baalbaki R, Maunder ME, Talhouk SN (2000) Conservation of the Cedrus libani populations in Lebanon: history, current status and experimental application of somatic embryogenesis. Biodivers Conserv 9:1261–1273
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H et al (2012) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy 8(4):1–100
Kurata T, Okada K, Wada T (2005) Intercellular movement of transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:600–605
Larsson E, Sitbon F, Ljung K, von Arnold S (2008a) Inhibited polar auxin transport results in aberrant embryo development in Norway spruce. New Phytol 177:356–366
Larsson E, Sitbon F, von Arnold S (2008b) Polar auxin transport controls suspensor fate. Plant Signal Behav 3:469–470
Ma X, Bucalo K, Determann RO, Cruse-Sanders JM, Pullman GS (2012) Somatic embryogenesis, plant regeneration, and cryopreservation for Torreya taxifolia, a highly endangered coniferous species. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 48:324–334
Maruyama E, Hosoi Y, Ishii K (2007) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in yakutanegoyou, Pinus armandii Franch. var. amamiana (koidz) Hatusima, an endemic and endangered species in Japan. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:28–34
Nagl W (1977) ‘Plastolysomes’—plastids involved in the autolysis of the embryo-suspensor in Phaseolus. Z Pflanzenphysiol 85:45–51
Ouriques LC, Bouzon ZL (2008) Organização estrutural e ultra-estrutural das células vegetativas e da estrutura plurilocular de Hincksia mitchelliae (Harvey) P C Silva (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae). Rodriguesia 59:435–447
Pullman GS, Bucalo K (2011) Pine somatic embryogenesis using zygotic embryos as explants. Methods Mol Biol 710:267–291
Pullman GS, Johnson S, Peter G, Cairney J, Xu N (2003) Improving loblolly pine somatic embryo maturation: comparison of somatic and zygotic embryo morphology, germination, and gene expression. Plant Cell Rep 21:747–758
Rogge-Renner GD, Steiner N, Schmidt EC, Bouzon ZL, Farias FL, Guerra MP (2013) Structural and component characterization of meristem cells in Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Kuntze zygotic embryo. Protoplasma 250:731–739
Santa-Catarina C, Silveira V, Steiner N, Guerra MP, Floh EIS, dos Santos ALW (2013) The use of somatic embryogenesis for mass clonal propagation and biochemical and physiological studies in woody plants. Curr Top Plant Biol 13:103–119
Santos ALW, Silveira V, Steiner N, Vidor M, Guerra MP (2002) Somatic embryogenesis in Paraná Pine (Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Kuntze). Braz Arch Biol Technol 45:97–106
Schlögl PS, dos Santos ALW, do Nascimento Vieira L, Floh EIS, Guerra MP (2012) Gene expression during early somatic embryogenesis in Brazilian pine (Araucaria angustifolia (Bert) O. Ktze). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 108:173–180
Schmidt EC, dos Santos R, Horta PA, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL (2010) Effects of UVB radiation on the agarophyte Gracilaria domingensis (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales): changes in cell organization, growth and photosynthetic performance. Micron 41:919–930
Schmidt EC, Pereira B, Pontes CLM, Santos R, Scherner F, Horta PA, Paula MR, Latini A, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL (2012) Alterations in architecture and metabolism induced by ultraviolet radiation-B in the carragenophyte Chondracanthus teedei (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales). Protoplasma 249:353–367
Silveira V, Steiner N, Santos ALW, Nodari RO, Guerra MP (2002) Biotechnology tools in Araucaria angustifolia conservation and improvement: inductive factors affecting somatic embryogenesis. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 2:463–470
Singh H (1978) Embryology of gymnosperms. In: Zimmerman W, Carlquist Z, Ozenda P, Wulff HD (eds) Handbuch der Pflanzen anatomie. Stuttgart, Berlin, pp 187–241
Smertenko AP, Bozhkov PV, Filonova LF, Von Arnold S, Hussey PJ (2003) Re-organization of the cytoeskeleton during developmental programmed cell death in Picea abies embryos. Plant J 33:813–824
Souter M, Lindsey K (2000) Polarity and signaling in plant embryogenesis. J Exp Bot 51:971–983
Spurr AR (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin-embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Stefenon VM, Steiner N, Guerra MP, Nodari RO (2009) Integrating approaches towards the conservation of forest genetic resources: a case study of Araucaria angustifolia. Biodivers Conserv 18:2433–2448
Steiner N, Vieira FN, Maldonado S, Guerra MP (2005) Carbon source affects morphogenesis and histodifferentiation of A. angustifolia embryogenic cultures. Braz Arch Biol Technol 48:896–903
Steiner N, Santa-Catarina C, Silveira V, Floh EI, Guerra MP (2007) Polyamine effects on growth and endogenous hormones levels in Araucaria angustifolia embryogenic cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 89:55–62
Steiner N, Santa-Catarina C, Andrade JBR, Balbuena TS, Guerra MP, Handro W, Floh EIS, Silveira V (2008) Araucaria angustifolia biotechnology. Functional Plant Sci Biotechnol 2:20–28
Steiner N, Santa-Catarina C, Guerra MP, Cutri L, Dornelas MC, Floh EIS (2012) A gymnosperm homolog of SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE-1 (SERK1) is expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109:41–50
Tereso S, Zoglauer K, Milhinhos A, Miguel A, Oliveira MM (2007) Zygotic and somatic embryo morphogenesis in Pinus pinaster: comparative histological and histochemical study. Tree Physiol 27:661–669
Verdeil JL, Hocher V, Huet C, Grosdemange F, Escoute J, Ferriére N, Nicole M (2001) Ultrastructural changes in coconut calli associated with the acquisition of embryogenic competence. Ann Bot 88:9–18
Verdeil JL, Alemanno L, Niemenak N, Tranbarger TJ (2007) Pluripotent versus totipotent plant stem cells: dependence versus autonomy? Trends Plant Sci 12:245–252
Vieira LN, Santa-Catarina C, Fraga HPF, Santos ALW, Steinmacher DA, Schlogl PS, Silveira V, Steiner N, Floh EIS, Guerra MP (2012) Glutathione improves early somatic embryogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia (Bert) O. Kuntze by alteration in nitric oxide emission. Plant Sci 195:80–87
von Arnold S, Clapham D (2008) Spruce embryogenesis. In: Suárez MF, Bozhkov PV (eds). Plant embryogenesis methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, NJ, 427:31–47
von Arnold S, Sabala I, Bozkov P, Dyachok J, Filonova LH (2002) Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 69:233–249
von Arnold S, Bozhkov P, Clapham D, Dyachok J, Filonova LH, Hogberg KA, Ingouff M, Wiweger M (2005) Propagation of Norway spruce via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 1:323–329
Weigel D, Jürgens G (2002) Stem cells that make stems. Nature 415:751–754
Williams CG (2009) Conifer reproductive biology. Springer, New York. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9602-0
Winkelmann T (2013) Recent advances in propagation of woody plants. Acta Horticult 990:375–382
Yeung EC (1995) Structural and developmental patterns in somatic embryogenesis. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Kluwer, Netherlands, pp 205–247
Yeung EC, Stasolla C, Kong L (1998) Apical meristem formation during zygotic embryo development of white spruce. Can J Bot 76:751–761
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the staff of the Central Laboratory of Electron Microscopy (LCME) of the Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil. This study was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brazil) and the Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa Cientifica e Inovação Tecnológica do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Neusa Steiner and Francine L. Farias-Soares contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1080-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steiner, N., Farias-Soares, F.L., Schmidt, É.C. et al. Toward establishing a morphological and ultrastructural characterization of proembryogenic masses and early somatic embryos of Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Kuntze. Protoplasma 253, 487–501 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0827-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0827-0