Abstract
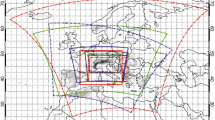
A suite of high-resolution (10 km) simulations were performed with the International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Regional Climate Model (RegCM3) to study the effect of various lateral boundary conditions (LBCs), domain size, and intermediate domains on simulated precipitation over the Great Alpine Region. The boundary conditions used were ECMWF ERA-Interim Reanalysis with grid spacing 0.75∘, the ECMWF ERA-40 Reanalysis with grid spacing 1.125 and 2.5∘, and finally the 2.5∘ NCEP/DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis. The model was run in one-way nesting mode with direct nesting of the high-resolution RCM (horizontal grid spacing Δx = 10 km) with driving reanalysis, with one intermediate resolution nest (Δx = 30 km) between high-resolution RCM and reanalysis forcings, and also with two intermediate resolution nests (Δx = 90 km and Δx = 30 km) for simulations forced with LBC of resolution 2.5∘. Additionally, the impact of domain size was investigated. The results of multiple simulations were evaluated using different analysis techniques, e.g., Taylor diagram and a newly defined useful statistical parameter, called Skill-Score, for evaluation of daily precipitation simulated by the model. It has been found that domain size has the major impact on the results, while different resolution and versions of LBCs, e.g., 1.125∘ ERA40 and 0.7∘ ERA-Interim, do not produce significantly different results. It is also noticed that direct nesting with reasonable domain size, seems to be the most adequate method for reproducing precipitation over complex terrain, while introducing intermediate resolution nests seems to deteriorate the results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer I, Boehm R, Jurkovic A, Lipa W, Orlik A, Potzmann R, Schoener W, Ungersboeck M, Matulla C, Briffa K, Jones P, Efthymiadis D, Brunetti M, Nanni T, Maugeri M, Mercalli L, Mestre O, Moisselin JM, Begert M, Mueller-Westermeier G, Kveton V, Bochnicek O, Stastny P, Lapin M, Szalai S, Szentimrey T, Cegnar T, Dolinar M, Gajic-Capka M, Zaninovic K, Majstorovic Z, Nieplova E (2007) HISTALP—historical instrumental climatological surface time series of the Greater Alpine Region. Int J Climatol 27(1):17–46. doi:10.1002/joe.1377
Awan N, Gobiet A, Suklitsch M (2014) The role of regional climate model setup in simulating two extreme precipitation events in the European Alpine region. Clim Dyn:1–16. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2323-1
Awan NK, Truhetz H, Gobiet A (2011) Parameterization-induced error characteristics of MM5 and WRF operated in climate mode over the Alpine Region: an ensemble-based analysis. J Clim 24(12):3107–3123. doi:10.1175/2011JCLI3674.1
Bao X, Zhang F (2013) Evaluation of NCEP-CFSR, NCEP-NCAR, ERA-Interim, and ERA-40 Reanalysis Datasets against independent sounding observations over the Tibetan Plateau. J Clim 26(1):206–214. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00056.1
Beck A, Ahrens B, Stadlbacher K (2004) Impact of nesting strategies in dynamical downscaling of reanalysis data. Geophys Res Lett 31(19). doi:10.1029/2004GL020115
Bergant K, Belda M, Halenka T (2007) Systematic errors in the simulation of European climate (1961–2000) with RegCM3 driven by NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Int J Climatol 27(4):455–472. doi:10.1002/joc.1413
Betts AK, Koehler M, Zhang Y (2009) Comparison of river basin hydrometeorology in ERA-Interim and ERA-40 reanalyses with observations. J Geophys Res Atmos:114. doi:10.1029/2008JD010761
Bhaskaran B, Ramachandran A, Jones R, Moufouma-Okia W (2012) Regional climate model applications on sub-regional scales over the Indian monsoon region: the role of domain size on downscaling uncertainty. J Geophys Res Atmos:117. doi:10.1029/2012JD017956
Bray M, Han D, Xuan Y, Bates P, Williams M (2011) Rainfall uncertainty for extreme events in NWP downscaling model. Hydrol Process 25(9):1397–1406. doi:10.1002/hyp.7905
Chatré B, Lanzinger G, Macaluso M, Mayrhofer W, Morandini M, Onida M, Polajnar B (2010) The Alps: People and Pressures in the Mountains, the Facts at a Glance. Permanent Secretariat of the Alpine Convention, Innsbruck, www.alpconv.org/en/publications/alpine/Documents/Vademecum_web.pdf
Davies H, Turner R (1977) Updating prediction models by dynamical relaxation—examination of technique. Q J R Meteorol Soc 103(436):225–245. doi:10.1002/qj.49710343602
Davies T (2014) Lateral boundary conditions for limited area models. Q J R Meteorol Soc 140(678, A):185–196. doi:10.1002/qj.2127
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ, Berrisford P, Poli P, Kobayashi S, Andrae U, Balmaseda MA, Balsamo G, Bauer P, Bechtold P, Beljaars ACM, van de Berg L, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Delsol C, Dragani R, Fuentes M, Geer AJ, Haimberger L, Healy SB, Hersbach H, Hlm EV, Isaksen L, Kllberg P, Khler M, Matricardi M, McNally AP, Monge-Sanz BM, Morcrette JJ, Park BK, Peubey C, de Rosnay P, Tavolato C, Thpaut JN, Vitart F (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137(656):553–597. doi:10.1002/qj.828
Denis B, Laprise R, Caya D (2003) Sensitivity of a regional climate model to the resolution of the lateral boundary conditions. Clim Dyn:20107–126. doi:10.1007/s00382-002-0264-6
Dickinson R, Henderson-Sellers A, Kennedy P (1993) Biosphereatmosphere transfer scheme (BATS) version 1E as coupled to the NCAR Community Climate Model. NCAR Technical Note NCAR/TN–387+STR, Natl. Cent. for Atmos. Res., Boulder
Frank A, Formayer H, Seibert P, Krüger B, Kromp-Kolb H (2005) Reclip:more, Research for Climate Protection: Model Run Evaluation. Project Report (in German), Institute of Meteorology, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, 1180, Vienna, Austria, https://imp.boku.ac.at/klima/Literatur/Teilbericht_Reclip.pdf
Frei C, Schär C (1998) A precipitation climatology of the Alps from high-resolution rain-gauge observations. Int J Climatol 18(8):873–900. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(19980630)18:8%3C873::AID-JOC255%3E3.0.CO;2-9
Frei C, Christensen J, Deque M, Jacob D, Jones R, Vidale P (2003) Daily precipitation statistics in regional climate models: evaluation and intercomparison for the European Alps. J Geophys Res Atmos 108(D3). doi:10.1029/2002JD002287
Fritsch J, Chappel C (1980) Numerical prediction of convectively driven mesoscale pressure systems. Part I: convective parameterization. J Atmos Sci 37(8):1722–1733. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1980)037%3C1722:NPOCDM%3E2.0.CO;2
Giorgi F, Marinucci M, Bates G, Decanio G (1993) Development of a Second-Generation Regional Climate Model (RegCM2). Part II: Convective Processes and Assimilation of Lateral Boundary Conditions. Mon Weather Rev 121(10):2814–2832. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121%3C2814:DOASGR%3E2.0.CO;2
Giorgi F, Francisco R, Pal J (2003) Effects of a subgrid-scale topography and land use scheme on the simulation of surface climate and hydrology. Part I: effects of temperature and water vapor disaggregation. J Hydrometeorol 4(2):317–333. doi:10.1175/1525-7541(2003)4%3C317:EOASTA%3E2.0.CO;2
Giorgi F, Coppola E, Solmon F, Mariotti L, Sylla MB, Bi X, Elguindi N, Diro GT, Nair V, Giuliani G, Turuncoglu UU, Cozzini S, Guettler I, O’Brien TA, Tawfik AB, Shalaby A, Zakey AS, Steiner AL, Stordal F, Sloan LC, Brankovic C (2012) RegCM4: model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains. Clim Res 52(1, 29):7–29. doi:10.3354/cr01018
Goswami P, Himesh S, Goud B (2013) Simulation of high-impact tropical weather events: comparative analysis of three heavy rainfall events. Nat Hazards 65(3):1703–1722. doi:10.1007/s11069-012-0440-x
Grell G (1993) Prognostic evaluation of assumptions used by cumulus parameterizations. Mon Weather Rev 121(3):764–787. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121%3C0764:PEOAUB%3E2.0.CO;2
Halenka T (2010) Cecilia EC FP6 Project on the Assessment of Climate Change Impacts in Central and Eastern Europe. In: Alexandrov V, Gajdusek MF, Knight CGF, Yotova A (eds) Global Environmental Change: Challenges to Science and Society in Southeastern Europe. Springer, Netherlands, pp 125–137
Haylock MR, Hofstra N, Tank AMGK, Klok EJ, Jones PD, New M (2008) A European daily high-resolution gridded data set of surface temperature and precipitation for 1950–2006. J Geophys Res Atmos 113(D20). doi:10.1029/2008JD010201
Hofstra N, New M, McSweeney C (2010) The influence of interpolation and station network density on the distributions and trends of climate variables in gridded daily data. Clim Dyn 35(5):841–858. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0698-1
Holtslag A, Debruijn E, Pan H (1990) A high resolution air mass transformation model for short-range weather forecasting. Mon Weather Rev 118(8):1561–1575. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118%3C1561:AHRAMT%3E2.0.CO;2
Im ES, Coppola E, Giorgi F, Bi X (2010) Validation of a high-resolution regional climate model for the Alpine Region and effects of a subgrid-scale topography and land use representation. J Clim 23(7):1854–1873. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI3262.1
Isotta FA, Frei C, Weilguni V, Tadic MP, Lassegues P, Rudolf B, Pavan V, Cacciamani C, Antolini G, Ratto SM, Munari M, Micheletti S, Bonati V, Lussana C, Ronchi C, Panettieri E, Marigo G, Vertacnik G (2014) The climate of daily precipitation in the Alps: development and analysis of a high-resolution grid dataset from pan-Alpine rain-gauge data. Int J Climatol 34(5):1657–1675. doi:10.1002/joc.3794
Jacob D, Barring L, Christensen OB, Christensen JH, de Castro M, Deque M, Giorgi F, Hagemann S, Lenderink G, Rockel B, Sanchez E, Schaer C, Seneviratne SI, Somot S, van Ulden A, van den Hurk B (2007) An inter-comparison of regional climate models for Europe: model performance in present-day climate. Clim Chang 81(1):31–52. doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9213-4
Jones P (1999) First- and second-order conservative remapping schemes for grids in spherical coordinates. Mon Weather Rev 127(9):2204–2210. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1999)127%3C2204:FASOCR%3E2.0.CO;2
Jones RG, Murphy JM, Noguer M (1995) Simulation of climate change over Europe using a nested regional-climate model. I: assessment of control climate, including sensitivity to location of lateral boundaries. Q J R Meteorol Soc 121(526):1413–1449. doi:10.1002/qj.49712152610
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang S, Hnilo J, Fiorino M, Potter G (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(11):1631–1643. doi:10.1175/BAMS-83-11-1631
Kiehl J, Hack J, Bonan G, Boville B, Briegleb B, Williamson D, Rasch P (1996) Description of the NCAR Community Climate Model (CCM3). NCAR Technical Note NCAR/TN–420+STR, Natl. Cent. for Atmos. Res., Boulder
Kopparla P, Fischer EM, Hannay C, Knutti R (2013) Improved simulation of extreme precipitation in a high-resolution atmosphere model. Geophys Res Lett 40(21):5803–5808. doi:10.1002/2013GL057866
Leduc M, Laprise R (2009) Regional climate model sensitivity to domain size. Clim Dyn 32(6):833–854. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0400-z
Mooney PA, Mulligan FJ, Fealy R (2011) Comparison of ERA-40, ERA-Interim and NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data with observed surface air temperatures over Ireland. Int J Climatol 31(4):545–557. doi:10.1002/joc.2098
Pal J, Small E, Eltahir E (2000) Simulation of regional-scale water and energy budgets: representation of subgrid cloud and precipitation processes within RegCM. J Geophys Res Atmos 105(D24):29,579–29,594. doi:10.1029/2000JD900415
Pal JS, Giorgi F, Bi X, Elguindi N, Solmon F, Gao X, Rauscher SA, Francisco R, Zakey A, Winter J, Ashfaq M, Syed FS, Bell JL, Diffenbaugh NS, Karmacharya J, Konare A, Martinez D, da Rocha RP, Sloan LC, Steiner AL (2007) Regional climate modeling for the developing world—the ICTP RegCM3 and RegCNET. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 88(9):1395+. doi:10.1175/BAMS-88-9-1395
Rauscher SA, Coppola E, Piani C, Giorgi F (2010) Resolution effects on regional climate model simulations of seasonal precipitation over Europe. Clim Dyn 35(4):685–711. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0607-7
Reynolds R, Rayner N, Smith T, Stokes D, Wang W (2002) An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J Clim 15(13):1609–1625. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015%3C1609:AIISAS%3E2.0.CO;2
Skalak P, Deque M, Belda M, Farda A, Halenka T, Csima G, Bartholy J, Caian M, Spiridonov V (2014) CECILIA regional climate simulations for the present climate: validation and inter-comparison. J Clim 60(1):1–12. doi:10.3354/cr01207
Suklitsch M, Gobiet A, Truhetz H, Awan N, Gttel H, Jacob D (2011) Error characteristics of high resolution regional climate models over the Alpine area. Clim Dyn:37377–390. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0848-5
Taylor K (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D7):7183–7192. doi:10.1029/2000JD900719
Torma C, Bartholy J, Pongracz R, Barcza Z, Coppola E, Giorgi F (2008) Adaptation of the RegCM3 climate model for the Carpathian Basin. IDOJARAS 112(3-4):233–247. doi:10.1175/2010JHM1234.1
Torma C, Coppola E, Giorgi F, Bartholy J, Pongracz R (2011) Validation of a high-resolution version of the regional climate model RegCM3 over the Carpathian Basin. J Hydrometeorol 12(1):84–100. doi:10.5194/nhess-13-1457-2013
Turco M, Zollo AL, Ronchi C, De Luigi C, Mercogliano P (2013) Assessing gridded observations for daily precipitation extremes in the Alps with a focus on northwest Italy. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13(6):1457–1468. doi:10.1256/qj.04.176
Uppala SM, Kllberg PW, Simmons AJ, Andrae U, Bechtold VDC, Fiorino M, Gibson JK, Haseler J, Hernandez A, Kelly GA, Li X, Onogi K, Saarinen S, Sokka N, Allan RP, Andersson E, Arpe K, Balmaseda MA, Beljaars ACM, Berg LVD, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Caires S, Chevallier F, Dethof A, Dragosavac M, Fisher M, Fuentes M, Hagemann S, Hlm E, Hoskins BJ, Isaksen L, Janssen PAEM, Jenne R, Mcnally AP, Mahfouf JF, Morcrette JJ, Rayner NA, Saunders RW, Simon P, Sterl A, Trenberth KE, Untch A, Vasiljevic D, Viterbo P, Woollen J (2005) The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 131(612):2961–3012. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078%3C2599:ATOLBC%3E2.0.CO;2
Warner TT, Peterson RA, Treadon RE (1997) A tutorial on lateral boundary conditions as a basic and potentially serious limitation to regional numerical weather prediction. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78(11):2599–2617. doi:10.1175/JCLI4239.1
Xue Y, Vasic R, Janjic Z, Mesinger F, Mitchell KE (2007) Assessment of dynamic downscaling of the continental US regional climate using the Eta/SSiB regional climate model. J Clim 20(16):4172–4193
Xue Y, Janjic Z, Dudhia J, Vasic R, De Sales F (2014) A review on regional dynamical downscaling in intraseasonal to seasonal simulation/prediction and major factors that affect downscaling ability. Atmos Res:14768–85. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.05.001
Zeng X, Zhao M, Dickinson R (1998) Intercomparison of bulk aerodynamic algorithms for the computation of sea surface fluxes using TOGA COARE and TAO data. J Clim 11(10):2628–2644. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011%3C2628:IOBAAF%3E2.0.CO;2
Acknowledgments
This work was completed as part of the EU project CECILIA as well as through a scholarship of the first author by the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan. We acknowledge the E-OBS dataset from the EU-FP6 project ENSEMBLES (http://ensembles-eu.metoffice.com) and the data providers in the ECA&D project (http://eca.knmi.nl). We are thankful to ECMWF for providing the ERA-40 and ERA-Interim datasets. We further acknowledge observational precipitation dataset from Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH, Zurich, Switzerland). We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their careful reading of our manuscript and their many insightful comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadeem, I., Formayer, H. Sensitivity studies of high-resolution RegCM3 simulations of precipitation over the European Alps: the effect of lateral boundary conditions and domain size. Theor Appl Climatol 126, 617–630 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1586-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1586-8