Abstract
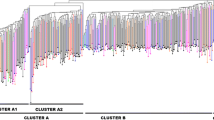
The genus Corylus, a member of the birch family Betulaceae, includes several species that are widely distributed throughout temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. This study assesses the genetic diversity in 26 international cultivars and 32 accessions of Corylus avellana L. from Portugal: 13 wild genotypes and 19 landraces. The genetic relationships among the 58 hazelnuts (Corylus avellana L.) were analyzed using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers. Eighteen ISSR primers and seven AFLP primer pairs generated a total of 570 unambiguous and repeatable bands, respectively, from which 541 (95.03 %) were polymorphic for both markers. Genetic similarity index values ranged from 0.239 for wild types and cultivars to 0.143 for landraces and wild types. The genetic relationships were presented as a Neighbor-Joining method dendrogram and a two-dimensional principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plot. The Neighbor-Joining dendrogram showed three main clusters, and the PCoA analysis has shown to be congruent with the hierarchical analysis. Bayesian analysis clustered all individuals into three groups showing a good separation among wild genotypes, landraces and cultivars. The genetic diversity found on wild genotypes and Portuguese landraces may provide relevant information for the diversity conservation and it will be useful in breeding programs and to identify local selections for preservation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertini E, Torricelli R, Bitocchi E, Raggi L, Marconi G, Pollastri L, Di Minco G, Basttistini A, Papa R, Veronesi F (2011) Structure of genetic diversity in Olea europaea L. cultivars from central Italy. Mol Breed 27:533–547
Biswas MK, Chai L, Amar MH, Zhang X, Deng XX (2011) Comparative analysis of genetic diversity in Citrus germplasm collection using AFLP, SSAP. SAMPL and SSR markers. Sci Hortic 129(4):798–803
Boccacci P, Botta R (2009) Investigating the origin of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars using chloroplast microsatellites. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:851–859
Boccacci P, Rovira Botta M (2008) Genetic diversity of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) germplasm in northeastern Spain. HortScience 43:667–672
Boccacci P, Akkak A, Botta R (2006) DNA typing and genetic relations among European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars using microsatellite markers. Genome 49:598–611
Boccacci P, Aramini M, Valentini N et al (2013) Molecular and morphological diversity of on-farm hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) landraces from southern Europe and their role in the origin and diffusion of cultivated germplasm. Tree Gene Genom. doi:10.1007/s11295-013-0651-7
Campa A, Trabanco N, Pérez-Vega E, Rovira M, Ferreira JJ (2011) Genetic relationship between cultivated and wild hazelnuts (Corylus avellana L.) collected in northern Spain. Plant Breed 130:360–366
Chen H, Mehlenbacher SA, Smith DC (2005) AFLP markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance from OSU 408.040 hazelnut. J Am Soc Hort Sci 130:412–417
Erfatpour M, Hamidogli Y, Kaviani B, Fatahi R, Falahati M, Javadi D, Hashemabadi D (2011) Assessment of genetic diversity among some Iranian hazelnut genotypes using SSR markers. Aust J Crop Sci 5(10):1286–1291
Ergül A, Kazan K, Aras S, Cevik V, Celik H, Söylemezoğlu G (2006) AFLP analysis of genetic variation within the two economically important Anatolian grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) varietal groups. Genome 49(5):467–475
Essadki M, Ouazzani N, Lumaret R, Moumni M (2006) ISSR variation in olive-tree cultivars from Morocco and other western countries of the Mediterranean Basin. Gene Resour Crop Evol 53:475–482
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Excoffier L, Slatkin M (1992) Maximum-likelihood estimation of molecular haplotype frequencies in a diploid population. Mol Biol Evol 12:921–927
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure: extensions to linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Fang DQ, Roose ML (1997) Identification of closely related citrus cultivars with inter-simple sequence repeat markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:408–417
FAO Production Yearbook (2011) http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx Accessed 26 March 2013
Ferrari M, Gori M, Monnanni R, Buiatti M, Scarascia Mugnozza GT, De Pace C (2004) DNA fingerprinting of Corylus Avellana L. accessions revealed by AFLP molecular markers. Acta Hort 686:125–134
Ferreira JJ, Garcia-González C, Tous J, Rovira M (2010) Genetic diversity revealed by morphological traits and ISSR markers in hazelnut germplasm from northern Spain. Plant Breed 129:435–441
Francisco-Ortega J, Santos-Guerra A, Kim SC, Crawford DJ (2000) Plant genetic diversity in the Canary Islands: a conservation perspective. Am J Bot 87:909–919
Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Bernardo GD, De Masi L, Galano G, Cascino A (1999) Identification of hazelnut (Corylus avellana) cultivars by RAPD analysis. Plant Cell Rep 18:652–655
Gökirmak T, Mehlenbacher SA, Bassil NV (2009) Characterization of European hazelnut (Corylus avellana) cultivars using SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:147–172
Gower JC (1966) Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 53:325–338
Guo X, Elston RC (1999) Linkage information content of polymorphic genetic markers. Hum Hered 49(2):112–118
Gürcan K, Mehlenbacher SA (2010) Development of microsatellite marker loci for European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from ISSR fragments. Mol Breed 26(3):551–559
Kafkas S, Ozkan H, Ak BE, Acar I, Atli HS, Koyuncu S (2006) Detecting DNA polymorphism and genetic diversity in a wide pistachio germplasm: comparison of AFLP, ISSR and RAPD markers. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 131:522–529
Kafkas S, Dogan Y, Sabir A, Turan A, Seker H (2009) Genetic characterization of Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars from Turkey using molecular markers. HortScience 44(6):1557–1561
Kasapligil B (1972) A bibliography on Corylus (Betulaceae) with annotations. Annu Rep North Nut Growers Assoc 63:107–162
Kuster H (2000) The history and culture of food and drink in Europe: northern Europe–Germany and surrounding regions. In: Kiple KF, Ornelas KC (eds) The Cambridge world history of food, vol 2. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1226–1232
Lagerstedt HB (1975) Filberts. In: Janick J, Moore JN (eds) Advances in fruit breeding. Purdue University Press, West Lafayette, pp 456–489
Leinemann L, Steiner W, Hosius B, Kuchma O, Arenhövel W, Fussi B, Haase B, Kätzel R, Rogge M, Finkeldey R (2013) Genetic variation of chloroplast and nuclear markers in natural populations of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) in Germany. Plant Syst Evol 299:369–378
Martins S, Simões F, Mendonça D, Matos J, Silva AP, Carnide V (2012) Chloroplast SSR genetic diversity indicates a refuge for Corylus avellana in northern Portugal. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60(4):1289–1295. doi:10.1007/s10722-012-9919-2
McDermott JM, McDonald BA (1993) Gene flow in plant pathosystems. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31:353–373
Mehlenbacher SA (1991) Hazelnuts (Corylus). Genetic resources of temperate fruit and nut crops. Acta Hort 290:791–836
Mehlenbacher SA (1997) Revised dominance hierarchy for S alleles in Corylus avellana L. Theor Appl Genet 94:360–366
Mehlenbacher SA, Brown RN, Davis JW, Chen H, Bassil NV, Smith DC, Kubisiak TL (2004) RAPD markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance in Corylus avellana. Theor Appl Genet 108:651–656
Miaja ML, Vallania R, Me C, Akkak A, Nassi O, Lepori G (2001) Varietal characterization in hazelnut by RAPD markers. Acta Hort 556:247–250
Milligan BG, Leebens-Mack J, Strand AE (1994) Conservation genetics: beyond the maintenance of marker diversity. Mol Ecol 3(4):423–435. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.1994.tb00082.x
Moreno S, Martin JP, Ortiz JM (1998) Inter-simple sequence repeats PCR for characterization of closely related grapevine germplasm. Euphytica 101:117–125
Nagy S, Poczai P, Cernák I, Gorji AM, Hegedús G, Taller J (2012) PICcalc: an online program to calculate polymorphic information content for molecular genetic studies. Biochem Genet 50(9–10):670–672
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individual. Genetics 89:583–590
Nybom H (2004) Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Mol Ecol 13:1143–1155
Patzak J (2001) Comparison of RAPD, STS, ISSR and AFLP molecular methods used for assessment of genetic diversity in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 121:129–138
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) Genalex 6: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01155.x
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software. http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin. Accessed 04 Nov 2013
Pomper KW, Azarenko AN, Bassil NV, Davis JW, Mehlenbacher SA (1998) Identification of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers for self-incompatibility alleles in Corylus avellana L. Theor Appl Genet 97:479–487
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey MM, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:107–112
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) Arlequin: a software for population genetics data analysis. User manual ver 2.000. Genetics and Biometry Lab, Dept of Anthropology, University of Geneva, Geneva
Shannon C, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Slatkin M, Barton NH (1989) A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution 43:1349–1368
Talhinhas P, Neves-Martins J, Leitao J (2003) AFLP, ISSR and RAPD markers reveal high levels of genetic diversity among Lupinus spp. Plant Breed 122:507–510
Tallantire PA (2002) The early-holocene spread of hazel (Corylus avellana L.) in Europe north and west of the Alps: an ecological hypothesis. Holocene 12:81–96. doi:10.1191/0959683602hl523rr
Tasias Valls J (1975) El avellano en la provincia de Tarragona. Excma Diputación Provincial de Tarragona, Tarragona
Thompson MM, Lagerstedt HB, Mehlenbacher SA (1996) Hazelnuts. In: Janick J, Moore JN (eds) Fruit breeding nuts, vol 3. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 125–184
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van De Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kulper M, Zabeu M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 21(23):4407–4414
Wright S (1978) Evolution and genetics of populations. Variability within and among natural populations, 4th edn. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1999) POPGENE 32-version 1.31. Population Genetics Software http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/fyeh/
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the PhD grant SFRH/BD/40686/2007 from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins, S., Simões, F., Matos, J. et al. Genetic relationship among wild, landraces and cultivars of hazelnut (Corylus avellana) from Portugal revealed through ISSR and AFLP markers. Plant Syst Evol 300, 1035–1046 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0942-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0942-3