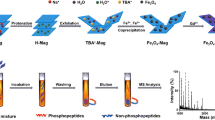
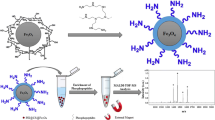
Abstract
Magnetic mesoporous carbon composites incorporating hydrophilic metallic nanoparticles were synthesized from resol, ZrO(NO3)2, ferric acetylacetonate, and triblock copolymer F127. The method involves a multi-component co-assembly strategy associated with direct carbonization. The resulting carbon material is shown to be useful as a metal oxide affinity chromatography (MOAC) material for enrichment of phosphopeptides owing to its large mesoporous (4.8 nm) surface area (442 m2 g−1), large pore volume (0.37 cm3 g−1) and excellent hydrophilicity. The metallic iron and ferric oxide particles modified on the mesoporous carbon exert a magnetic force and, in combination with the metallic zirconia, is a viable MOAC material for enrichment of low-abundance phosphopeptides. Because of metal chelation between metallic nanoparticles and the phosphate groups of phosphopeptides, the zirconia/magnetic mesoporous carbon displays high selectivity even at a phosphopeptide/nonphosphopeptide molar ratio of 1:500. As little as 1.5 fmol of phosphopeptides become detectable. The MOAC was successfully applied to the identification by MALDI-TOF MS of phosphopeptides in human serum and nonfat milk.

Magnetic mesoporous carbon composites incorporating hydrophilic metallic nanoparticles were prepared and successfully applied to the enrichment of low-abundance phosphopeptides from human serum and nonfat milk by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pawson T, Scott JD (2005) Protein phosphorylation in signaling–50 years and counting. Trends Biochem Sci 6:286
Hunter T (2005) Signaling–2000 and Beyond. Cell 100:113
Liu CM, Li YM, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH, Tan Y, Zhang ZH, Lin XH, He X (2002) Control of β-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell 108:837
Liu F, Iqbal K, Iqbal IG, Hart GW, Gong CX (2004) O-GlcNAcylation regulates phosphorylation of tau: a mechanism involved in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:10804
Danielsson A, Ost A, Nystrom FH, Stalfors P (2005) Attenuation of insulin-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 serine 307 phosphorylation in insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes. J Biol Chem 280:34389
Chen YJ, Xiong ZC, Peng L, Gang YY, Zhao YM, Shen J, Qian JH, Zhang LY, Zhang WB (2015) Facile preparation of Core–Shell magnetic metal–organic framework nanoparticles for the selective capture of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:16338
Xiong ZC, Zhang LY, Fang CL, Zhang QQ, Ji YS, Zhang Z, Zhang WB, Zou HF (2014) Ti4+-immobilized multilayer polysaccharide coated magnetic nanoparticles for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. J Mater Chem B 2:44730
Liu W, Zheng JN, Li SH, Wang RR, Lin Z, Yang HH (2015) Aluminium glycinate functionalized silica nanoparticles for highly specific separation of phosphoproteins. J Mater Chem B 3:6528
Xu L, Zhu W, Sun R, Ding Y (2015) A Ti4+-immobilized phosphate polymer-patterned silicon substrate for on-plate selective enrichment and self-desalting of phosphopeptides. Analyst 140:3216
Zheng LY, Dong HP, Hu LJ (2013) Zirconium-cation-immobilized Core/Shell (Fe3O4@polymer) microspheres as an IMAC material for the selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:7729
Chen Y, Li DJ, Bie ZJ, He XP, Liu Z (2016) Coupling of phosphate-imprinted mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based selective enrichment with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for highly efficient analysis of protein phosphorylation. Anal Chem 88:1447
Qin YP, Li DY, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2016) Preparation of high-efficiency cytochrome c-imprinted polymer on the surface of magnetic carbon nanotubes by epitope approach via metal chelation and six-membered ring. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:10155
Tseng HC, Ovaa H, Wei NJC, Ploegh H, Tsai LH (2015) Phosphoproteomic analysis with a solid-phase capture-release-tag approach. Chem Biol 12:769
Hennrich ML, Toorn HWP, Groenewold V, Heck AJR, Mohammed S (2012) Ultra acidic strong cation exchange enabling the efficient enrichment of basic phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 84:1804
Zarei M, Sprenger A, Gretzmeier C, Dengjel J (2012) Polydopamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles for enrichment and direct detection of small molecule pollutants coupled with MALDI-TOF-MS. J Proteome Res 11:4269
Alpert AJ, Hudecz O, Mechtler K (2015) Anion-exchange chromatography of phosphopeptides: weak anion exchange versus strong anion exchange and anion-exchange chromatography versus electrostatic Repulsion − Hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Anal Chem 87:4704
Yang XQ, Xia Y (2016) Urea-modified metal-organic framework of type MIL-101(Cr) for the preconcentration of phosphorylated peptides. Microchim Acta 183:2235
Liu HL, Yang TY, Dai JY, Zhu JY, Li XR, Wen R, Yang XH (2015) Hydrophilic modification of titania nanomaterials as a biofunctional adsorbent for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Analyst 140:6652
Wang ZG, Lv N, Bi WZ, Zhang JL, Ni JZ (2015) Development of the affinity materials for phosphorylated proteins/peptides enrichment in Phosphoproteomics analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:8377
Hu Y, Shan CX, Wang J, Zhu JM, Gu CQ, Ni WT, Zhu D, Zhang AH (2015) Fabrication of functionalized SiO2/TiO2 nanocomposites via amidation for the fast and selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. New J Chem 39:6540
Ma WF, Zhang C, Zhang YT, Yu M, Guo J, Zhang Y, Lu HJ, Wang CC (2014) Magnetic MSP@ZrO2 microspheres with yolk–Shell structure: designed synthesis and application in highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Langmuir 30:6602
Zhang YT, Li LL, Ma WF, Zhang Y, Yu M, Guo J, Lu HJ, Wang CC (2013) Two-in-one strategy for effective enrichment of phosphopeptides using magnetic mesoporous γ-Fe2O3 Nanocrystal clusters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:614
Çelikbıçak Ö, Atakay M, Güler Ü, Salih B (2013) A novel tantalum-based sol-gel packed microextraction syringe for highly specific enrichment of phosphopeptides in MALDI-MS applications. Analyst 138:4403
Huang X, Wang JP, Wang JY, Liu CC, Wang S (2015) Preparation of graphene–hafnium oxide composite for selective enrichment and analysis of phosphopeptides. RSC Adv 5:89644
Kailasa SK, Wu HF (2012) Rapid enrichment of phosphopeptides by BaTiO3 nanoparticles after microwave-assisted tryptic digest of phosphoproteins, and their identification by MALDI-MS. Microchim Acta 179:83
Long XY, Song Q, Lian HZ (2015) Development of magnetic LuPO4 microspheres for highly selective enrichment and identification of phosphopeptides for MALDI-TOF MS analysis. J Mater Chem B 3:9330
Pang H, Lu Q, Gao F (2011) Graphene oxide induced growth of one-dimensional fusiform zirconia nanostructures for highly selective capture of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 47:11772
Wan H, Li JA, Yu WG, Liu ZY, Zhang QQ, Zhang WB, Zou HF (2014) Fabrication of a novel magnetic yolk–shell Fe3O4@mTiO2@mSiO2 nanocomposite for selective enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides from a complex sample. RSC Adv 4:45804
Zhang XL, Wang F, Xia Y (2013) Trypsin functionalization and zirconia coating of mesoporous silicananotubes for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization massspectrometry analysis of phosphoprotein. J Chromatogr A 1306:20
Zhang L, Xiong ZC, Chen YJ, Peng L, Yu BH, Gao XD, Zhang RS, Zhang LY, Zhang WB (2016) Soft-template synthesis of hydrophilic metallic zirconia nanoparticle-incorporated ordered mesoporous carbon composite and its application in phosphopeptide enrichment. RSC Adv 6:30014
Sun ZK, Sun B, Qiao MH, Wei J, Yue Q, Wang C, Deng YH, Kaliaguine S, Zhao DY (2012) A general chelate-assisted Co-assembly to metallic nanoparticles-incorporated ordered mesoporous carbon catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 134:17635
Xiong ZC, Chen YJ, Zhang LY, Ren J, Zhang QQ, Ye ML, Zhang WB, Zou HF (2014) Facile synthesis of guanidyl-functionalized magnetic polymer microspheres for tunable and specific capture of global phosphopeptides or only multiphosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 24:22743
Lu ZD, Duan JC, He L, Hu YX, Yin YD (2010) Mesoporous TiO2 Nanocrystal clusters for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 82:7249
Atakay M, Celikbicak O, Salih B (2012) Amine-functionalized Sol–gel-based lab-in-a-pipet-tip approach for the fast enrichment and specific purification of phosphopeptides in MALDI-MS applications. Anal Chem 84:2713
Kailasa SK, Wu HF (2010) Multifunctional ZrO2 nanoparticles and ZrO2-SiO2 nanorods for improved MALDI-MS analysis of cyclodextrins, peptides, and phosphoproteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:1115
Yan YH, Zheng ZF, Deng CH, Li Y, Zhang XM, Yang PY (2013) Hydrophilic Polydopamine-coated graphene for metal ion immobilization as a novel immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography platform for Phosphoproteome analysis. Anal Chem 85:8483
Cheng G, Wang ZG, Liu YL, Zhang JL, Sun DH, Ni JZ (2013) Magnetic affinity microspheres with Meso−/Macroporous shells for selective enrichment and fast separation of phosphorylated biomolecules. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:3182
Zhang LY, Zhao Q, Liang Z, Yang KQ, Sun LL, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2012) Synthesis of adenosine functionalized metal immobilized magnetic nanoparticles for highly selective and sensitive enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 48:6274
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (21235005), the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project (2012YQ120044), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21475044), the model Project of the Research and Application of the Common Key Technology about Chemical Reagent of Basis Scientific Research (2015BAK44B00) and foundation of Shanghai Research Institute of Criminal Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 4.83 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Gan, Y., Sun, H. et al. Magnetic mesoporous carbon composites incorporating hydrophilic metallic nanoparticles for enrichment of phosphopeptides prior to their determination by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Microchim Acta 184, 547–555 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2046-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2046-6