Abstract
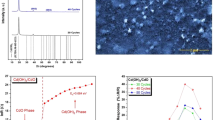
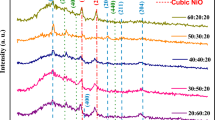
A resistive gas sensor for hydrogen (H2) was developed using CdO-TiO2 nanocomposite films deposited onto a glass substrate in a thickness of typically 300–450 nm by co-sputtering. X-ray diffraction patterns confirmed the formation of a perovskite CdTiO3 phase. Field emission-scanning electron micrographs showed spherically shaped grains which decreased in size on increasing the TiO2 concentration, most probably due to difference in the size of the ions of Cd and Ti. The nanostructured films with lower concentration of TiO2 exhibited good response to H2 at an operating temperature of 275 °C and an operating voltage of 250 mV. The sensors give a 3 % relative resistance change on exposure to 500 ppm of H2, have a 45 s response time and a 90 s recovery time. The H2 sensor described here does not require expensive additives and thus may find both civilian and industrial applications.

When CdO-TiO2 films are exposed to H2 it will react with adsorbed atomic oxygen species available on the sensor surface. CdO-TiO2 films with lower concentration of TiO2 exhibited maximum response of 3 % towards 500 ppm of H2 at an operating temperature of 275 °C.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moriarty P, Honnery D (2009) Hydrogen’s role in an uncertain energy future. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:31–39. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.10.060
Ball M, Wietschel M (2009) The future of hydrogen - opportunities and challenges. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:615–627. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.014
Boon-Brett L, Bousek J, Black G et al (2010) Identifying performance gaps in hydrogen safety sensor technology for automotive and stationary applications. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:373–384. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.10.064
Hübert T, Boon-Brett L, Black G, Banach U (2011) Hydrogen sensors - a review. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 157:329–352. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2011.04.070
Mitra P, Chatterjee AP, Maiti HS (1998) ZnO thin film sensor. Mater Lett 35:33–38. doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(97)00215-2
Steinebach H, Kannan S, Rieth L, Solzbacher F (2010) H2 gas sensor performance of NiO at high temperatures in gas mixtures. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 151:162–168. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2010.09.027
Calavia R, Mozalev A, Vazquez R et al (2010) Fabrication of WO3 nanodot-based microsensors highly sensitive to hydrogen. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 149:352–361. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2010.06.055
Choi Y-H, Hong S-H (2007) H2 sensing properties in highly oriented SnO2 thin films. Sensors Actuators B Chem 125:504–509. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2007.02.043
Wang B, Zhu LF, Yang YH et al (2008) Fabrication of a SnO2 nanowire Gas sensor and sensor performance for hydrogen. J Phys Chem C 112:6643–6647. doi:10.1021/jp8003147
Arakelyan VM, Galstyan VE, Martirosyan KS et al (2007) Hydrogen sensitive gas sensor based on porous silicon/TiO2-x structure. Physica E 38:219–221. doi:10.1016/j.physe.2006.12.037
Shen Y, Yamazaki T, Liu Z et al (2009) Hydrogen sensing properties of Pd-doped SnO2 sputtered films with columnar nanostructures. Thin Solid Films 517:6119–6123. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2009.05.036
Lange U, Hirsch T, Mirsky VM, Wolfbeis OS (2011) Hydrogen sensor based on a graphene-palladium nanocomposite. Electrochim Acta 56:3707–3712. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.10.078
Nag P, Majumdar S, Bumajdad A, Devi PS (2014) Enhanced gas sensing performance of tin dioxide-based nanoparticles for a wide range of concentrations of hydrogen gas. RSC Adv 4:18512–18521. doi:10.1039/c3ra48060g
Kaniyoor A, Imran Jafri R, Arockiadoss T, Ramaprabhu S (2009) Nanostructured Pt decorated graphene and multi walled carbon nanotube based room temperature hydrogen gas sensor. Nanoscale 1:382–386. doi:10.1039/b9nr00015a
Xiang C, She Z, Zou Y et al (2014) A room-temperature hydrogen sensor based on Pd nanoparticles doped TiO2 nanotubes. Ceram Int 40:16343–16348. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.07.073
Boudiba A, Zhang C, Navio C et al (2010) Preparation of highly selective, sensitive and stable hydrogen sensors based on Pd-doped tungsten trioxide. Procedia Eng 5:180–183. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2010.09.077
Zeng XQ, Latimer ML, Xiao ZL et al (2011) Hydrogen gas sensing with networks of ultrasmall palladium nanowires formed on filtration membranes. Nano Lett 11:262–268. doi:10.1021/nl103682s
Walter EC, Favier F, Penner RM (2002) Palladium mesowire arrays for fast hydrogen sensors and hydrogen-actuated switches. Anal Chem 74:1546–1553. doi:10.1021/ac0110449
Dhivya P, Prasad AK, Sridharan M (2012) Nanostructured cadmium oxide thin films for hydrogen sensor. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:18575–18578. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.08.098
Ibrahim IM, Rao GM (2012) Characterization and gas sensitivity of cadmium oxide thin films prepared by thermal evaporation technique. J Electron Devices 13:965–974
Shubham K, Khan RU, Chakrabarti P (2012) TiO2 thin film-based low concentration MIS hydrogen sensor. IEEE Conf Proc of Nirma University International Conference on Engineering, Ahmedabad, p 1–5
Haidry AA, Schlosser P, Durina P et al (2011) Hydrogen gas sensors based on nanocrystalline TiO2 thin films. Cent Eur J Phys 9:1351–1356. doi:10.2478/s11534-011-0042-3
Lee J, Kim DH, Hong SH, Jho JY (2011) A hydrogen gas sensor employing vertically aligned TiO2 nanotube arrays prepared by template-assisted method. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 160:1494–1498. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2011.08.001
Dhivya P, Prasad AK, Sridharan M (2014) Magnetron sputtered nanostructured cadmium oxide films for ammonia sensing. J Solid State Chem 214:24–29. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2013.11.030
Dhivya P, Prasad AK, Sridharan M (2015) Effect of sputtering power on the methane sensing properties of nanostructured cadmium oxide films. J Alloys Compd 620:109–115. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.107
Yun S, Lim S (2011) Effect of Al-doping on the structure and optical properties of electrospun zinc oxide nanofiber films. J Colloid Interface Sci 360:430–439. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.05.022
Yang H, Wang S, Yang Y (2012) Zn-doped In2O3 nanostructures: preparation, structure and gas-sensing properties. CrystEngComm 14:1135–1142. doi:10.1039/c1ce06143g
Mizsei J (1995) How can sensitive and selective semiconductor gas sensors be made? Sensors Actuators B Chem 23:173–176. doi:10.1016/0925-4005(94)01269-N
Mondal B, Basumatari B, Das J et al (2014) ZnO-SnO2 based composite type gas sensor for selective hydrogen sensing. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 194:389–396. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2013.12.093
Stamataki M, Fasaki I, Tsonos G et al (2009) Annealing effects on the structural, electrical and H2 sensing properties of transparent ZnO thin films, grown by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 518:1326–1331. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2009.02.156
Gupta D, Dutta D, Kumar M et al (2014) A low temperature hydrogen sensor based on palladium nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 196:215–222. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.106
Reddy CVG, Manorama SV (2000) Room temperature hydrogen sensor based on SnO2:La2O3. J Electrochem Soc 147:390–393. doi:10.1149/1.1393206
Bayata F, Saruhan-Brings B, Ürgen M (2014) Hydrogen gas sensing properties of nanoporous Al-doped titania. Sensors Actuators B Chem 204:109–118. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.079
Wu W, Liu Z, Jauregui LA et al (2010) Wafer-scale synthesis of graphene by chemical vapor deposition and its application in hydrogen sensing. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 150:296–300. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2010.06.070
Park S, Park S, Lee S et al (2014) Hydrogen sensing properties of multiple networked Nb2O5/ZnO core–shell nanorod sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:840–845. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.06.028
Sadek AZ, Partridge JG, McCulloch DG et al (2009) Nanoporous TiO2 thin film based conductometric H2 sensor. Thin Solid Films 518:1294–1298. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2009.02.151
Acknowledgments
One of the authors MS sincerely thanks DRDO (0903810-1229) for the financial support and the authors sincerely thank SASTRA University, Thanjavur and IGCAR, Kalpakkam for providing necessary experimental facilities. PD sincerely thanks SASTRA University for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponnusamy, D., Prasad, A.K. & Madanagurusamy, S. CdO-TiO2 nanocomposite thin films for resistive hydrogen sensing. Microchim Acta 183, 311–317 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1653-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1653-y