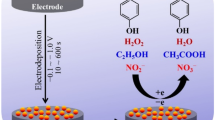
Abstract
A glassy carbon electrode was modified with gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) on a quaternized cellulose support in a film composed of poly(ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether) (PEGDGE), and Hb was immobilized on the Au-NPs. The sensor film was characterized by UV–vis spectra, scanning electron microscopy, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Cyclic voltammetry of the Hb in the Au@Qc/PEGDGE film revealed a pair of well-defined and quasi reversible peaks for the protein heme Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox couple at about −0.333 V (vs. SCE). The sensor film also exhibited good electrocatalytic activity for the reduction of nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide. The amperometric response of the biosensor depends linearly on the concentration of nitric oxide in the 0.9 to 160 μM range, and the detection limit is as low as 12 nM (at 3σ). The response to hydrogen peroxide is linear in the 59 nM to 4.6 μM concentration range, and the detection limit is 16 nM (at 3σ). This biosensor is sensitive, reproducible, and long-term stable.

An electrochemical biosensor based on the immobilization of hemoglobin in Au@Qc NPs /Poly ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether composite film is developed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li P, Ding Y, Lu Z et al (2013) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on the water-soluble phosphonate functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and its application to nitric oxide biosensing. Talanta 115:228
Wang J (2012) Electrochemical biosensing based on noble metal nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 177:245
Shi X, Gu W, Li B et al (2014) Enzymatic biosensors based on the use of metal oxide nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:1
Chen S, Yuan R, Chai Y et al (2013) Electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using metal nanoparticles: a review. Microchim Acta 180:15
Scheller FW, Bistolas N, Liu S et al (2005) Thirty years of haemoglobin electrochemistry. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 116:111
Wang YH, Yu CM, Pan ZQ et al (2013) A gold electrode modified with hemoglobin and the chitosan@ Fe3O4 nanocomposite particles for direct electro- chemistry of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 180:659
Pang H, Gao F, Chen Q et al (2012) Dendrite-like Co3O4 nanostructure and its applications in sensors, supercapacitors and catalysis. Dalton Trans 41:5862
Li SJ, Shi YF, Liu L et al (2012) Electrostatic self-assembly for preparation of sulfonated graphene/gold nanoparticle hybrids and their application for hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electrochim Acta 85:628
Ren L, Dong J, Cheng X et al (2013) Hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on gold nanoparticles in a hierarchically porous zeolite. Microchim Acta 180:1333
Chen H, Wang Y, Wang Y et al (2006) One-step preparation and characterization of PDDA-protected gold nanoparticles. Polymer 47:763
Dimitrijevic NM, Bartels DM, Jonah CD et al (2001) Radiolytically induced formation and optical absorption spectra of colloidal silver nanoparticles in supercritical ethane. J Phys Chem B 105:954
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C et al (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112:2739
Park DH, Kim MS, Joo J (2010) Hybrid nanostructures using π-conjugated polymers and nanoscale metals: synthesis, characteristics, and optoelectronic applications. Chem So Rev 39:2439
Chen PJ, Hu SH, Fan CT et al (2013) A novel multifunctional nano-platform with enhanced anti-cancer and photoacoustic imaging modalities using gold-nanorod-filled silica nanobeads. Chem Commun 49:892
Panigrahi S, Basu S, Praharaj S et al (2007) Synthesis and size-selective catalysis by supported gold nanoparticles: study on heterogeneous and homogeneous catalytic process. J Phys Chem C 111:4596
Shan J, Tenhu H (2007) Recent advances in polymer protected gold nanoparticles: synthesis, properties and applications. Chem Commun 4580–4598
Saha S, Pal A, Kundu S et al (2009) Photochemical green synthesis of calcium-alginate-stabilized Ag and Au nanoparticles and their catalytic application to 4-nitrophenol reduction. Langmuir 26:2885
Nishiyama Y, Langan P, Chanzy H (2002) Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Iβ from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 124:9074
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP et al (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material]. Angew Chem In Ed 44:3358
Niculescu M, Nistor C, Frébort I, Pec P, Mattiasson B, Csöregi E (2000) Redox hydrogel-based amperometric bienzyme electrodes for fish freshness monitoring. Anal Chem 72:1591
Belfer S, Purinson Y, Fainshtein R, Radchenko Y, Kedem O (1998) Surface modification of commercial composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. J Membr Sci 139:175
Asca F, Gorton L, Wagner JB, Nöll G (2008) Increasing amperometric biosensor sensitivity by length fractionated single-walled carbon nanotubes. Biosens Bioelectron 24:272
Lu X, Xu Y, Zheng C, Zhang G, Su Z (2006) Ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether as a protein cross-linker: a case study for cross-linking of hemoglobin. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:767
Vasylieva N, Barnych B, Meiller A, Maucler C, Pollegioni L, Lin JS, Marinesco S (2011) Covalent enzyme immobilization by poly (ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDE) for microelectrode biosensor preparation. Biosen Bioelectron 26:3993
Song Y, Sun Y, Zhang X et al (2008) Homogeneous quaternization of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solutions as gene carriers. Biomacromolecules 9:2259
George P, Hanania G (1953) A spectrophotometric study of ionizations in methaemoglobin. Biochem J 55:236
Bobacka J, Lewenstam A, Ivaska A (2000) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of oxidized poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) film electrodes in aqueous solutions. J Electroanal Chem 489:17
Murray RW, Bard AJ (1984) Electroanalytical chemistry. J Electroanal Chem 13:191
Muirhead H, Perutz MF (1963) Structure of haemoglobin. A three-dimensional Fourier synthesis of reduced human heamoglobin at 5.5 A resolution. Nature 199:633
Trushina E, Oda R, Landers J, McMurray C (1997) Determination of nitrite and nitrate reduction by capillary ion electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 18:1890
Liu HH, Tian ZQ, Lu ZX, Zhang ZL, Zhang M, Pang DW (2004) Direct electrochem-istry and electrocatalysis of heme-proteins entrapped in agarose hydrogel films. Biosens Bioelectron 20:294
Bayachou M, Lin R, Cho W, Farmer PJ (1998) Electrochemical reduction of NO by myoglobin in surfactant film:characterization and reactivity of the nitroxyl (NO-) Adduct. J Am Chem Soc 120:9888
Kamin RA, Wilson GS (1980) Rotating ring-disk enzyme electrode for biocatalysis kinetic studies and characterization of the immobilized enzyme layer. Anal Chem 52:1198
Xu YX, Hu CG, Hu SS (2010) A reagentless nitric oxide biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin adsorbed on the gold colloids modified carbon paste electrode. Sens Actuators B Chem 148:253
Liu KP, Zhang JJ, Yang GH, Wang CM, Zhu JJ (2010) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin based on poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) functionalized graphene sheets/room temperature ionic liquid composite film. Electrochem Commun 12:402–405
Chen HM, Zhao GC (2012) Nanocomposite of polymerized ionic liquid and graphene used as modifier for direct electrochemistry of cytochrome c and nitric oxide biosensing. J Solid State Electrochem 16:3289
Liu X, Shang L, Sun Z et al (2005) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin in dimethyldioctadecyl ammonium bromide film and its electrocatalysis to nitric oxide[J]. J Biochem Biophys Methods 62:143
Pang J, Fan C, Liu X et al (2003) A nitric oxide biosensor based on the multi-assembly of hemoglobin/montmorillonite/polyvinyl alcohol at a pyrolytic graphite electrode[J]. Biosens Bioelectron 19:441
Sun A, Sheng Q, Zheng J (2012) A hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin in palladium nanoparticles/graphene–chitosan nanocomposite film. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:764
Li J, Tang J, Zhou L, Han X, Liu H (2012) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin immobilized on polyacrylamide-P123 film modified glassy carbon electrode. Bioel Ectrochemistry 86:60
Zhang Y, Sun X, Jia N (2011) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin immobilized into poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/room temperature ionic liquid composite film. Sens Actuators B Chem 157:527
Li J, Yuan R, Chai Y et al (2010) Direct electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide at a glassy carbon electrode modified with polypyrrole nanowires and platinum hollow nanospheres. Microchim Acta 171:125
Song J, Xu JM, Zhao PS et al (2011) A hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on direct electron transfer from hemoglobin to an electrode modified with Nafion and activated nanocarbon. Microchim Acta 172:117
Xu J, Liu C, Wu Z (2011) Direct electrochemistry and enhanced electrocatalytic activity of hemoglobin entrapped in graphene and ZnO nanosphere composite film[J]. Microchim Acta 172:425
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the NSF of China (Grants No. 21275123 and 20975088 for J. Fei, 21105085 and 31270988 for B. Feng), Project of Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (14JJ1019 and 12JJ7002), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China, Ministry of Education of China (20134301110005), Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation For Postgraduate (CX2012B268) and National Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (201310530006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 318 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Nie, M., He, X. et al. Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin on a glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether) and gold nanoparticles on a quaternized cellulose support. A sensor for hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide. Microchim Acta 181, 1541–1549 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1228-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1228-3