Abstract
Background
The standard for rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) remains unclear. Cases often require positioning of the tibial component, prioritizing adequate coverage of resected bone surface rather than alignment with the tibial rotational axis. We investigated tibial component position in TKA, prioritizing maximum coverage of resected bone surface, and evaluated the correlation with the tibial anteroposterior (AP) axis.
Methods
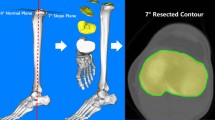
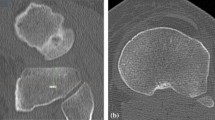
We analyzed preoperative computed tomography images for primary TKA in 106 cases and 157 knees, using three-dimensional planning software. Tibial component position prioritizing maximum coverage of resected bone surface was simulated, and results were compared with the AP axis. Rotational alignment angle was defined as that between a line perpendicular to the tibial AP axis and a line connecting the posterior edge of the tibial component.
Results
The simulated tibial component was more externally rotated by a mean 4.5° ± 4.2°. The alignment angle showed normal distribution, but variability was large, ranging from 5.1° internal rotation to 16.2° external rotation. In 138 of 157 (87.9 %) knees, the tibial component was positioned in the externally rotated position with respect to the AP axis. The tibial component was aligned within the medial one-third of the patellar tendon in 122 of 157 (77.7 %) knees.
Conclusions
The tibial component aligned using coverage prioritizing was externally rotated, although large variability was observed. Rotational alignment was optimal in 79 % of cases when the tibial component was aligned with coverage prioritizing, but hyperexternal rotation was observed in patients with severe knee deformation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:46–55
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Lewis P, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB, Devane P (1994) Posteromedial tibial polyethylene failure in total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:11–17
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
Aglietti P, Sensi L, Cuomo P, Ciardullo A (2008) Rotational position of femoral and tibial components in TKA using the femoral transepicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2751–2755
Chowdhury EA, Porter ML (2005) How is the tibial tray aligned to the femoral prosthesis in a total knee arthroplasty? A survey of opinion from BASK? Knee 12:79–80
Ikeuchi M, Yamanaka N, Okanoue Y, Ueta E, Tani T (2007) Determining the rotational alignment of the tibial component at total knee replacement: a comparison of two techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:45–49
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Berhouet J, Beaufils P, Boisrenoult P, Frasca D, Pujol N (2011) Rotational positioning of the tibial tray in total knee arthroplasty: a CT evaluation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97(7):699–704
Hsu HP, Garg A, Walker PS, Spector M, Ewald FC (1989) Effect of knee component alignment on tibial load distribution with clinical correlation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:135–144
Nicoll D, Rowley DI (2010) Internal rotational error of the tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(9):1238–1244
Completo A, Fonseca F, Simões JA (2008) Strain shielding in proximal tibia of stemmed knee prosthesis: experimental study. J Biomech 41(3):560–566
Abraham R, Malkani AL, Lewis J, Beck D (2007) An anatomical study of tibial metaphyseal/diaphyseal mismatch during revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 22(2):241–244
Scott CE, Biant LC (2012) The role of the design of tibial components and stems in knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 94(8):1009–1015
Barrack RL, Rorabeck C, Burt M, Sawhney J (1999) Pain at the end of the stem after revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 367:216–225
Barrack RL, Stanley T, Burt M, Hopkins S (2004) The effect of stem design on end-of-stem pain in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 19(7):119–124
Glenn JC, Sokoloski SN, Damer BM, Tabit JM (2010) Tibia pain at end of stem with stemmed revision total knee arthroplasty: treatment with cortical strut graft technique. J Arthroplasty 25(3):497
Tei K, Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Sasaki H, Shibanuma N, Akisue T, Nishida K, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) Novel image-matching software for postoperative evaluation after TKA. Orthopedics 35(12):e1711–e1715
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2004) An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:213–219
Dalury DF, Jiranek W, Pierson J, Pearson SE (2003) The long-term outcome of total knee patients with moderate loss of motion. J Knee Surg 16(4):215–220
Uehara K, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Ohashi H, Yamano Y (2002) Bone anatomy and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 402:196–201
Lutzner J, Krummenauer F, Gunther KP, Kirschner S (2010) Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty is better at the medial third of tibial tuberosity than at the medial border. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:57
Bedard M, Vince KG, Redfern J, Collen SR (2011) Internal rotation of the tibial component is frequent in stiff total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:2346–2355
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Merkow RL, Soudry M, Insall JN (1985) Patellar dislocation following total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67(9):1321–1327
Nagamine R, Whiteside LA, White SE, McCarthy DS (1994) Patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. The effect of tibial tray malrotation and articular surface configuration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 304:262–271
Rhoads DD, Noble PC, Reuben JD, Mahoney OM, Tullos HS (1990) The effect of femoral component position on patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 260:43–51
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Hyldahl HC, Meding JB, Redelman R (2008) Implant migration and failure in total knee arthroplasty is related to body mass index and tibial component size. J Arthroplasty 23(6 Suppl 1):104–109
Bindelglass DF, Cohen JL, Dorr LD (1993) Patellar tilt and subluxation in total knee arthroplasty. Relationship to pain, fixation, and design. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:103–109
Branson PJ, Steege JW, Wixson RL, Lewis J, Stulberg SD (1989) Rigidity of initial fixation with uncemented tibial knee implants. J Arthroplasty 4(1):21–26
Incavo SJ, Ronchetti PJ, Howe JG, Tranowski JP (1994) Tibial plateau coverage in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:81–85
Westrich GH, Laskin RS, Haas SB, Sculco TP (1994) Resection specimen analysis of tibial coverage in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 309:163–175
Martin S, Saurez A, Ismaily S, Ashfaq K, Noble P, Incavo SJ (2014) Maximizing tibial coverage is detrimental to proper rotational alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:121–125
Baldini A, Indelli PF, De Luca L, Marcucci PC, Marcucci M (2013) Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty: the anterior tibial cortex is a reliable landmark. Joints 21:155–160
Matsui Y, Kadoya Y, Uehara K, Kobayashi A, Takaoka K (2005) Rotational deformity in varus osteoarthritis of the knee: analysis with computed tomography. Clin Orthop Relat Res 433:147–151
Eckhoff DG, Johnston RJ, Stamm ER, Kilcoyne RF, Wiedel JD (1994) Version of the osteoarthritic knee. J Arthroplasty 9(1):73–79
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Each author certifies that he or she, or a member of their immediate family, has no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Ethical standard
The local institutional review board approved this study. All patients provided informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirakawa, M., Miyazaki, M., Ikeda, S. et al. Evaluation of the rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty: position prioritizing maximum coverage. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 27, 119–124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-016-1850-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-016-1850-3