Abstract
Background
Stiffness complicating TKA is a complex and multifactorial problem. We suspected internally rotated components compromised motion because of pain, patellar maltracking, a tight medial flexion gap, and limited femoral rollback on a conforming lateral tibial condyle.
Questions/purposes
We sought to determine: (1) the incidence of internal rotation of the femoral and tibial components in stiff TKAs; (2) if revision surgery that included correction of rotational positioning improved pain, ROM, and patellar tracking; and (3) if revision altered nonrotational radiographic parameters.
Methods
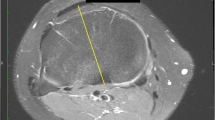
From a cohort of 52 patients with TKAs revised for stiffness, we performed CT scans of 34 before and 18 after revision to quantify rotational positioning of the femoral and tibial components using a previously validated scanning protocol.
Results
All 34 patients with TKAs had internal rotation of the summed values for tibial and femoral components (mean, 14.8°; range, 2.7°–33.7°) before revision for stiffness. The incidence of internal rotation was 24 of 34 femoral (mean, 3.1°; internal) and 33 of 34 tibial components (mean, 13.7° internal). Revision arthroplasty improved Knee Society function, knee, and pain scores. Mean extension improved from a contracture of 10.1° to 0.8° and flexion from 71.5° to 100°. Postrevision CT scans confirmed correction of component rotation. Nonrotational parameters were unchanged.
Conclusions
We recommend CT scanning of patients with stiff TKAs before surgical intervention to identify the presence of internally rotated components.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babis GC, Trousdale RT, Pagnano MW, Morrey BF. Poor outcomes of isolated tibial insert exchange and arthrolysis for the management of stiffness following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:1534–1536.
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L. Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;392:46–55.
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;356:144–153.
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS. Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;286:40–47.
Bindelglass DF, Cohen JL, Dorr LD. Patellar tilt and subluxation in total knee arthroplasty: relationship to pain, fixation, and design. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;286:103–109.
Bindelglass DF, Vince KG. Patellar tilt and subluxation following subvastus and parapatellar approach in total knee arthroplasty: implication for surgical technique. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:507–511.
Boldt JG, Munzinger UK, Zanetti M, Hodler J. Arthrofibrosis associated with total knee arthroplasty: gray-scale and power Doppler sonographic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182:337–340.
Boldt JG, Stiehl JB, Hodler J, Zanetti M, Munzinger U. Femoral component rotation and arthrofibrosis following mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2006;30:420–425.
Bong MR, Di Cesare PE. Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004;12:164–171.
Christensen CP, Crawford JJ, Olin MD, Vail TP. Revision of the stiff total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:409–415.
Daluga D, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH, Vaughn BK. Knee manipulation following total knee arthroplasty: analysis of prognostic variables. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6:119–128.
Dennis DA. The stiff total knee arthroplasty: causes and cures. Orthopedics. 2001;24:901–902.
Fehring TK, Odum S, Griffin WL, Mason JB. Outcome comparison of partial and full component revision TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;440:131–134.
Freedman KB, Bernstein J. Sample size and statistical power in clinical orthopaedic research. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:1454–1460.
Gandhi R, de Beer J, Leone J, Petruccelli D, Winemaker M, Adili A. Predictive risk factors for stiff knees in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:46–52.
Haidukewych GJ, Jacofsky DJ, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT. Functional results after revision of well-fixed components for stiffness after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:133–138.
Hutchinson JR, Parish EN, Cross MJ. Results of open arthrolysis for the treatment of stiffness after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:1357–1360.
Incavo S, Wild J, Coughlin K, Beynnon B. Early revision for component malrotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;458:131–136.
Insall J. A midline approach to the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53:1584–1586.
Insall J, Goldberg V, Salvati E. Recurrent dislocation and the high-riding patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972;88:67–69.
Insall J, Salvati E. Patella position in the normal knee joint. Radiology. 1971;101:101–104.
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;248:13–14.
Jazrawi LM, Birdzell L, Kummer FJ, Di Cesare PE. The accuracy of computed tomography for determining femoral and tibial total knee arthroplasty component rotation. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:761–766.
Jiang CC, Yip KM, Liu DH. Patellar thickness in total knee replacement. J Formos Med Assoc. 1994;93:417–420.
Kim J, Nelson CL, Lotke PA. Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty: prevalence of the complication and outcomes of revision. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:1479–1484.
Knutson K, Lewold S, Robertsson O, Lidgren L. The Swedish knee arthroplasty register: a nation-wide study of 30,003 knees 1976–1992. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994;65:375–386.
Mackay DC, Siddique MS. The results of revision knee arthroplasty with and without retention of secure cemented femoral components. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85:517–520.
Malo M, Vince KG. The unstable patella after total knee arthroplasty: etiology, prevention, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11:364–371.
Mason JB, Fehring TK, Odum SM, Griffin WL, Nussman DS. The value of white blood cell counts before revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18:1038–1043.
Mauerhan DR, Nelson CL, Smith DL, Fitzgerald RH Jr, Slama TG, Petty RW, Jones RE, Evans RP. Prophylaxis against infection in total joint arthroplasty: one day of cefuroxime compared with three days of cefazolin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:39–45.
Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH, Cool CR. Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56:1391–1396.
Merkow RL, Soudry M, Insall JN. Patellar dislocation following total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67:1321–1327.
Nelson CL, Kim J, Lotke PA. Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(suppl 1):264–270.
Nicholls DW, Dorr LD. Revision surgery for stiff total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1990;5(suppl):S73–77.
Parvizi J, Tarity TD, Steinbeck MJ, Politi RG, Joshi A, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF. Management of stiffness following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(suppl 4):175–181.
Ries MD, Badalamente M. Arthrofibrosis after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;380:177–183.
Ritter MA, Berend ME, Harty LD, Davis KE, Meding JB, Keating EM. Predicting range of motion after revision total knee arthroplasty: clustering and log-linear regression analyses. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:338–343.
Ritter MA, Harty LD, Davis KE, Meding JB, Berend ME. Predicting range of motion after total knee arthroplasty: clustering, log-linear regression, and regression tree analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1278–1285.
Scott WN, Clarke HD. The stiff knee: causes and cures. Orthopedics. 2000;23:987–988.
Scranton PE Jr. Management of knee pain and stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:428–435.
Scuderi GR. The stiff total knee arthroplasty: causality and solution. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(4 suppl 2):23–26.
Sharkey PF, Homesley HD, Shastri S, Jacoby SM, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH. Results of revision total knee arthroplasty after exposure of the knee with extensor mechanism tenolysis. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:751–756.
Shoji H, Solomonow M, Yoshino S, D’Ambrosia R, Dabezies E. Factors affecting postoperative flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 1990;13:643–649.
Suter T, Zanetti M, Schmid M, Romero J. Reproducibility of measurement of femoral component rotation after total knee arthroplasty using computer tomography. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:744–748.
Vince K, Bedard M. Implanting the Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. In: Lotke PA, Lonner J, eds. Master Techniques in Orthopedic Surgery: Knee Arthroplasty. 3rd ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2008:203–228.
Vince K, Eissmann E. The Stiff TKA. In: Fu FH, Harner CD, Vince K, eds. Knee Surgery. Vol 2. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 1994:1529–1538.
Vince KG. A step-wise approach to revision TKA. Orthopedics. 2005;28:999–1001.
Vince KG, McPherson EJ. The patella in total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1992;23:675–686.
Williams RJ 3rd, Westrich GH, Siegel J, Windsor RE. Arthroscopic release of the posterior cruciate ligament for stiff total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;331:185–191.
Yercan HS, Sugun TS, Bussiere C, Ait Si Selmi T, Davies A, Neyret P. Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty: prevalence, management and outcomes. Knee. 2006;13:111–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (KGV) has a consultancy agreement and has received royalties from Zimmer Inc (Warsaw, IN).
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
This work was performed at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
About this article
Cite this article
Bédard, M., Vince, K.G., Redfern, J. et al. Internal Rotation of the Tibial Component is Frequent in Stiff Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469, 2346–2355 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1889-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1889-8