Abstract
Purpose
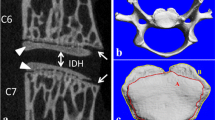
To evaluate the influence of osteoporosis on the microarchitecture and vascularization of the endplate in rhesus monkeys with or without intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration using micro-computerized tomography (micro-CT), and to further analyze the correlation between osteoporosis and IVD degeneration.
Methods
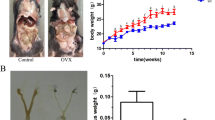
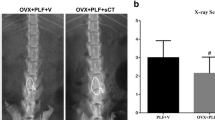
Twelve rhesus monkeys were randomly divided into the ovariectomy (OVX, n = 6) and the sham group (n = 6). The subchondral bone adjacent to the lumbar IVDs (from L4/5 to L6/7) of each monkey was randomly injected with 4 ml pingyangmycin (PYM) solution (1.5 mg/ml, PYM), or 4 ml phosphate buffered saline (PBS) as vehicle treatment, or exteriorized but not injected anything as control (Cntrl). Degenerative and osteoporotic processes were evaluated at different time points. Micro-CT and histology were performed to analyze microarchitecture, calcification area and vascularization of the endplate.
Results
OVX resulted in significant decrease of bone mineral density (BMD). PYM injection induced progressively IVD degeneration, which was more progressive when combined with OVX. There was a negative correlation between BMD and Pfirrmann grade in the subgroups with PYM injection. The micro-CT analysis showed the combination of osteoporosis and IVD degeneration led to more calcification of endplate than any one thereof. The decrease of vascular volume percent in the endplate of the OVX-PYM subgroup was significantly greater than that in the Sham-PYM subgroup, both of which showed significant less vascularization compared to the other subgroups.
Conclusion
In conclusion the osteoporosis could accumulate the calcification and decrease the vascularization in the endplates adjacent to the degenerated IVDs, which subsequently exacerbated degeneration of the degenerated IVDs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tenne M, McGuigan F, Besjakov J, Gerdhem P, Akesson K (2013) Degenerative changes at the lumbar spine—implications for bone mineral density measurement in elderly women. Osteoporos Int 24(4):1419–1428
Steiger P, Cummings SR, Black DM, Spencer NE, Genant HK (1992) Age-related decrements in bone mineral density in women over 65. J Bone Miner Res 7(6):625–632
Wang YX, Griffith JF, Ma HT, Kwok AW, Leung JC, Yeung DK, Ahuja AT, Leung PC (2011) Relationship between gender, bone mineral density, and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine: a study in elderly subjects using an eight-level MRI-based disc degeneration grading system. Osteoporos Int 22(1):91–96
Wang Y, Boyd SK, Battie MC, Yasui Y, Videman T (2011) Is greater lumbar vertebral BMD associated with more disk degeneration? A study using microCT and discography. J Bone Miner Res 26(11):2785–2791
Miyakoshi N, Itoi E, Murai H, Wakabayashi I, Ito H, Minato T (2003) Inverse relation between osteoporosis and spondylosis in postmenopausal women as evaluated by bone mineral density and semiquantitative scoring of spinal degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(5):492–495
Verstraeten A, Van Ermen H, Haghebaert G, Nijs J, Geusens P, Dequeker J (1991) Osteoarthrosis retards the development of osteoporosis. Observation of the coexistence of osteoarthrosis and osteoporosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 264:169–177
Mattei TA (2013) Osteoporosis delays intervertebral disc degeneration by increasing intradiscal diffusive transport of nutrients through both mechanical and vascular pathophysiological pathways. Med Hypotheses 80(5):582–586
Roberts S, Menage J, Eisenstein SM (1993) The cartilage end-plate and intervertebral disc in scoliosis: calcification and other sequelae. J Orthop Res 11(5):747–757
Gruber HE, Gordon B, Williams C, James NH (2003) Hanley EJ (2003) Bone mineral density of lumbar vertebral end plates in the aging male sand rat spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(16):1766–1772
Wei F, Zhong R, Wang L, Zhou Z, Pan X, Cui S, Sun H, Zou X, Gao M, Jiang B, Chen W, Zhuang W, Sun H, Liu S (2015) Pingyangmycin-induced in vivo lumbar disc degeneration model of rhesus monkeys. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 40(4):E199–E210
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2001) Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(17):1873–1878
Hee HT, Chuah YJ, Tan BH, Setiobudi T, Wong HK (2011) Vascularization and morphological changes of the endplate after axial compression and distraction of the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36(7):505–511
Gruber HE, Ashraf N, Kilburn J, Williams C, Norton HJ, Gordon BE, Hanley EJ (2005) Vertebral endplate architecture and vascularization: application of micro-computerized tomography, a vascular tracer, and immunocytochemistry in analyses of disc degeneration in the aging sand rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:2593–2600
Gao X, Ma W, Dong H, Yong Z, Su R (2014) Establishing a rapid animal model of osteoporosis with ovariectomy plus low calcium diet in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(8):5123–5128
Ding Y, Jiang J, Zhou J, Wu X, Huang Z, Chen J, Zhu Q (2014) The effects of osteoporosis and disc degeneration on vertebral cartilage endplate lesions in rats. Eur Spine J 23(9):1848–1855
Miller MA, Chin J, Miller SC, Fox J (1998) Disparate effects of mild, moderate, and severe secondary hyperparathyroidism on cancellous and cortical bone in rats with chronic renal insufficiency. Bone 23(3):257–266
Kramer PA, Newell-Morris LL, Simkin PA (2002) Spinal degenerative disk disease (DDD) in female macaque monkeys: epidemiology and comparison with women. J Orthop Res 20(3):399–408
Wang T, Zhang L, Huang C, Cheng AG, Dang GT (2004) Relationship between osteopenia and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Calcif Tissue Int 75(3):205–213
Motoie H, Kanoh H, Ogata S, Kawamuki K, Shikama H, Fujikura T (1996) Prevention of bone loss by bisphosphonate YM175 in ovariectomized dogs with dietary calcium restriction. Jpn J Pharmacol 71(3):239–246
Smith SY, Jolette J, Turner CH (2009) Skeletal health: primate model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Am J Primatol 71(9):752–765
Videman T, Gibbons LE, Battie MC (2008) Age- and pathology-specific measures of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33(25):2781–2788
Bian Q, Liang QQ, Wan C, Hou W, Li CG, Zhao YJ, Lu S, Shi Q, Wang YJ (2011) Prolonged upright posture induces calcified hypertrophy in the cartilage end plate in rat lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36(24):2011–2020
Kobayashi S, Baba H, Takeno K, Miyazaki T, Uchida K, Kokubo Y, Nomura E, Morita C, Yoshizawa H, Meir A (2008) Fine structure of cartilage canal and vascular buds in the rabbit vertebral endplate, Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine 9(1):96–103
Laffosse JM, Accadbled F, Molinier F, Bonnevialle N, de Gauzy JS, Swider P (2010) Correlations between effective permeability and marrow contact channels surface of vertebral endplates. J Orthop Res 28(9):1229–1234
Urban JP, Smith S, Fairbank JC (2004) Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(23):2700–2709
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81401839) National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB619105) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
R. Zhong and F. Wei contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, R., Wei, F., Wang, L. et al. The effects of intervertebral disc degeneration combined with osteoporosis on vascularization and microarchitecture of the endplate in rhesus monkeys. Eur Spine J 25, 2705–2715 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4593-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4593-2