Abstract
Background
Traditional Japanese medicine, known as Kampo medicine, consists of mixtures of several medicinal herbs widely used to treat upper gastrointestinal disorders in Japan. Rikkunshito, one of these medicines, has not been evaluated with respect to its influence on gastrointestinal motor activity. We investigated the effect of rikkunshito on upper gastrointestinal motility and plasma ghrelin concentrations in conscious dogs.
Methods
Contractile response to intragastric administration of rikkunshito was studied via surgically implanted force transducers. A powdered extract of rikkunshito (1.3, 2.7, and 4.0 g) dissolved in water was administered into the stomachs of normal and vagotomized dogs before feeding and gastric emptying was evaluated. Several inhibitors of gastrointestinal motility (atropine, hexamethonium, and ondansetron) were injected intravenously before intragastric administration of rikkunshito. Plasma acylated ghrelin levels after intragastric administration of rikkunshito were measured.
Results
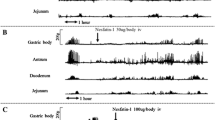
In a fasting state, intragastric administration of rikkunshito induced phasic contractions in the duodenum and jejunum in normal dogs. Rikkunshito-induced contractions were inhibited by atropine, hexamethonium and ondansetron. In vagotomized dogs, rikkunshito induced phasic contractions, similar to normal dogs. Gastric emptying was accelerated by intragastric administration of rikkunshito in a dose-dependent manner. The plasma acylated ghrelin level 150 min after intragastric administration of 4.0 g of rikkunshito was significantly higher than the control value.
Conclusions
Intragastric administration of rikkunshito stimulates gastrointestinal contractions in the interdigestive state through cholinergic neurons and 5-HT type 3 receptors. Moreover, rikkunshito increases plasma acylated ghrelin levels. Rikkunshito may alleviate gastrointestinal disorders through its prokinetic effects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tatsuta M, Iishi H. Effect of treatment with liu-jun-zi-tang (TJ-43) on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in dyspeptic patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1993;7:459–62.
Kusunoki H, Haruma K, Hata J, Ishii M, Kamada T, Yamashita N, et al. Efficacy of Rikkunshito, a traditional Japanese medicine (Kampo), in treating functional dyspepsia. Intern Med. 2010;49:2195–202.
Tominaga K, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Fujiwara Y, Tanaka M, Shimoyama Y, et al. Rikkunshito improves symptoms in PPI-refractory GERD patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47(3):284–92.
Kawahara H, Kubota A, Hasegawa T, Okuyama H, Ueno T, Ida S, et al. Effects of rikkunshito on the clinical symptoms and esophageal acid exposure in children with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23:1001–5.
Kawahara H, Mitani Y, Nomura M, Nose K, Yoneda A, Hasegawa T, et al. Impact of rikkunshito, an herbal medicine, on delayed gastric emptying in profoundly handicapped patients. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009;25:987–90.
Yagi M, Homma S, Kubota M, Iinuma Y, Kanada S, Kinoshita Y, et al. The herbal medicine Rikkunshi-to stimulates and coordinates the gastric myoelectric activity in post-operative dyspeptic children after gastrointestinal surgery. Pediatr Surg Int. 2004;19:760–5.
Takahashi T, Endo S, Nakajima K, Souma Y, Nishida T. Effect of rikkunshito, a Chinese herbal medicine, on stasis in patients after pylorus-preserving gastrectomy. World J Surg. 2009;33:296–302.
Tomono H, Ito Y, Watanabe T. Successful antiemetic treatment of TSUMURA Rikkunshi-to Extract Granules for ethical use in addition to other antiemetic agents in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for an advanced breast cancer patient. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2006;33:1129–31.
Hayakawa T, Arakawa T, Kase Y, Akiyama S, Ishige A, Takeda S, et al. Liu-Jun-Zi-Tang, a kampo medicine, promotes adaptive relaxation in isolated guinea pig stomachs. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1999;25:211–8.
Kito Y, Suzuki H. Properties of Rikkunshi-to (TJ-43)-induced relaxation of rat gastric fundus smooth muscles. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;298:G755–63.
Kido T, Nakai Y, Kase Y, Sakakibara I, Nomura M, Takeda S, et al. Effects of rikkunshi-to, a traditional Japanese medicine, on the delay of gastric emptying induced by N(G)-nitro-l-arginine. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;98:161–7.
Tominaga K, Kido T, Ochi M, Sadakane C, Mase A, Okazaki H, et al. The traditional Japanese medicine rikkunshito promotes gastric emptying via the antagonistic action of the 5-HT3 receptor pathway in rats. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2011;2011:248481.
Arakawa T, Higuchi K, Fujiwara Y, Watanabe T, Tominaga K, Hayakawa T, et al. Gastroprotection by Liu-Jun-Zi-Tang (TJ-43): possible mediation of nitric oxide but not prostaglandins or sulfhydryls. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1999;25:207–10.
Goso Y, Ogata Y, Ishihara K, Hotta K. Effects of traditional herbal medicine on gastric mucin against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol. 1996;113:17–21.
Nakazato M, Murakami N, Date Y, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K, et al. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature. 2001;409:194–8.
Tack J, Depoortere I, Bisschops R, Delporte C, Coulie B, Meulemans A, et al. Influence of ghrelin on interdigestive gastrointestinal motility in humans. Gut. 2006;55:327–33.
Wren AM, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, Brynes AE, Frost GS, Murphy KG, et al. Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5992.
Shinomiya T, Fukunaga M, Akamizu T, Irako T, Yokode M, Kangawa K, et al. Plasma acylated ghrelin levels correlate with subjective symptoms of functional dyspepsia in female patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:648–53.
Isomoto H, Ueno H, Nishi Y, Yasutake T, Tanaka K, Kawano N, et al. Circulating ghrelin levels in patients with various upper gastrointestinal diseases. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:833–8.
Shindo T, Futagami S, Hiratsuka T, Horie A, Hamamoto T, Ueki N, et al. Comparison of gastric emptying and plasma ghrelin levels in patients with functional dyspepsia and non-erosive reflux disease. Digestion. 2009;79:65–72.
Takeda H, Muto S, Hattori T, Sadakane C, Tsuchiya K, Katsurada T, et al. Rikkunshito ameliorates the aging-associated decrease in ghrelin receptor reactivity via phosphodiesterase III inhibition. Endocrinology. 2010;151:244–52.
Matsumura T, Arai M, Yonemitsu Y, Maruoka D, Tanaka T, Suzuki T, et al. The traditional Japanese medicine Rikkunshito increases the plasma level of ghrelin in humans and mice. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:300–7.
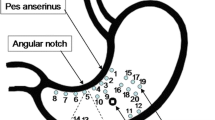
Itoh Z, Honda R, Takeuchi S, Aizawa I, Takayanagi R. An extraluminal force transducer for recording contractile activity of the gastrointestinal smooth muscle in the conscious dogs: its construction and implantation. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1977;12:275–83.
Inatomi N, Satoh H, Maki Y, Hashimoto N, Itoh Z, Omura S. An erythromycin derivative, EM-523, induces motilin-like gastrointestinal motility in dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;251:707–12.
Itoh Z, Mizumoto A, Iwanaga Y, Yoshida N, Torii K, Wakabayashi K. Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptors in regulation of interdigestive gastric contractions by motilin in the dog. Gastroenterology. 1991;100:901–8.
Shiba Y, Mizumoto A, Inatomi N, Haga N, Yamamoto O, Itoh Z. Stimulatory mechanism of EM523-induced contractions in postprandial stomach of conscious dogs. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:1513–21.
Park HJ, Jung JK, Song KS, Lee SI, Itoh Z, Park IS. Effect of erythromycin on gastric emptying in healthy individuals assessed by radio-opaque markers and plasma acetaminophen levels. J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:734–9.
Sato F, Marui S, Inatomi N, Itoh Z, Omura S. EM574, an erythromycin derivative, improves delayed gastric emptying of semi-solid meals in conscious dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;395:165–72.
Yokoyama M, Murakami N, Naganobu K, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Nakahara K. Relationship between growth and plasma concentrations of ghrelin and growth hormone in juvenile beagle dogs. J Vet Med Sci. 2005;67:1189–92.
Shiratori M, Shoji T, Kanazawa M, Hongo M, Fukudo S. Effect of rikkunshito on gastric sensorimotor function under distention. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;23(323–9):e155–6.
Hasegawa T, Yamaki K, Nadai M, Muraoka I, Wang L, Takagi K, et al. Lack of effect of Chinese medicines on bioavailability of ofloxacin in healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;32:57–61.
Yoshida N, Mizumoto A, Iwanaga Y, Itoh Z. Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptor antagonists on gastrointestinal motor activity in conscious dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991;256:272–8.
Kawasaki N, Nakada K, Nakayoshi T, Furukawa Y, Suzuki Y, Hanyu N, et al. Effect of Dai-kenchu-to on gastrointestinal motility based on differences in the site and timing of administration. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:2684–94.
Shibata C, Sasaki I, Naito H, Ueno T, Matsuno S. The herbal medicine Dai-Kenchu-Tou stimulates upper gut motility through cholinergic and 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptors in conscious dogs. Surgery. 1999;126:918–24.
Hashimoto K, Kase Y, Murata P, Kido T, Nakai Y, Sakakibara I, et al. Pharmacological evaluation of Shokyo and Kankyo (1). Biol Pharm Bull. 2002;25:1183–7.
Nakai Y, Kido T, Hashimoto K, Kase Y, Sakakibara I, Higuchi M, et al. Effect of the rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea and its constituents on the delay of gastric emptying. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;84:51–5.
Masuda Y, Tanaka T, Inomata N, Ohnuma N, Tanaka S, Itoh Z, et al. Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;276:905–8.
Fujino K, Inui A, Asakawa A, Kihara N, Fujimura M, Fujimiya M. Ghrelin induces fasted motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract in conscious fed rats. J Physiol. 2003;550:227–40.
Ohno T, Kamiyama Y, Aihara R, Nakabayashi T, Mochiki E, Asao T, et al. Ghrelin does not stimulate gastrointestinal motility and gastric emptying: an experimental study of conscious dogs. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006;18:129–35.
Takeda H, Sadakane C, Hattori T, Katsurada T, Ohkawara T, Nagai K, et al. Rikkunshito, an herbal medicine, suppresses cisplatin-induced anorexia in rats via 5-HT2 receptor antagonism. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:2004–13.
Sadakane C, Muto S, Nakagawa K, Ohnishi S, Saegusa Y, Nahata M, et al. 10-Gingerol, a component of rikkunshito, improves cisplatin-induced anorexia by inhibiting acylated ghrelin degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;412:506–11.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a Grant from Tsumura and Company (Tokyo, Japan).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanai, M., Mochiki, E., Ogawa, A. et al. Intragastric administration of rikkunshito stimulates upper gastrointestinal motility and gastric emptying in conscious dogs. J Gastroenterol 48, 611–619 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0687-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0687-8