Abstract
Background
Understanding of pathogenesis and treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is growing. However, studies regarding the outcomes and late effects among AML survivors are relatively limited.
Methods
This nationwide population-based study used medical records from the Taiwanese National Health Insurance Research Database. A total of 3356 AML patients diagnosed from 2000 to 2008 were analyzed. The physiological and psychological morbidities in AML survivors were compared to those identified from a normal population. This study also compared late effects among AML survivors treated by intensive chemotherapy alone and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT).
Results
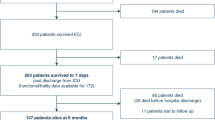
The incidence of AML in Taiwan has increased from 1.07 per 100,000 persons in 2000 to 2.17 per 100,000 persons in 2008 (p < 0.0001). With the median overall survival (OS) time of 0.98 years, 25.0 % of AML patients in this study cohort received best supportive care alone. Compared to the normal population, AML survivors had higher rates of hypertension (hazard ratio [HR] 1.69; 95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.18–2.42; p < 0.01), cardiovascular disease (HR 2.53; 95 % CI 1.39–4.61; p < 0.01), diabetes (HR 2.27; 95 % CI 1.48–3.48; p < 0.001), and psychological disorders (HR 1.45; 95 % CI 1.04–2.04; p < 0.05). Although patients undergoing allo-HSCT had a better OS than did patients treated with intensive chemotherapy alone (median not reached vs. 1.53 years; p < 0.0001), diabetes was found more often among allo-HSCT recipients than among patients receiving intensive chemotherapy only (HR 2.93; 95 % CI 1.21–7.08; p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Regular physical and psychological surveillance of AML survivors is needed especially for those receiving allo-HSCT.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Tefferi A, Bloomfield CD (2009) The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 114:937–951
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30
Sant M, Allemani C, Tereanu C, De Angelis R, Capocaccia R, Visser O, Marcos-Gragera R, Maynadie M, Simonetti A, Lutz JM, Berrino F, Group HW (2010) Incidence of hematologic malignancies in Europe by morphologic subtype: results of the HAEMACARE project. Blood 116:3724–3734
Dohner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD (2015) Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 373:1136–1152
Cheng MJ, Hourigan CS, Smith TJ (2014) Adult acute myeloid leukemia long-term survivors. J Leuk (Los Angel) 2
Wilson IB, Cleary PD (1995) Linking clinical variables with health-related quality of life. A conceptual model of patient outcomes. JAMA 273:59–65
Mehta HB, Sura SD, Sharma M, Johnson ML, Riall TS (2016) Comparative performance of diagnosis-based and prescription-based comorbidity scores to predict health-related quality of life. Med Care.
Teng CL, JT Y, Chen YH, Lin CH, Hwang WL (2014) Early colonoscopy confers survival benefits on colon cancer patients with pre-existing iron deficiency anemia: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS One 9:e86714
Teng CL, Wang CY, Chen YH, Lin CH, Hwang WL (2015) Optimal sequence of irinotecan and oxaliplatin-based regimens in metastatic colorectal cancer: a population-based observational study. PLoS One 10:e0135673
Lin CH, Sheu WH (2013) Hypoglycaemic episodes and risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: 7-year follow-up study. J Intern Med 273:102–110
Schoch C, Kern W, Schnittger S, Hiddemann W, Haferlach T (2004) Karyotype is an independent prognostic parameter in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML): an analysis of 93 patients with t-AML in comparison to 1091 patients with de novo AML. Leukemia 18:120–125
Huang SY, Yao M, Tang JL, Lee WC, Tsay W, Cheng AL, Wang CH, Chen YC, Shen MC, Tien HF (2007) Epidemiology of multiple myeloma in Taiwan: increasing incidence for the past 25 years and higher prevalence of extramedullary myeloma in patients younger than 55 years. Cancer 110:896–905
Patel MI, Ma Y, Mitchell BS, Rhoads KF (2015) Age and genetics: how do prognostic factors at diagnosis explain disparities in acute myeloid leukemia? Am J Clin Oncol 38:159–164
Patel MI, Ma Y, Mitchell B, Rhoads KF (2015) How do differences in treatment impact racial and ethnic disparities in acute myeloid leukemia? Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 24:344–349
Byrd JC, Mrozek K, Dodge RK, Carroll AJ, Edwards CG, Arthur DC, Pettenati MJ, Patil SR, Rao KW, Watson MS, Koduru PR, Moore JO, Stone RM, Mayer RJ, Feldman EJ, Davey FR, Schiffer CA, Larson RA, Bloomfield CD, Cancer, Leukemia Group B (2002) Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from cancer and leukemia group B (CALGB 8461). Blood 100:4325–4336
Hahn A, Giri S, Yaghmour G, Martin MG (2015) Early mortality in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 39:505–509
Appelbaum FR, Gundacker H, Head DR, Slovak ML, Willman CL, Godwin JE, Anderson JE, Petersdorf SH (2006) Age and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 107:3481–3485
Ho AD, Schetelig J, Bochtler T, Schaich M, Schafer-Eckart K, Hanel M, Rosler W, Einsele H, Kaufmann M, Serve H, Berdel WE, Stelljes M, Mayer J, Reichle A, Baldus CD, Schmitz N, Kramer M, Rollig C, Bornhauser M, Thiede C, Ehninger G, Study Alliance L (2016) Allogeneic stem cell transplantation improves survival in patients with acute myeloid leukemia characterized by a high allelic ratio of mutant FLT3-ITD. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22:462–469
Yoon JH, Cho BS, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Shin SH, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Lee S, Min CK, Cho SG, Kim DW, Lee JW, Min WS, Park CW (2013) Outcomes of elderly de novo acute myeloid leukemia treated by a risk-adapted approach based on age, comorbidity, and performance status. Am J Hematol 88:1074–1081
Aoki J, Kanamori H, Tanaka M, Yamasaki S, Fukuda T, Ogawa H, Iwato K, Ohashi K, Okumura H, Onizuka M, Maesako Y, Teshima T, Kobayashi N, Yasuo M, Hirokawa M, Atsuta Y, Yano S, Takami A (2015) Impact of age on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced intensity conditioning in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol.
Leunis A, Redekop WK, Uyl-de Groot CA, Lowenberg B (2014) Impaired health-related quality of life in acute myeloid leukemia survivors: a single-center study. Eur J Haematol 93:198–206
Alibhai SM, Breunis H, Timilshina N, Brignardello-Petersen R, Tomlinson G, Mohamedali H, Gupta V, Minden MD, Li M, Buckstein R, Brandwein JM (2015) Quality of life and physical function in adults treated with intensive chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia improve over time independent of age. J Geriatr Oncol 6:262–271
Jarfelt M, Andersen NH, Glosli H, Jahnukainen K, Jonmundsson GK, Malmros J, Nysom K, Hasle H, Nordic Society of Pediatric H, Oncology (2015) Cardiac function in survivors of childhood acute myeloid leukemia treated with chemotherapy only: a NOPHO-AML study. Eur J Haematol.
Ghodraty-Jabloo V, Alibhai SM, Breunis H, Puts MT (2015) Keep your mind off negative things: coping with long-term effects of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Support Care Cancer.
Ghodraty-Jabloo V, Alibhai SM, Breunis H, Puts MT (2015) One day at a time: improving the patient experience during and after intensive chemotherapy for younger and older AML patients. Leuk Res 39:192–197
Thewes B, Lebel S, Seguin Leclair C, Butow P (2016) A qualitative exploration of fear of cancer recurrence (FCR) amongst Australian and Canadian breast cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer 24:2269–2276
van Laarhoven HW, Schilderman J, Bleijenberg G, Donders R, Vissers KC, Verhagen CA, Prins JB (2011) Coping, quality of life, depression, and hopelessness in cancer patients in a curative and palliative, end-of-life care setting. Cancer Nurs 34:302–314
Baker KS, Ness KK, Weisdorf D, Francisco L, Sun CL, Forman S, Bhatia S (2010) Late effects in survivors of acute leukemia treated with hematopoietic cell transplantation: a report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study. Leukemia 24:2039–2047
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Chung Y. Hsu and Chieh-Lin Jerry Teng contributed equally to this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Table 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Supplemental Table 2
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, KH., Hwang, WL., Muo, CH. et al. Outcome and late effects among acute myeloid leukemia survivors: a nationwide population-based study. Support Care Cancer 24, 4993–5000 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3361-5