Abstract
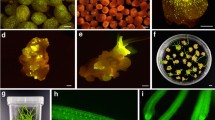
A mutation in the maize Ms45 gene results in a male-sterile phenotype due to the absence of pollen. Cytological examination of microspores in ms45 mutant plants reveals that the cell wall of the developing male gametophyte is poorly formed, while genetic analysis indicates that mutations at Ms45 are sporophytic. The Ms45 gene has been isolated by transposon tagging and transcription was shown by RNA hybridization analysis to be tassel-specific. In this report, an efficient system for molecular complementation is described and used to confirm that a transformed copy of the wild-type gene was able to fully restore fertility to ms45 mutant maize and to characterize MS45 protein expression in maize anthers. The MS45 protein was localized to the tapetum and expressed maximally during the early-vacuolate microspore stage of development. Based on these observations, phenotypic complementation of ms45 was used as an assay to determine tapetal cell-layer activity of other anther-specific and constitutive promoters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 April 2001 / Accepted: 8 May 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cigan, A., Unger, E., Xu, Rj. et al. Phenotypic complementation of ms45 maize requires tapetal expression of MS45. Sex Plant Reprod 14, 135–142 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004970100099
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004970100099