Abstract
Background
When comparing a single-stroke dissection maneuver among surgeons with differing experience levels, there are major differences in the force applied to the instrument tip. It is difficult to explain to surgeons in training the appropriate force and for the surgeons to ascertain the force intuitively. We quantified the force pattern during single-stroke laparoscopic dissection maneuvers to reveal the factors related to expertise.
Methods
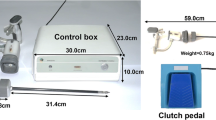
We recorded the force pattern of a single maneuver and measured the magnitude of vertical (VF) and horizontal forces (HF) on the instrument tip using a box trainer (ex vivo). We compared VF and HF among surgeons: experts (n = 10), intermediates (n = 10), and novices (n = 10). The dissection time of a single stroke (T), magnitude of the VF and HF, and the timing of the peak vertical force (TPV) and horizontal force (TPH) were evaluated as performance parameters.
Results
The dissection time of a single stroke (T) was shortest in the expert group (p < 0.05). The average maximum magnitude of VF and HF was smallest in the expert group. TPV occurred significantly earlier than TPH in all three groups (p < 0.05). TPV in the expert group occurred earlier than in the intermediate and novice groups (p < 0.05). With increasing experience, TPV occurred earlier.
Conclusions
Expert surgeons apply the most efficient vertical forces to make an initial dissection point and then change to the horizontal direction to separate surrounding tissues from the target organ. Measuring instrument tip force could help in understanding and improving the safety margin in laparoscopic surgical dissection.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Visser H, Heijnsdijk EA, Herder JL, Pistecky PV (2002) Forces and displacements in colon surgery. Surg Endosc 16:1426–1430
Wagner CR, Stylopoulos N, Jackson PG, Howe RD (2007) The benefit of force feedback in surgery: examination of blunt dissection. Presence 16:252–262
Peirs J, Clijnen J, Reynaerts D, Brussel HV, Herigers P, Corteville B, Boone S (2004) A micro optical force sensor for force feedback during minimally invasive robotic surgery. Sens Actuators A115:447–455
Hanna G, Drew T, Arnold G, Fakhry M, Cuschieri A (2008) Development of force measurement system for clinical use in minimal access surgery. Surg Endosc 22:467–471
Chmarra MK, Jansen FW, Grimbergen CA, Dankelman J (2008) Retracting and seeking movements during laparoscopic goal-oriented movements. Is the shortest path length optimal? Surg Endosc 22:943–949
Chmarra MK, Kolkman W, Jansen FW, Grimbergen CA, Dankelman J (2007) The influence of experience and camera holding on laparoscopic instrument movements measured with the TrEndo tracking system. Surg Endosc 21:2069–2075
Chmarra MK, Grimbergen CA, Dankelman J (2007) Systems for tracking minimally invasive surgical instruments. Minim Invasive Ther 16:328–340
Egi H, Okajima M, Yoshimitsu M, Ikeda S, Miyata Y, Masugami H, Kawahara T, Kurita Y, Kaneko M, Asahara T (2008) Objective assessment of endoscopic surgical skills by analyzing direction-dependent dexterity using the Hiroshima University Endoscopic Surgical Assessment Device (HUESAD). Surg Today 38:705–710
Scott-Conner CEH (1999) The SAGES manual: fundamentals of laparoscopy and GI endoscopy. Springer, New York
Metha NY, Haluck RS, Frecker MI, Snyder AJ (2002) Sequence and task analysis of instrument use in common laparoscopic procedures. Surg Endosc 16:280–285
Ito A, Tsujiuchi N, Koizumi T, Oshima H, Nojiri Y, Tsuchiya Y, Hirama N, Kurogi S (2005) Relative movement evaluation between developed distributed-type tactile sensor and the contacting object. IEEE/RSJ Int Conf Intell Robots Syst 2–6:1659–1664
Matsuda T, Ono Y, Terachi T, Naito S, Baba S, Miki T, Hirao Y, Okuyama A (2006) The endoscopic surgical skill qualification system in urological laparoscopy: a novel system in Japan. J Urol 176:2168–2172
Habuchi T, Terachi T, Mimata H, Kondo Y, Kanayama H, Ichikawa T, Nutahara K, Miki T, Ono Y, Baba S, Naito S, Matsuda T (2012) Evaluation of 2,590 urological laparoscopic surgeries undertaken by urological surgeons accredited by an endoscopic surgical skill qualification system in urological laparoscopy in Japan. Surg Endosc 26:1656–1663
Camarillo DB, Krummell TM, Salisbury JK (2004) Robotic technology in surgery: past, present, and future. Am J Surg 188:2S–15S
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japan and a Japanese Foundation for Research and Promotion of Endoscopy (JFE) grant.
Disclosures
Kenji Yoshida, Hidefumi Kinoshita, Yoshihiro Kuroda, Osamu Oshiro, and Tadashi Matsuda have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, K., Kinoshita, H., Kuroda, Y. et al. Analysis of laparoscopic dissection skill by instrument tip force measurement. Surg Endosc 27, 2193–2200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2739-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2739-9