Abstract
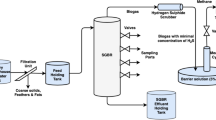
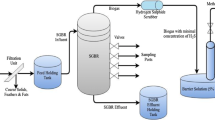
The performance and operational stability of a pilot-scale static granular bed reactor (SGBR) for the treatment of dairy processing wastewater were investigated under a wide range of organic and hydraulic loading rates and temperature conditions. The SGBR achieved average chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD), and total suspended solids (TSS)-removal efficiencies higher than 90 % even at high loading rates up to 7.3 kg COD/m3/day, with an hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 9 h, and at low temperatures of 11 °C. The average methane yield of 0.26 L CH4/g CODremoved was possibly affected by a high fraction of particulate COD and operation at low temperatures. The COD mass balance indicated that soluble COD was responsible for most of the methane production. The reactor showed the capacity of the methanogens to maintain their activity and withstand organic and hydraulic shock loads.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danalewich JR, Papagiannis TG, Belyea RL, Tumbleson ME, Raskin L (1998) Characterization of dairy waste streams, current treatment practices, and potential for biological nutrient removal. Water Res 32:3555–3568
Demirel B, Yenigun O, Onay TT (2005) Anaerobic treatment of dairy wastewaters: a review. Process Biochem 40(8):2583–2595
Speece RE (1996) Anaerobic Biotechnology for Industrial Wastewaters. Archae Press, Nashville
Tawfik A, Sobhey M, Badawy M (2008) Treatment of a combined dairy and domestic wastewater in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor followed by activated sludge (AS system). Desalination 227:167–177
Debik E, Coskun T (2009) Use of the static granular bed reactor (SGBR) with anaerobic sludge to treat poultry slaughterhouse wastewater and kinetic modeling. Bioresour Technol 100:2777–2782
Park J, Oh JH, Ellis TG (2012) Evaluation of an on-site pilot static granular bed reactor (SGBR) for the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:459–468
Turkdogan FI, Park J, Ellis TG (2013) Evaluation of pretreatment using UASB and SGBR reactors for pulp and paper plants wastewater treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1512
California Regional Water Quality Control Board; Central Valley Region (2013) Information sheet order R5-2013-0019 waste discharge requirements and master recycling permit for City of Tulare Wastewater Treatment Facility Tulare County. Rancho Cordova, California
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Rinzema A, van Lier J, Lettinga G (1988) Sodium inhibition of acetoclastic methanogens in granular sludge from a UASB reactor. Enzyme Microb Tech 10:24–32
Lettinga G, Roersma R, Grin P (1983) Anaerobic treatment of raw domestic sewage at ambient temperatures using a granular bed UASB reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 25:1701–1723
Sanz I, Fdz-Polanco F (1990) Low temperature treatment of municipal sewage in anaerobic fluidized bed reactors. Water Res 24:463–469
Uemura S, Harada H (2000) Treatment of sewage by a UASB reactor under moderate to low temperature conditions. Bioresour Technol 72:275–282
Elmitwalli TA, Sklyar V, Zeeman G, Lettinga G (2002) Low temperature pre-treatment of domestic sewage in anaerobic hybrid or an anaerobic filter reactor. Bioresour Technol 82:233–239
Zeeman G, Lettinga G (1999) The role of anaerobic digestion of domestic sewage in closing the water and nutrients cycle at community level. Water Sci Technol 39(5):187–194
Ripley LE, Boyle WC, Converse JC (1986) Improved alkalimetric monitoring for anaerobic digestion of high-strength wastes. J Water Pollut Control Fed 58(5):406–411
Water Pollution Control Federation Manual of Practice No.16, Second Edition (1987) Anaerobic sludge digestion, water pollution control federation, pp 118
Liu T, Sung S (2002) Ammonia inhibition on thermophilic acetoclastic methanogens. Water Sci Technol 45:113–120
Vandenburgh CR, Ellis TG (2002) Effect of varying solids concentration and organic loading on the performance of temperature phased anaerobic digestion process. Water Environ Res 74:142–148
Grotenhuis JTC, Plugge CM, Stams AJM, Zehnder AJB (1991) Role of substrate concentration in particle size distribution of methanogenic granular sludge in UASB reactors. Water Res 25:21–27
Kato MT, Field JA, Lettinga G (1997) The anaerobic treatment of low strength wastewaters in UASB and EGSB reactors. Water Sci Technol 36(6–7):375–382
Kettunen RH, Rintala JA (1997) The effect of low temperature (5–29°C) and adaptation on the methanogenic activity of biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:570–576
Ho J, Sung S (2010) Methanogenic activities in anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR) treating synthetic municipal wastewater. Bioresour Technol 101:2191–2196
Lin CY, Noike T, Sato K, Matsumoto J (1987) Temperature characteristics of the methanogenesis process in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 19(1–2):299–310
Enright AM, McHugh S, Collins G, O’Flaherty V (2005) Low temperature anaerobic biological treatment of solvent-containing pharmaceutical wastewater. Water Res 39:4587–4596
Lettinga G, Rebac S, Parshina S, Nozhevnikova A, van Lier J, Stams A (1999) High-rate anaerobic treatment of wastewater at low temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1696–1702
McHugh S, Carton M, Collins G, O’Flaherty V (2004) Reactor performance and microbial community dynamics during anaerobic biological treatment of wastewaters at 16–37°C. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:369–378
Kalyuzhnyi SV, Sklyar VI, Davlyatshina MA, Parshina SN, Simankova MV, Kostrikina NA, Nozhevnikova AN (1996) Organic removal and microbiological features of UASB-reactor under various organic loading rates. Bioresour Technol 55:47–54
Ruiz I, Veiga MC, Santiago P, Blazquez R (1997) Treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in a UASB reactor and an anaerobic filter. Bioresour Technol 60:251–258
Fang HHP, Yu HQ (2000) Effect of hydraulic retention time (HRT) on mesophilic acidogenesis of dairy wastewater. J Environ Eng 126(12):1145–1148
Jawed M, Tare V (1996) Methanogenic activity and performance of UASB, DSFF and USFF reactors. Water Sci Technol 34(5–6):483–487
Elefsiniotis P, Oldham WK (1994) Effect of HRT on acidogenic digestion of primary sludge. J Environ Eng 120(3):645–660
Sayed S, Campen L, Lettinga G (1987) Anaerobic treatment of slaughterhouse waste using a granular sludge UASB reactor. Biol Wastes 21(1):11–28
Mohammad J, Vinod T (1999) Microbial composition assessment of anaerobic biomass through methanogenic activity tests. Water SA 25(3):345–350
Elmitwalli TA, Oahn KLT, Zeeman G, Lettinga G (2002) Treatment of domestic sewage in a two-step system anaerobic filter/anaerobic hybrid reactor at low temperature. Water Res 36:2225–2232
Rössle WH, Pretorius WA (2001) A review of characterization requirements for in-line prefermenters. Water SA 27(3):405–412
Pavlostathis SG, Giraldo-Gomez E (1991) Kinetics of anaerobic treatment: a critical review. Crit Rev Env Contr 21:411–490
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, J.H., Park, J. & Ellis, T.G. Performance of on-site pilot static granular bed reactor (SGBR) for treating dairy processing wastewater and chemical oxygen demand balance modeling under different operational conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 353–363 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1275-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1275-5