Abstract
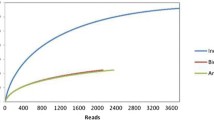
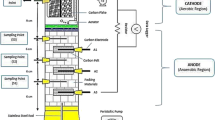
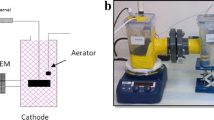
Anode biofilm is a crucial component in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for electrogenesis. Better knowledge about the biofilm development process on electrode surface is believed to improve MFC performance. In this study, double-chamber microbial fuel cell was operated with diluted POME (initial COD = 1,000 mg L−1) and polyacrylonitrile carbon felt was used as electrode. The maximum power density, COD removal efficiency and Coulombic efficiency were found as 22 mW m−2, 70 and 24 %, respectively. FTIR and TGA analysis confirmed the formation of biofilm on the electrode surface during MFC operation. The impact of anode biofilm on anodic polarization resistance was investigated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and microbial community changes during MFC operation using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). The EIS-simulated results showed the reduction of charge transfer resistance (R ct) by 16.9 % after 14 days of operation of the cell, which confirms that the development of the microbial biofilm on the anode decreases the R ct and therefore improves power generation. DGGE analysis showed the variation in the biofilm composition during the biofilm growth until it forms an initial stable microbial community, thereafter the change in the diversity would be less. The power density showed was directly dependent on the biofilm development and increased significantly during the initial biofilm development period. Furthermore, DGGE patterns obtained from 7th and 14th day suggest the presence of less diversity and probable functional redundancy within the anodic communities possibly responsible for the stable MFC performance in changing environmental conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gong X-B, You S-J, Wang X-H, Gan Y, Zhang R-N, Ren N-Q (2013) Silver–tungsten carbide nanohybrid for efficient electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cell. J Power Sources 225:330–337
Pant D, Van Bogaert G, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2010) A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1533–1543
Zhou M, Chi M, Wang H, Jin T (2012) Anode modification by electrochemical oxidation: a new practical method to improve the performance of microbial fuel cells. Biochem Eng J 60:151–155
Liu H, Ramnarayanan R, Logan BE (2004) Production of electricity during wastewater treatment using a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 38(7):2281–2285
Min B, Kim J, Oh S, Regan JM, Logan BE (2005) Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res 39(20):4961–4968
Kim B, Park H, Kim H, Kim G, Chang I, Lee J, Phung N (2004) Enrichment of microbial community generating electricity using a fuel-cell-type electrochemical cell. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(6):672–681
Luo H, Liu G, Zhang R, Jin S (2009) Phenol degradation in microbial fuel cells. Chem Eng J 147(2):259–264
Liu H, Cheng S, Logan BE (2005) Production of electricity from acetate or butyrate using a single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 39(2):658–662
Kim BH, Chang IS, Gadd GM (2007) Challenges in microbial fuel cell development and operation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(3):485–494
Kim HJ, Park HS, Hyun MS, Chang IS, Kim M, Kim BH (2002) A mediator-less microbial fuel cell using a metal reducing bacterium, <i> Shewanella putrefaciens </i>. Enzym Microb Technol 30(2):145–152
Wei J, Liang P, Huang X (2011) Recent progress in electrodes for microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102(20):9335–9344
Hays S, Zhang F, Logan BE (2011) Performance of two different types of anodes in membrane electrode assembly microbial fuel cells for power generation from domestic wastewater. J Power Sources 196(20):8293–8300
González-García J, Bonete P, Expósito E, Montiel V, Aldaz A, Torregrosa-Maciá R (1999) Characterization of a carbon felt electrode: structural and physical properties. J Mater Chem 9(2):419–426
Rabaey K, Boon N, Siciliano SD, Verhaege M, Verstraete W (2004) Biofuel cells select for microbial consortia that self-mediate electron transfer. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(9):5373–5382
Franks AE, Malvankar N, Nevin KP (2010) Bacterial biofilms: the powerhouse of a microbial fuel cell. Biofuels 1(4):589–604
Read ST, Dutta P, Bond PL, Keller J, Rabaey K (2010) Initial development and structure of biofilms on microbial fuel cell anodes. BMC Microbiol 10(1):98
Toutain CM, Caiazza NC, O'Toole GA (2004) Molecular basis of biofilm development by pseudomonads. In: Microbial biofilms. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 43–63
Xiao Y, Wu S, Zhang F, Wu Y, Yang Z, Zhao F (2013) Promoting electrogenic ability of microbes with negative pressure. J Power Sources 229:79–83
Ramasamy RP, Ren Z, Mench MM, Regan JM (2008) Impact of initial biofilm growth on the anode impedance of microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 101(1):101–108
Sekar N, Ramasamy RP (2013) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for microbial fuel cell characterization. J Microb Biochem Technol S 6:2
Cheng S, Xing D, Call DF, Logan BE (2009) Direct biological conversion of electrical current into methane by electromethanogenesis. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3953–3958
Baranitharan E, Khan MR, Prasad D, Salihon JB (2013) Bioelectricity generation from palm oil mill effluent in microbial fuel cell using polacrylonitrile carbon felt as electrode. Water Air Soil Pollut 224(5):1–11
Borja R, Banks CJ, Sánchez E (1996) Anaerobic treatment of palm oil mill effluent in a two-stage up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) system. J Biotechnol 45(2):125–135
Chae K-J, Choi M-J, Lee J-W, Kim K-Y, Kim IS (2009) Effect of different substrates on the performance, bacterial diversity, and bacterial viability in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 100(14):3518–3525
Zuo Y, Xing D, Regan JM, Logan BE (2008) Isolation of the exoelectrogenic bacterium Ochrobactrum anthropi YZ-1 by using a U-tube microbial fuel cell. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(10):3130–3137
Yu Y–Y, Chen H-l, Yong Y-C, Kim D-H, Song H (2011) Conductive artificial biofilm dramatically enhances bioelectricity production in Shewanella-inoculated microbial fuel cells. Chem Commun 47(48):12825–12827
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
He Z, Mansfeld F (2009) Exploring the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in microbial fuel cell studies. Energy Environ Sci 2(2):215–219
Rabaey K, Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Verstraete W (2005) Tubular microbial fuel cells for efficient electricity generation. Environ Sci Technol 39(20):8077–8082
He Z, Minteer SD, Angenent LT (2005) Electricity generation from artificial wastewater using an upflow microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 39(14):5262–5267
Min B, Logan BE (2004) Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 38(21):5809–5814
Bond DR, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity production by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1548–1555
Jahim J, Wan Ramli W, Ismail M, Anuar N, Kamarudin SK, Shari SN (2010) Optimization of electricity generation and Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) treatment from microbial fuel cell. J Appl Sci 10(24):3355–3360
Marcus (2008) Fuel cell that uses bacteria to generate electricity science daily. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/01/080103101137.htm. Accessed 01 June 2014
Marsili E, Rollefson JB, Baron DB, Hozalski RM, Bond DR (2008) Microbial biofilm voltammetry: direct electrochemical characterization of catalytic electrode-attached biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(23):7329–7337
Kim G, Webster G, Wimpenny J, Kim B, Kim H, Weightman A (2006) Bacterial community structure, compartmentalization and activity in a microbial fuel cell. J Appl Microbiol 101(3):698–710
Kramer J, Soukiazian S, Mahoney S, Hicks-Garner J (2012) Microbial fuel cell biofilm characterization with thermogravimetric analysis on bare and polyethyleneimine surface modified carbon foam anodes. J Power Sources 210:122–128
Karnnet S, Potiyaraj P, Pimpan V (2005) Preparation and properties of biodegradable stearic acid-modified gelatin films. Polym Degrad Stab 90(1):106–110
Nanda PK, Krishna Rao K, Nayak PL (2007) Biodegradable polymers. XI. Spectral, thermal, morphological, and biodegradability properties of environment‐friendly green plastics of soy protein modified with thiosemicarbazide. J Appl Polym Sci 103(5):3134–3142
Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2005) Microbial fuel cells: novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol 23(6):291–298
Briones A, Raskin L (2003) Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in engineered environments and their implications for process stability. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14(3):270–276
Fernandez AS, Hashsham SA, Dollhopf SL, Raskin L, Glagoleva O, Dazzo FB, Hickey RF, Criddle CS, Tiedje JM (2000) Flexible community structure correlates with stable community function in methanogenic bioreactor communities perturbed by glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(9):4058–4067
Barsoukov E, Macdonald JR (2005) Impedance spectroscopy: theory, experiment, and applications. Wiley, New York
Orazem ME, Tribollet B (2011) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, vol 48. Wiley, New York
Scully JR, Silverman DC, Kendig MW (1993) Electrochemical impedance: analysis and interpretation, vol 1188. ASTM International, Philadelphia
He Z, Wagner N, Minteer SD, Angenent LT (2006) An upflow microbial fuel cell with an interior cathode: assessment of the internal resistance by impedance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5212–5217
Srikanth S, Marsili E, Flickinger MC, Bond DR (2008) Electrochemical characterization of Geobacter sulfurreducens cells immobilized on graphite paper electrodes. Biotechnol Bioeng 99(5):1065–1073
Meland A-K, Bedeaux D, Kjelstrup S (2005) A Gerischer phase element in the impedance diagram of the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell anode. J Phys Chem B 109(45):21380–21388
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia and Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia for funding (RDU120611 and RDU110341) this project. We also acknowledge the High Impact Research Funds from Ministry of Higher Education (F000005-21001) and Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI) e-science (04-01-03-SF0666). We are thankful to Baiju Vidyadaran, Faculty of Science and Technology, Universiti malaysia Pahang for helping to conduct EIS experiments and valuable consultations. Authors are also thankful to the anonymous reviewers for the valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baranitharan, E., Khan, M.R., Prasad, D.M.R. et al. Effect of biofilm formation on the performance of microbial fuel cell for the treatment of palm oil mill effluent. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 15–24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1239-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1239-9