Abstract
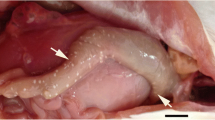
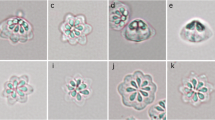
In the present study, 100 samples of different sizes of the common sea bream fish Pagrus pagrus were collected from the Egyptian water along the Gulf of Suez, Red Sea and examined for the prevalence of myxosporidian parasites in general and Kudoa spp. in particular. Fish samples were thoroughly externally examined. After dissection, all the internal organs were removed and examined. A total of 60 out of 100 fish specimens were found to be infected with Kudoa stages. Parasitic infection was restricted to the heart muscles of the examined fish. None of the other organs was found to be infected. Macroscopic cysts (plasmodia) heavily infested the different parts of the heart muscles. Each plasmodium measured 1.2–2.5 (1.53 ± 0.2) mm × 0.63–0.80 (0.65 ± 0.2) mm. Mature spores are quadratic in shape in the apical view showing four equal valves and four symmetrical polar capsules. Fresh spores were 5.0–7.1 (5.7 ± 0.2) μm long × 5.4–8.5 (6.1 ± 0.3) μm wide. On the basis of spore morphology, the present species was identified as Kudoa pagrusi. Morphometric characterization revealed that the relatively small size of this Kudoa species was the distinctive feature that separates it from all previously described species. Molecular analysis based on small subunit ribosomal DNA (SSU rDNA) sequences revealed that the highest percentage of identity was observed with K. scomberomori and followed by K. shiomitsui, K. hypoepicarclialis, K. amamiensis, and K. kenti. The kudoid spores showed morphometric variations to some extents but had essentially identical nucleotide sequences of the SSU rDNA gene sequences closest to those of K. scomberomori and K. shiomitsui recorded from elasmobranchs in the Indo-Pacific Ocean. The present findings support the identification of an ancestral marine origin of the present Kudoa species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Bashtar AR, Mehlhorn H, Al-Rasheid K, Al-Olayan E, Abdel-Baki AA, Morsy K (2009) Ultrastructure and host parasite relationships of Kudoa pagrusi (Myxozoa) infecting the heart muscles of sea bream Pagrus pagrus (L.) from the Red Sea. Parasitol Res 106:121–129
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Morsy K, Mehlhorn H, Bashtar AR, Shazly MA, Saad AH, Abdel-Gaber R (2012) First report of Kudoa species (Myxozoa: Kudoidae) infecting the spotted coral grouper Plectropomus maculates from the Red Sea. A light and ultrastructural study. Parasitol Res 111:1579–1585
AITschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Al Quraishy S, Koura E, Abdel-Baki AS, Bashtar AR, El Deep N, Al Rasheid K, Abdel Ghaffar F (2008) Light and electron microscopic studies on Kudoa pagrusi n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) infecting the heart of sea bream Pagrus pagrus (L.) from the Red Sea. Parasitol Res 102:205–209
Andree KB, Szekely C, Molnar K, Gresoviac SJ, Hedrick RP (1999) Relationships among members of the genus Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Bivalvulida) based on small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. J Parasitol 85:68–74
Banerjee S, Patra A, Adikesavalu H, Mondal A, Abraham T (2015) The phylogenetic position of Myxobolus carnaticus (Myxozoa, Myxosporea, Bivalvulida) infecting gill lamellae of Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton, 1822) based on 18S rRNA sequence analysis. Mol Biol Res Commun 4(3):125–132
Blaylock RB, Bullard SA, Whipps CM (2004) Kudoa hypoepicardialis n. sp. (Myxozoa: Kudoidae) and associated lesions from the heart of seven perciform fishes in the northern Gulf of Mexico. J Parasitol 90(3):584–593
Buchmann K, Skovgaard A, Kania PR (2012) Myxobolus groenlandicus n. sp. (Myxozoa) distorting skeletal structures and musculature of Greenland halibut Reinhardtius hippoglossoides (Teleostei: Pleuronectidae). Dis Aquat Org 98:133–141
Burger MAA, Barnes AC, Adlard RD (2008) Wildlife as reservoirs for parasites infecting commercial species: host specificity and a re-description of Kudoa amamiensis from teleost fish in Australia. J Fish Dis 31:835–844
De Oliveira CJ, Velasco M, Sacco dos Santos PF, Viana Silva JM, Carmona de São Clemente S, Matos E (2015) Kudoa spp. (Myxozoa) infection in musculature of Plagioscion squamosissimus (Sciaenidae) in the Amazon region, Brazil. Braz J Vet Parasitol Jaboticabal 24(2):235–240
Diamant A, Ucko M, Colorni A, Lipshitz A (2005) Kudoa iwati (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in wild cultured fish in the Red Sea: re-description and molecular phylogeny. Parasitology 91(5):1175–1189
Dyková I, Avila EJF, Fiala I (2002) Kudoa dianae sp. n. (Mysozoa: Multivalvulida), a new parasite of bullseye puffer, Sphoeroides annylatus (Tetraodonitormes: Tetraodonitidae). Folia Parasitol 49:17–23
Egusa S, Nakajiima K (1980) Kudoa amamiensis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) found in cultured yellow tails and wild damsel fishes from Amami-Ohshima and Okinawa, Japan. Bull Jap Soc Sci Fish 46:1193–1198
Eiras JC, Saraiva A, Cruz C (2014) Synopsis of the species of Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida). Syst Parasitol 87(2):153–180
Ferguson JA, Atknson SD, Whipps CM, Kent ML (2008) Molecular and morphological analysis of Myxobolus spp. of salmonid fishes with the description of a new Myxobolus species. J Parasitol 94(6):1322–1334
Fiala I (2006) The phylogeny of Myxosporea (Myxozoa) based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene analysis. Int J Parasitol 36:1521–1534
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Heiniger H, Cribb TH, Adlard RD (2013) Intra-specific variation of Kudoa spp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from apogonid fishes (Perciformes), including the description of two new species, K. cheilodipteri n. sp. and K. cookii n. sp., from Australian waters. Syst Parasitol 84:193–215
Hillis DM, Dixon MT (1991) Ribosomal DNA: molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q Rev Biol 66:411–453
Holzer AS, Sommerville C, Wootten R (2004) Molecular relationships and phylogeny in a community of myxosporeans and actinosporeans based on their 18S rDNA sequences. Int J Parasitol 34:1099–1111
Holzer AS, Blasco-Costa I, Sarabeev VL, Ovcharenko MO, Balbuena JA (2006) Kudoa trifolia n. sp. molecular phylogeny suggests a new spore morphology and unusual tissue location for a well-known genus. J Fish Dis 29:743–755
Iwashita Y, Kamijo Y, Nakahashi S, Shindo A, Yokoyama K, Yamamoto A, Omori Y, Ishikura K, Fujioka M, Hatada T, Takeda T, Maruyama K, Imai H (2013) Food poisoning associated with Kudoa septempunctata. J Emerg Med 44:943–945
Kent ML, Andree KB, Bartholomew JL, El-Matbouli M, Desser SS, Devlin RH, Feist SW, Hedrick RP, Hoffmann RW, Khattra J, Hallett SL, Lester RJG, Longshaw M, Palenzeula O, Siddall ME, Xiao C (2001) Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa. J Eukaryot Microbiol 48:395–413
Koura EA (2000) Kudoa aegyptia n. sp. (Myxozoa: Multivalvulida), in the heart muscles of haffara fish Rhabdosargus haffara. Egypt J Zool 34:1–26
Langdon JS (1990) Myoliquefaction post-mortem (milky flesh) due to Kudoa thyrsites (Gilchrist) (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in mahi mahi, Coryphaena hippurus L. J Fish Dis 14:45–54
Lewisch E, Soliman H, Schmidt P, El-Matbouli M (2015) Morphological and molecular characterization of Thelohanellus hoffmanni sp. nov. (Myxozoa) infecting goldfish Carassius auratus auratus. Dis Aquat Org 115:37–46
Lom J, Arthur JR (1989) A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J Fish Dis 12:151–156
Lom J, Dykova I (1992) Protozoan parasites of fishes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 315
Lom J, Dykova I (2006) Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitol 53:1–36
Molnar K, Szekely C, Mohamed K, Shaharom-Harrison F (2006) Myxozoan pathogens in cultured Malaysian fishes. II. Myxozoan infections of red tail catfish Hemibagrus nemurus in freshwater cage cultures. Dis Aquat Org 68:219–226
Moran JDW, Margolis L, Webster JM, Kent ML (1999) Development of Kudoa thyrsites (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in net-pen reared Atlantic salmon determined by light microscopy and polymerase chain reaction test. Dis Aquat Org 37:185–193
Negredo C, Dillane E, Mulcahy MF (2003) Small subunit ribosomal DNA characterization of an unidentified aurantiactinomyxon form and its oligochaete host Tubifex ignotus. Dis Aquat Org 54:229–241
Paperna I, Zwerner DE (1974) Kudoa cerebralis n. sp. (Myxosporidae: Chloromyxidae) from the stripped bass, Morone saxatilis (Walbaum). J Protozool 21:15–19
Schlegel M, Lom J, Stechmanm A, Bernhard D, Detlcf L, Dykova I, Sogin ML (1996) Phylogenetic analysis of complete small subunit ribosomal RNA coding region of Myxidium lieberkuehni: evidence that Myxozoa are Metazoa and related to the Bilateria. Arch Protisten kd 147:1–9
Schmidt-Posthaus H, Bettge K, Forster U, Segner H, Wahli T (2012) Kidney pathology and parasite intensity in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss surviving proliferative kidney disease: time course and influence of temperature. Dis Aquat Org 97:207–218
Swearer SE, Robertson DR (1999) Life history, pathology and description of Kudoa ovivora n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea): an ovarian parasite of Caribbean labroid fishes. J Parasitol 85:337–353
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL-X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Urawa S, Freeman MA, Johnson SC, Jones SR, Yokoyama H (2011) Geographical variation in spore morphology, gene sequences, and host specificity of Myxobolus arcticus (Myxozoa) infecting salmonid nerve tissues. Dis Aquat Org 96:229–237
Whipps CM, Kent LM (2006) Phylogeography of the cosmopolitan marine parasite Kudoa thyrsites (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). J Eukaryot Microbiol 53:364–373
Whipps CM, Adlard RD, Bryant MS, Lester RJG, Findlay V, Kent ML (2003) First report of three Kudoa species from Eastern Australia: Kudoa thyrsites from mahi mahi (Coryphaena hippurus), Kudoa amamiensis and Kudoa minithyrsites n. sp. from sweeper (Pempheris ypsilychnus). J Eukaryot Microbiol 50:215–219
Whitaker DJ, Kent ML, Sakanari JA (1996) Kudoa miniauriculata n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) from the musculature of boccacio (Sebastes paucispinis) from California. J Parasitol 82:312–315
Zhang JY, Wang JG, Li AH, Gong XN (2010) Infection of Myxobolus turpisrotundus n. sp. in allogynogenetic gibel carp, Carassius auratus gibelio (Bloch), with revision of Myxobolus rotundus (S.L.) Nemeczek reported from C. auratus auratus (L.). J Fish Dis 33:625–638
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, for providing all the facilities to complete this work. In addition, the authors extend their appreciations to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the work through the international research group project IRG14-23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Ghaffar, F., Abdel-Gaber, R., Maher, S. et al. Morphological re-description and molecular characterization of Kudoa pagrusi (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) infecting the heart muscles of the common sea bream fish Pagrus pagrus (Perciformes: Sparidae) from the Red Sea, Egypt. Parasitol Res 115, 3175–3184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5077-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5077-3