Abstract
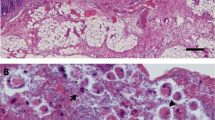
Parasitic Entamoeba spp. are found in many vertebrate species including humans, as well as many livestock including pigs. In pigs, three Entamoeba spp., E. suis, and E. polecki and E. histolytica as zoonotic species, have been identified, but their pathogenicity has not been fully characterized. Here, we report the bacteriological, virological, and histopathological examination of three piglets with chronic diarrhea. Two animals appeared to be additionally infected with Lawsonia intracellularis, which caused a characteristic proliferative ileitis. In the piglet infected with Entamoeba spp., the trophozoites (approximately 10–15 μm with one nucleus in their cytoplasm) invaded into the lamina propria and the disease was worsened by the formation of ulcers and pseudomembranes. Genetic analysis identified the parasite as E. polecki (99.5 % identity). Although E. polecki in humans or animals might be less pathogenic in the case of a single infection, coinfections with other pathogens including L. intracellularis may increase the severity of the disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark CG (1995) Axenic cultivation of Entamoeba dispar Brumpt 1925, Entamoeba insolita Geiman and Wichterman 1937 and Entamoeba ranarum Grassi 1879. J Eukaryot Microbiol 42:590–593
Clark CG, Diamond LS (1991) Ribosomal RNA genes of ‘pathogenic’ and ‘nonpathogenic’ Entamoeba histolytica are distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol 49:297–302
Clark CG, Kaffashian F, Tawari B, Windsor JJ, Twigg-Flesner A, Davies-Morel MC, Blessmann J, Ebert F, Peschel B, Le Van A, Jackson CJ, Macfarlane L, Tannich E (2006) New insights into the phylogeny of Entamoeba species provided by analysis of four new small-subunit rRNA genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2235–2239
Desowitz RS, Barnish G (1986) Entamoeba polecki and other intestinal protozoa in Papua New Guinea highland children. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 80:399–402
Evangelopoulos A, Spanakos G, Patsoula E, Vakalis N, Legakis N (2000) A nested, multiplex, PCR assay for the simultaneous detection and differentiation of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar in faeces. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 94:233–240
Fotedar R, Stark D, Beebe N, Marriott D, Ellis J, Harkness J (2007) Laboratory diagnostic techniques for Entamoeba species. Clin Microbiol Rev 20:511–532
Garcia LS, Bruckner DA (1997) Diagnostic medical parasitology. ASM Press, Washington
He GZ, Feng Y, Deng SX (2012) Evaluation of the intestinal microbial diversity in miniature pig after orally infected with Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Res 111:939–941
Kawashima K, Yamada S, Kobayashi H, Narita M (1996) Detection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and Mycoplasma hyorhinis antigens in pulmonary lesions of pigs suffering from respiratory distress. J Comp Pathol 114:315–323
Lawson GH, Gebhart CJ (2000) Proliferative enteropathy. J Comp Pathol 122:77–100
Matsubayashi M, Suzuta F, Terayama Y, Shimojo K, Yui T, Haritani M, Shibahara T (2014) Ultrastructural characteristics and molecular identification of Entamoeba suis isolated from pigs with hemorrhagic colitis: implications for pathogenicity. Parasitol Res 113:3023–3028. doi:10.1007/s00436-014-3965-y
McOrist S (2005) Defining the full costs of endemic porcine proliferative enteropathy. Vet J 170:8–9
Noble GA, Noble ER (1952) Entamoebae in farm mammals. J Parasitol 38:571–595
Prophet EB, Mills B, Arrington JB, Sobin LH (1992) Laboratory methods in histotechnology. American Registry of Pathology, Washington, pp 132–214
Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS (2004) Amebae and ciliated protozoa as causal agents of waterborne zoonotic disease. Vet Parasitol 126:91–120
Shimizu C, Shibahara T, Takai S, Kasuya K, Chikuba T, Murakoshi N, Kobayashi H, Kubo M (2010) Lawsonia intracellularis and virulent Rhodococcus equi infection in a thoroughbred colt. J Comp Pathol 143:303–308. doi:10.1016/j.jcpa.2010.03.005
Solaymani-Mohammadi S, Rezaian M, Hooshyar H, Mowlavi GR, Babaei Z, Anwar MA (2004) Intestinal protozoa in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in western Iran. J Wildl Dis 40:801–803
Tachibana H, Kobayashi S, Takekoshi M, Ihara S (1991) Distinguishing pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica by polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis 164:825–826
Tanyuksel M, Petri WA Jr (2003) Laboratory diagnosis of amebiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:713–729
Uga S, Matsuo J, Kono E, Kimura K, Inoue M, Rai SK, Ono K (2000) Prevalence of Cryptosporidium parvum infection and pattern of oocyst shedding in calves in Japan. Vet Parasitol 94:27–32
Verweij JJ, Polderman AM, Clark CG (2001) Genetic variation among human isolates of uninucleated cyst-producing Entamoeba species. J Clin Microbiol 39:1644–1646
Verweij JJ, Laeijendecker D, Brienen EA, van Lieshout L, Polderman AM (2003) Detection and identification of Entamoeba species in stool samples by a reverse line hybridization assay. J Clin Microbiol 41:5041–5045
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. M. Kobayashi and Ms. M. Shimada (National Institute of Animal Health, Japan) for a histopathological assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsubayashi, M., Kanamori, K., Sadahiro, M. et al. First molecular identification of Entamoeba polecki in a piglet in Japan and implications for aggravation of ileitis by coinfection with Lawsonia intracellularis . Parasitol Res 114, 3069–3073 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4509-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4509-9