Abstract
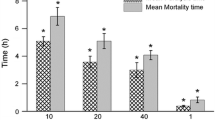
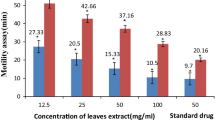
Bombax malabaricum (family Bombacaceae) is used as anthelmintic in traditional system of medicine in Southern Punjab of Pakistan. The objective of this study was to evaluate the anthelmintic activity of the methanol extract of B. malabaricum leaves (MEBM). Live parasites (trematode: Paramphistomum explanatum) were collected from buffalo in 0.9% phosphate-buffered saline. It was incubated in Petri dishes at 37 ± 1°C in media containing either no extract (control) or MEBM, the test drug at 10, 25, 50, and 100 mg/ml dose level or albendazole, the standard drug at 10 mg/ml. The efficacy of the extract or albendazole was measured on the basis of the loss of spontaneous movement and/or death of the trematodes. Paralysis was considered when there is no movement unless shaken vigorously. Death was confirmed when the trematodes completely lost their motility, even when vigorously shaken or dipped in warm water (50°C), followed by fading away of their body color. The trematodes, both drug treated and others, were further processed for SEM study using the standard method. All trematodes died with all the above-mentioned doses of MEBM within a short period of time (less than 45 min) which was statistically highly significant (p < 0.001). MEBM at 100 mg/ml showed maximum efficacy. It paralyzed and killed trematodes in 18.50 ± 0.62 and 22.17 ± 0.48 min, respectively. SEM study showed that MEBM-treated trematodes were stretched. The study established the anthelmintic activity of MEBM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agaie BM, Onyeyili PA (2007) Anthelmintic activity of the crude aqueous leaf extracts of Anogeissus leiocarpus in sheep. Afr J Biotech 6(13):1511–1515
Anonymous (1988) Wealth of India, volume II, New Delhi. Publication and Information Directorate, CSIR, New Delhi, pp 177–185
Anonymous (2000) Wealth of India, volume I, first supplement. Publication and Information Directorate, CSIR, New Delhi, p 145
Aswar M, Aswar U, Watkar B, Vyas M, Wagh A, Gujar KN (2008) Anthelmintic activity of Ficus benghalensis. Int J Green Phar 2(3):170–172. doi:10.4103/0973-8258.42737
Athanasiadou S, Githiori J, Kyriazakis I (2007) Medicinal plants for helminth parasite control: facts and fiction. Animal 1:1392–1400. doi:10.1017/S1751731107000730
Balamurugan G, Selvarajan S (2009) Preliminary phytochemical screening and anthelmintic activity of Indigofera tinctoria Linn. Int J Drug Dev Res 1(1):157–160
Brown M (2005) Intestinal helminths. Medicine 33(8):54–57
Ferraz ABF, Balbino JM, Zini CA, Ribeiro VLS, Bordignon SAL, Poser GV (2010) Acaricidal activity and chemical composition of the essential oil from three Piper species. Parasitol Res 107:243–248. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-1878-y
Hossain E, Mandal SC, Gupta JK (2011a) Phytochemical screening and in vivo antipyretic activity of the methanol leaf-extract of Bombax malabaricum DC (Bombacaceae). Trop J Pharm Res 10(1):55–60
Hossain E, Chandra G, Nandy AP, Mandal SC, Gupta JK (2011b) Anthelmintic effect of a methanol extract of leaves of Dregea volubilis on Paramphistomum explanatum. Parasitol Res (in press)
Jabbar A, Raza MA, Iqbal Z, Khan MN (2006) An inventory of the ethnobotanicals used as anthelmintics in the southern Punjab (Pakistan). J Ethnopharmacol 108:152–154. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2006.04.015
Lal SS (2006) A text book of practical zoology invertebrate, 9th edn. Rastogi Publications, Meerut, pp 271–272
McKinstry B, Fairweather, Brennan GP, Forbes AB (2003) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface alterations following treatment in vivo and in vitro with nitroxynil (Trodax). Parasitol Res 91:251–263
Mehlhorn H, Quraishy SA, Rasheid KASA, Jatzlau A, Ghaffar FA (2011) Addition of a combination of onion (Allium cepa) and coconut (Cocos nucifera) to food of sheep stops gastrointestinal helminthic infections. Parasitol Res 108:1041–1046. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-2169-3
Nandi AP (2005) Data on the morphology of Viguiera dicrurusi Gupta, 1960 (Nematoda: Habronematidae) with notes on related forms. Folia Parasitol 52:261–266
Panyarachun B, Sobhon P, Yotsawan Tinikul Y, Chotwiwatthanakun C, Anupunpisit V, Anuracpreeda P (2010) Paramphistomum cervi: surface topography of the tegument of adult fluke. Exp Parasitol 125:95–99
Rhee JK, Kang CW, Lee HI (1986) The karyotype of Paramphistomum explanatum (Creplin, 1849) obtained from Korean cattle. Korean J Parasitol 24(1):42–48
Rolfe PF, Boray JC (1988) Chemotherapy of paramphistornosis in sheep. Australian Vet J 65(5):148–150
Roy B, Swargiary A (2009) Anthelmintic efficacy of ethanolic shoot extract of Alpinia nigra on tegumental enzymes of Fasciolopsis buski, a giant intestinal parasite. J Parasit Dis 33(1&2):48–53
Roy B, Lalchhandama K, Dutta BK (2008) Scanning electron microscopic observations on the in vitro anthelmintic effects of Millettia pachycarpa on Raillietina echinobothrida. Phcog Mag 4:20–26
Schmahl G, Rasheid KASA, Ghaffar FA, Klimpel S, Mehlhorn H (2010) The efficacy of neem seed extracts (Tre-san®, MiteStop®) on a broad spectrum of pests and parasites. Parasitol Res 107:261–269. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-1915-x
Seshadri V, Batta AK, Rangaswami S (1971) Phenolic components of Bombax malabaricum. Curr Sci 23:630
Tandon V, Pal P, Roy B, Rao HSP, Reddy KS (1997) In vitro anthelmintic activity of root-tuber extract of Flemingia vestita, an indigenous plant in Shillong, India. Parasitol Res 83:492–498
Yadav AK, Tangpu V (2009) Therapeutic efficacy of Zanthoxylum rhetsa DC extract against experimental Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda) infections in rats. J Parasit Dis 33(1&2):42–47
Zhang X, Zhu H, Zhang S, Yu Q, Xuan L (2007) Sesquiterpenoids from Bombax malabaricum. J Nat Prod 70:1526–1528
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Mr. Debobrata Devbhuti, Jadavpur University, Kolkata; Mr. Amit Kumar, Pharmacy College, Azamgarh; and Dr. Srikanta Bhattacharya of USIC & CIF, Burdwan University, for their technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, E., Chandra, G., Nandy, A.P. et al. Anthelmintic effect of a methanol extract of Bombax malabaricum leaves on Paramphistomum explanatum . Parasitol Res 110, 1097–1102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2594-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2594-y