Abstract
Background
CTDP1 catalyzes serine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the mobile carboxy-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase II. It is conserved among eukarya and is essential for cell growth for its ability in regulation of transcription machinery. However, its function in the process of tumorigenesis is unclear. In the present study, we aim to explore the roles of CTDP1 in the progression of human lung cancer. To our knowledge, this is the first study that reports the functions of CTDP1 in human lung cancer.
Methods
We first detected the expression level of CTDP1 in four human lung cancer cell lines: H-125, H1299, LTEP-A-2 and NCI-H446 by semiquantitative RT-PCR. We compared the expression level of CTDP1 in lung cancer tissues and paired adjacent normal tissues on 29 pathologically confirmed patients by real-time quantitative PCR. To further explore the effect of CTDP1 on cell proliferation, a lentiviral vector expressing CTDP1 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) was constructed and infected into human lung cell lines H1299. Interference efficiency was determined by western blot analysis and real-time quantitative PCR. The effects of knockdown of CTDP1 on cell growth, cell cycle and apoptosis and cell colony formation were explored by Cellomics, fluorescence-activated cells sorting and fluorescence microscopy, respectively.
Results
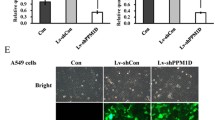
CTDP1 was expressed in all four human lung cancer cell lines. The expression of CTDP1 in tumor tissues was significantly higher than paired adjacent normal tissues in 29 patients with lung cancer. The expression of CTDP1 was markedly reduced in cells infected with lentivirus delivering shRNA against CTDP1. Inhibition of CTDP1 expression significantly suppressed cell growth, induced G0/G1 phase arrest and repressed cell colony formation.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrated that CTDP1 was upregulated in human lung cancer tissues. In addition, it implied that CTDP1 played an important role in cell proliferation and may be a useful therapeutic target in human lung cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Samet JM (2005) Epidemiology of lung cancer: looking to the future. J Clin Oncol 23:3175–3185
Brake OT, Konstantinova P, Ceylan M, Berkhout B (2006) Silencing of HIV-1 with RNA interference: a multiple shRNA approach. Mol Ther 14:883–892
Chambers RS, Wang BQ, Burton ZF, Dahmus ME (1995) The activity of COOH-terminal domain phosphatase is regulated by a docking site on RNA polymerase II and the by the general transcription factors IIF and IIB. J Biol Chem 270:14962–14969
Cho H, Kim TK, Mancebo H, Lane WS, Flores O et al (1999) A protein phosphatase functions to recycle RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 13:1540–1552
Cho EJ, Kobor MS, Kim M, Greenblatt J, Buratowski S (2001) Opposing effects of Ctk1 kinase and Fcp1 phosphatase at Ser 2 of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain. Genes Dev 15:3319–3329
Cramer P, Bushnell DA, Kornberg RD (2001) Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 Ångstrom resolution. Science 29:1863–1876
D’Amico TA, Massey M, Herndon JE II, Moore MB, Harpole DH Jr (1999) A biologic risk model for stage I lung cancer: immunohistochemical analysis of 408 patients with the use of ten molecular markers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 117:736–743
Ding XF, Huang GM, Shi Y, Li JA, Fang XD (2012) Med 19 promotes gastric cancer progression and cellular growth. Gene 504(2):262–267
Greenblatt MS, Bennett WP, Hollstein M, Harris CC (1994) Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res 54:4855–4878
Haga Y, Hiroshima K, Iyoda A, Shibuya K, Shimamura F, Iizasa T et al (2003) Ki-67 expression and prognosis for smokers with resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 75:1727–1732
Hahn WC, Counter CM, Lundberg AS, Beijersbergen RL, Brooks MW et al (1999) Creation of human tumour cells with defined genetic elements. Nature 400:464–468
Han H, Silverman JF, Santucci TS, Macherey RS, d’Amato TA et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer correlates with neoangiogenesis and a poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol 8:72–79
Hirsch FR, Herbst RS, Olsen C, Chansky K, Crowley J et al (2008) Increased EGFR gene copy number detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization predicts outcome in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with cetuximab and chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 26:3351–3357
Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R et al (2008) Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase III trial (INTEREST). Lancet 372:1809–1818
Kobor MS, Archambault J, Lester W, Holstege FC, Gileadi O et al (1999) An unusual eukaryotic protein phosphatase required for transcription by RNA polymerase II and CTD dephosphorylation in S. cerevisiae. Mol Cell 4:55–62
Li LH, He J, Hua D, Guo ZJ, Gao Q (2011) Lentivirus-mediated inhibition of Med19 suppresses growth of breast cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68(1):207–215
Liao M, Wang H, Lin Z, Feng J, Zhu D (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor and other biological predictors related to the postoperative survival rate on non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 33:125–132
Licciardo P, Ruggiero L, Lania L, Majello B (2001) Transcription activation by targeted recruitment of the RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase FCP1. Nucleic Acids Res 29:3539–3545
Lin PS, Marshall NF, Dahmus ME (2002) CTD phosphatase: role in RNA polymerase II cycling and the regulation of transcript elongation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 72:333–365
Mandal SS, Cho H, Kim S, Cabane K, Reinberg D (2002) FCP1, a phosphatase specific for the heptapeptide repeat of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, stimulates transcription elongation. Mol Cell Biol 22:7543–7552
Manjunath N, Wu H, Subramanya S, Shankar P (2009) Lentiviral delivery of short hairpin RNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:732–745
Mineo TC, Ambrogi V, Baldi A, Rabitti C, Bollero P et al (2004) Prognostic impact of VEGF, CD31, CD34, and CD105 expression and tumour vessel invasion after radical surgery for IB-IIA non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Pathol 57:591–597
Moldvay J, Scheid P, Wild P, Nabil K, Siat J et al (2000) Predictive survival markers in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 6:1125–1134
O’Byrne KJ, Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Cox G, Turley H et al (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor and angiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 82:1427–1432
Pastorino U, Andreola S, Tagliabue E, Pezzella F, Incarbone M et al (1997) Immunocytochemical markers in stage I lung cancer: relevance to prognosis. J Clin Oncol 15:2858–2865
Phatnani HP, Greenleaf AL (2006) Phosphorylation and functions of the RNA polymerase II CTD. Genes Dev 20:2922–2936
Qin XF, An DS, Chen IS, Baltimore D (2003) Inhibiting HIV-1 infection in human T cells by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering RNA against CCR5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:183–188
Sato M, Shames DS, Gazdar AF, Minna JD (2007) A translational view of the molecular pathogenesis of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2:327–343
Scagliotti G, Novello S (2003) Adjuvant chemotherapy after complete resection for early stage NSCLC. Lung Cancer 42:S47–S51
Son S, Osmani SA (2009) Analysis of all protein phosphatase genes in Aspergillus nidulans identifies a new mitotic regulator, fcp1. Eukaryot Cell 8(4):573–585
Sun S, Schiller JH, Gazdar AF (2007) Lung cancer in never smokers: a different disease. Nat Rev Cancer 7:778–790
Tammemagi MC, McLaughlin JR, Bull SB (1999) Meta-analyses of p53 tumor suppressor gene alterations and clinicopathological features in resected lung cancers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 8:625–634
Tang X, Shigematsu H, Bekele BN, Roth JA, Minna JD et al (2005) EGFR tyrosine kinase domain mutations are detected in histologically normal respiratory epithelium in lung cancer patients. Cancer Res 65:7568–7572
Weihua Z, Tsan R, Huang WC, Wu Q, Chiu CH et al (2008) Survival of cancer cells is maintained by EGFR independent of its kinase activity. Cancer Cell 13:385–393
Wright PA, Quirke P, Attanoos R, Williams GT (1992) Molecular pathology of gastric carcinoma: progress and prospects. Hum Pathol 23(8):848–859
Yu X, Chini CC, He M, Mer G, Chen J (2003) The BRCT domain is a phospho-protein binding domain. Science 302:639–642
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 81201770 81472642) , Shanghai committee of science and technology (Grant number: 14430723300, 124119a6300), Shanghai Chest Hospital Key Project (2014YZDC20700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Runbo Zhong and Xiaoxiao Ge contribute equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, R., Ge, X., Chu, T. et al. Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of CTDP1 inhibits lung cancer cell growth in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 723–732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2070-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2070-7