Abstract
Main conclusion
We projected meta-QTL (MQTL) for drought, salinity, and waterlogging tolerance to the physical map of barley through meta-analysis. The positions of these MQTL were refined and candidate genes were identified.
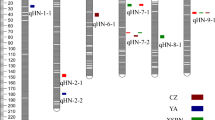
Drought, salinity and waterlogging are three major abiotic stresses limiting barley yield worldwide. Breeding for abiotic stress-tolerant crops has drawn increased attention, and a large number of quantitative trait loci (QTL) for drought, salinity, and waterlogging tolerance in barley have been detected. However, very few QTL have been successfully used in marker-assisted selection (MAS) in breeding. In this study, we summarized 632 QTL for drought, salinity and waterlogging tolerance in barley. Among all these QTL, only 195 major QTL were used to conduct meta-analysis to refine QTL positions for MAS. Meta-analysis was used to map the summarized major QTL for drought, salinity, and waterlogging tolerance from different mapping populations on the barley physical map. The positions of identified meta-QTL (MQTL) were used to search for candidate genes for drought, salinity, and waterlogging tolerance in barley. Both MQTL3H.4 and MQTL6H.2 control drought tolerance in barley. Fine-mapped QTL for salinity tolerance, HvNax4 and HvNax3, were validated on MQTL1H.4 and MQTL7H.2, respectively. MQTL2H.1 and MQTL5H.3 were also the target regions for improving salinity tolerance in barley. MQTL4H.4 is the main region controlling waterlogging tolerance in barley with fine-mapped QTL for aerenchyma formation under waterlogging conditions. Detected and refined MQTL and candidate genes are crucial for future successful MAS in barley breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed IM, Cao F, Zhang M, Chen X, Zhang G, Wu F (2013) Difference in yield and physiological features in response to drought and salinity combined stress during anthesis in Tibetan wild and cultivated barleys. PLoS One 8(10):e77869. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077869
Alam I, Sharmin S, Kim K-H, Kim Y-G, Lee J, Bahk J, Lee B-H (2011) Comparative proteomic approach to identify proteins involved in flooding combined with salinity stress in soybean. Plant Soil 346(1–2):45–62. doi:10.1007/s11104-011-0792-0
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon F, Charcosset A, Joets J (2004) BioMercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20(14):2324–2326
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2013) Crop breeding for salt tolerance in the era of molecular markers and marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 132(1):10–20. doi:10.1111/pbr.12000
Bailey-Serres J, Voesenek LA (2008) Flooding stress: acclimations and genetic diversity. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:313–339. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092752
Barrett-Lennard EG, Shabala SN (2013) The waterlogging/salinity interaction in higher plants revisited—focusing on the hypoxia-induced disturbance to K+ homeostasis. Funct Plant Biol 40(9):872–882. doi:10.1071/FP12235
Bertholdsson NO, Holefors A, Macaulay M, Crespo-Herrera LA (2015) QTL for chlorophyll fluorescence of barley plants grown at low oxygen concentration in hydroponics to simulate waterlogging. Euphytica 201(3):357–365. doi:10.1007/s10681-014-1215-0
Blum A (2005) Drought resistance, water-use efficiency, and yield potential—are they compatible, dissonant, or mutually exclusive? Aust J Agric Res 56(11):1159–1168. doi:10.1071/AR05069
Broughton S, Zhou G, Teakle N, Matsuda R, Zhou M, O’Leary R, Colmer T, Li C (2015) Waterlogging tolerance is associated with root porosity in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Mol Breed 35(1):1–15. doi:10.1007/s11032-015-0243-3
Buchanan-Wollaston V, Page T, Harrison E, Breeze E, Lim PO, Nam HG, Lin J-F, Wu S-H, Swidzinski J, Ishizaki K, Leaver CJ (2005) Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals significant differences in gene expression and signalling pathways between developmental and dark/starvation-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 42(4):567–585. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02399.x
Cattivelli L, Rizza F, Badeck F-W, Mazzucotelli E, Mastrangelo AM, Francia E, Mare C, Tondelli A, Stanca AM (2008) Drought tolerance improvement in crop plants: an integrated view from breeding to genomics. Field Crops Res 105(1–2):1–14. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2007.07.004
Chardon F, Virlon B, Moreau L, Falque M, Joets J, Decousset L, Murigneux A, Charcosset A (2004) Genetic architecture of flowering time in maize as inferred from quantitative trait loci meta-analysis and synteny conservation with the rice genome. Genetics 168(4):2169–2185. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.032375
Chardon F, Jasinski S, Durandet M, Lécureuil A, Soulay F, Bedu M, Guerche P, Masclaux-Daubresse C (2014) QTL meta-analysis in Arabidopsis reveals an interaction between leaf senescence and resource allocation to seeds. J Exp Bot 65(14):3949–3962. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru125
Chaves MM, Flexas J, Pinheiro C (2009) Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann Bot 103(4):551–560. doi:10.1093/aob/mcn125
Chen Z, Newman I, Zhou M, Mendham N, Zhang G, Shabala S (2005) Screening plants for salt tolerance by measuring K+ flux: a case study for barley. Plant, Cell Environ 28(10):1230–1246. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01364.x
Chen Z, Pottosin II, Cuin TA, Fuglsang AT, Tester M, Jha D, Zepeda-Jazo I, Zhou M, Palmgren MG, Newman IA, Shabala S (2007) Root plasma membrane transporters controlling K+/Na+ homeostasis in salt-stressed barley. Plant Physiol 145(4):1714–1725
Chen G, Krugman T, Fahima T, Chen K, Hu Y, Roder M, Nevo E, Korol A (2010) Chromosomal regions controlling seedling drought resistance in Israeli wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum C. Koch. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57(1):85–99. doi:10.1007/s10722-009-9453-z
Christianson JA, Wilson IW, Llewellyn DJ, Dennis ES (2009) The low-oxygen-induced NAC domain transcription factor ANAC102 affects viability of Arabidopsis seeds following low-oxygen treatment. Plant Physiol 149(4):1724–1738
Christianson JA, Llewellyn DJ, Dennis ES, Wilson IW (2010) Global gene expression responses to waterlogging in roots and leaves of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Physiol 51(1):21–37. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcp163
Collaku A, Harrison SA (2005) Heritability of waterlogging tolerance in wheat. Crop Sci 45:722–727
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142(1–2):169–196. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-1681-5
Collins NC, Fo Tardieu, Tuberosa R (2008) Quantitative trait loci and crop performance under abiotic stress: where do we stand? Plant Physiol 147(2):469–486
Colmer TD (2003) Aerenchyma and an inducible barrier to radial oxygen loss facilitate root aeration in upland, paddy and deep-water rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ann Bot 91(2):301–309
Colmer TD, Flowers TJ (2008) Flooding tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179(4):964–974. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02483.x
Colmer TD, Munns R, Flowers TJ (2005) Improving salt tolerance of wheat and barley: future prospects. Aust J Exp Agr 45:1425–1443
Darvasi A, Soller M (1997) A simple method to calculate resolving power and confidence interval of QTL map location. Behav Genet 27(2):125–132. doi:10.1023/a:1025685324830
de Dorlodot S, Forster B, Pagès L, Price A, Tuberosa R, Draye X (2007) Root system architecture: opportunities and constraints for genetic improvement of crops. Trends Plant Sci 12(10):474–481. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2007.08.012
Demidchik V, Straltsova D, Medvedev SS, Pozhvanov GA, Sokolik A, Yurin V (2014) Stress-induced electrolyte leakage: the role of K+-permeable channels and involvement in programmed cell death and metabolic adjustment. J Exp Bot 65(5):1259–1270. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru004
Diab A, Teulat-Merah B, This D, Ozturk N, Benscher D, Sorrells M (2004) Identification of drought-inducible genes and differentially expressed sequence tags in barley. Theor Appl Genet 109(7):1417–1425. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1755-0
Eagles HA, Bariana HS, Ogbonnaya FC, Rebetzke GJ, Hollamby GJ, Henry RJ, Henschke PH, Carter M (2001) Implementation of markers in Australian wheat breeding. Aust J Agric Res 52:1349–1356
Evans DE (2004) Aerenchyma formation. New Phytol 161:35–49
Fan Y, Shabala S, Ma Y, Xu R, Zhou M (2015) Using QTL mapping to investigate the relationships between abiotic stress tolerance (drought and salinity) and agronomic and physiological traits. BMC Genom 16(1):43
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179(4):945–963. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02531.x
Flowers TJ, Flowers SA (2005) Why does salinity pose such a difficult problem for plant breeders? Agric Water Manage 78(1–2):15–24. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2005.04.015
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Polyamines and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Signal Behav 5(1):26–33
Goffinet B, Gerber S (2000) Quantitative trait loci: a meta-analysis. Genetics 155:463–473
Guo P, Baum M, Varshney R, Graner A, Grando S, Ceccarelli S (2008) QTLs for chlorophyll and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in barley under post-flowering drought. Euphytica 163(2):203–214. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9629-6
Guo L, Yang H, Zhang X, Yang S (2013) Lipid transfer protein 3 as a target of MYB96 mediates freezing and drought stress in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 64(6):1755–1767. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert040
Hu H, Xiong L (2014) Genetic engineering and breeding of drought-resistant crops. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65(1):715–741. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040000
Jan A, Maruyama K, Todaka D, Kidokoro S, Abo M, Yoshimura E, Shinozaki K, Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2013) OsTZF1, a CCCH-tandem zinc finger protein, confers delayed senescence and stress tolerance in rice by regulating stress-related genes. Plant Physiol 161(3):1202–1216
Jones HG (2007) Monitoring plant and soil water status: established and novel methods revisited and their relevance to studies of drought tolerance. J Exp Bot 58(2):119–130. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl118
Khowaja F, Norton G, Courtois B, Price A (2009) Improved resolution in the position of drought-related QTLs in a single mapping population of rice by meta-analysis. BMC Genom 10(1):276
Khush GS (2001) Green revolution: the way forward. Nat Rev Genet 2(10):815–822
Korff M, Grando S, Del Greco A, This D, Baum M, Ceccarelli S (2008) Quantitative trait loci associated with adaptation to Mediterranean dryland conditions in barley. Theor Appl Genet 117(5):653–669. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0787-2
Lee TG, Jang CS, Kim JY, Kim DS, Park JH, Kim DY, Seo YW (2007) A Myb transcription factor (TaMyb1) from wheat roots is expressed during hypoxia: roles in response to the oxygen concentration in root environment and abiotic stresses. Physiol Plant 129(2):375–385. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00828.x
Lee Y-H, Kim K-S, Jang Y-S, Hwang J-H, Lee D-H, Choi I-H (2014) Global gene expression responses to waterlogging in leaves of rape seedlings. Plant Cell Rep 33(2):289–299. doi:10.1007/s00299-013-1529-8
Li H, Vaillancourt R, Mendham N, Zhou M (2008) Comparative mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with waterlogging tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Genom 9:401. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-401
Li W-T, Liu C, Liu Y-X, Pu Z-E, Dai S-F, Wang J-R, Lan X-J, Zheng Y-L, Wei Y-M (2013) Meta-analysis of QTL associated with tolerance to abiotic stresses in barley. Euphytica 189(1):31–49. doi:10.1007/s10681-012-0683-3
Luo X, Bai X, Zhu D, Li Y, Ji W, Cai H, Wu J, Liu B, Zhu Y (2012) GsZFP1, a new Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger protein, is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to cold and drought stress. Planta 235(6):1141–1155. doi:10.1007/s00425-011-1563-0
Ma Y, Shabala S, Li C, Liu C, Zhang W, Zhou M (2015) Quantitative trait loci for salinity tolerance identified under drained and waterlogged conditions and their association with flowering time in barley (Hordeum vulgare. L). PLoS One 10(8):e0134822. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134822
Mano Y, Takeda K (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance at germination and the seedling stage in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Euphytica 94(3):263–272. doi:10.1023/a:1002968207362
Mittler R (2006) Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci 11(1):15–19. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.11.002
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167(3):645–663. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01487.x
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59(1):651–681. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Munns R, James RA, Xu B, Athman A, Conn SJ, Jordans C, Byrt CS, Hare RA, Tyerman SD, Tester M, Plett D, Gilliham M (2012) Wheat grain yield on saline soils is improved by an ancestral Na+ transporter gene. Nat Biotech 30(4):360–364. doi:10.1038/nbt.2120
Nguyen V, Ribot S, Dolstra O, Niks R, Visser RF, van der Linden CG (2013) Identification of quantitative trait loci for ion homeostasis and salt tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Mol Breed 31(1):137–152. doi:10.1007/s11032-012-9777-9
Qi X-H, Xu X-W, Lin X-J, Zhang W-J, Chen X-H (2012) Identification of differentially expressed genes in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) root under waterlogging stress by digital gene expression profile. Genomics 99(3):160–168. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.12.008
Qin F, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) Achievements and challenges in understanding plant abiotic stress responses and tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 52(9):1569–1582. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcr106
Qiu F, Zheng Y, Zhang Z, Xu S (2007) Mapping of QTL associated with waterlogging tolerance during the seedling stage in maize. Ann Bot 99(6):1067–1081. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm055
Rabello AR, Guimarães CM, Rangel PH, da Silva FR, Seixas D, de Souza E, Brasileiro AC, Spehar CR, Ferreira ME, Mehta  (2008) Identification of drought-responsive genes in roots of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Genom 9(1):1–13. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-485
Rajhi I, Yamauchi T, Takahashi H, Nishiuchi S, Shiono K, Watanabe R, Mliki A, Nagamura Y, Tsutsumi N, Nishizawa NK, Nakazono M (2011) Identification of genes expressed in maize root cortical cells during lysigenous aerenchyma formation using laser microdissection and microarray analyses. New Phytol 190(2):351–368. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03535.x
Rivandi J, Miyazaki J, Hrmova M, Pallotta M, Tester M, Collins NC (2011) A SOS3 homologue maps to HvNax4, a barley locus controlling an environmentally sensitive Na+ exclusion trait. J Exp Bot 62(3):1201–1216. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq346
Roy SJ, Tucker EJ, Tester M (2011) Genetic analysis of abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14(3):232–239. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2011.03.002
Said J, Song M, Wang H, Lin Z, Zhang X, Fang D, Zhang J (2015) A comparative meta-analysis of QTL between intraspecific Gossypium hirsutum and interspecific G. hirsutum × G. barbadense populations. Mol Genet Genomics 290(3):1003–1025. doi:10.1007/s00438-014-0963-9
Salvi S, Tuberosa R (2005) To clone or not to clone plant QTLs: present and future challenges. Trends Plant Sci 10(6):297–304. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.04.008
Sayed M, Schumann H, Pillen K, Naz A, Leon J (2012) AB-QTL analysis reveals new alleles associated to proline accumulation and leaf wilting under drought stress conditions in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Genet 13(1):61
Semagn K, Beyene Y, Warburton M, Tarekegne A, Mugo S, Meisel B, Sehabiague P, Prasanna B (2013) Meta-analyses of QTL for grain yield and anthesis silking interval in 18 maize populations evaluated under water-stressed and well-watered environments. BMC Genom 14(1):313
Shabala S (2011) Physiological and cellular aspects of phytotoxicity tolerance in plants: the role of membrane transporters and implications for crop breeding for waterlogging tolerance. New Phytol 190(2):289–298. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03575.x
Shabala S, Pottosin I (2014) Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions: implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiol Plant 151(3):257–279. doi:10.1111/ppl.12165
Shabala S, Shabala S, Cuin TA, Pang J, Percey W, Chen Z, Conn S, Eing C, Wegner LH (2010) Xylem ionic relations and salinity tolerance in barley. Plant J 61(5):839–853. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04110.x
Shabala S, Shabala L, Barcelo J, Poschenrieder C (2014) Membrane transporters mediating root signalling and adaptive responses to oxygen deprivation and soil flooding. Plant, Cell Environ 37(10):2216–2233. doi:10.1111/pce.12339
Shavrukov Y, Gupta N, Miyazaki J, Baho M, Chalmers K, Tester M, Langridge P, Collins N (2010) HvNax3—a locus controlling shoot sodium exclusion derived from wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Funct Integr Genomics 10(2):277–291. doi:10.1007/s10142-009-0153-8
Singh S, Mackill DJ, Ismail AM (2009) Responses of SUB1 rice introgression lines to submergence in the field: yield and grain quality. Field Crops Res 113(1):12–23. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2009.04.003
Sosnowski O, Charcosset A, Joets J (2012) BioMercator V3: an upgrade of genetic map compilation and quantitative trait loci meta-analysis algorithms. Bioinformatics 28(15):2082–2083. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts313
Swamy BPM, Vikram P, Dixit S, Ahmed HU, Kumar A (2011) Meta-analysis of grain yield QTL identified during agricultural drought in grasses showed consensus. BMC Genom 12(1):319
Tester M, Langridge P (2010) Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 327(5967):818–822. doi:10.1126/science.1183700
Teulat B, This D, Khairallah M, Borries C, Ragot C, Sourdille P, Leroy P, Monneveux P, Charrier A (1998) Several QTLs involved in osmotic-adjustment trait variation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 96(5):688–698. doi:10.1007/s001220050790
Teulat B, Borries C, This D (2001) New QTLs identified for plant water status, water-soluble carbohydrate and osmotic adjustment in a barley population grown in a growth-chamber under two water regimes. Theor Appl Genet 103(1):161–170. doi:10.1007/s001220000503
Teulat B, Zoumarou-Wallis N, Rotter B, Ben Salem M, Bahri H, This D (2003) QTL for relative water content in field-grown barley and their stability across Mediterranean environments. Theor Appl Genet 108(1):181–188. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1417-7
This D, Borries C, Souyris I, Teulat B (2000) QTL study of chlorophyll content as a genetic parameter of drought tolerance in barley. Barley Genet Newslett 30:20–23
Tuberosa R (2012) Phenotyping for drought tolerance of crops in the genomics era. Front Physiol 3:347. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00347
Tuberosa R, Salvi S (2006) Genomics-based approaches to improve drought tolerance of crops. Trends Plant Sci 11(8):405–412. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2006.06.003
Veyrieras J-B, Goffinet B, Charcosset A (2007) MetaQTL: a package of new computational methods for the meta-analysis of QTL mapping experiments. BMC Bioinform 8(1):49
Voesenek LACJ, Sasidharan R, Visser EJW, Bailey-Serres J (2016) Flooding stress signaling through perturbations in oxygen, ethylene, nitric oxide and light. New Phytol 209(1):39–43. doi:10.1111/nph.13775
Wang T, Tohge T, Ivakov AA, Mueller-Roeber B, Fernie AR, Mutwil M, Schippers JH, Persson S (2015) Salt-Related MYB1 (SRM1) coordinates abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling during salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169:1027–1041
Wang F, Tong W, Zhu H, Kong W, Peng R, Liu Q, Yao Q (2016a) A novel Cys2/His2 zinc finger protein gene from sweetpotato, IbZFP1, is involved in salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 243(3):783–797. doi:10.1007/s00425-015-2443-9
Wang Y, Xu J, Deng D, Ding H, Bian Y, Yin Z, Wu Y, Zhou B, Zhao Y (2016b) A comprehensive meta-analysis of plant morphology, yield, stay-green, and virus disease resistance QTL in maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 243(2):459–471. doi:10.1007/s00425-015-2419-9
William HM, Trethowan R, Crosby-Galvan EM (2007) Wheat breeding assisted by markers: CIMMYT’s experience. Euphytica 157(3):307–319. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9405-7
Xu Y, Crouch JH (2008) Marker-Assisted selection in plant breeding: from publications to practice. Crop Sci 48(2):391–407. doi:10.2135/cropsci2007.04.0191
Xu K, Mackill D (1996) A major locus for submergence tolerance mapped on rice chromosome 9. Mol Breed 2(3):219–224. doi:10.1007/bf00564199
Xu K, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 442:705–708
Xu G-Y, Rocha PCF, Wang M-L, Xu M-L, Cui Y-C, Li L-Y, Zhu Y-X, Xia X (2011) A novel rice calmodulin-like gene, OsMSR2, enhances drought and salt tolerance and increases ABA sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Planta 234(1):47–59. doi:10.1007/s00425-011-1386-z
Yokotani N, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Iwabuchi M, Matsui M, Hirochika H, Oda K (2013) Role of the rice transcription factor JAmyb in abiotic stress response. J Plant Res 126(1):131–139. doi:10.1007/s10265-012-0501-y
Yu F, Han X, Geng C, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Qiu F (2015) Comparative proteomic analysis revealing the complex network associated with waterlogging stress in maize (Zea mays L.) seedling root cells. Proteomics 15(1):135–147. doi:10.1002/pmic.201400156
Zeng F, Shabala L, Zhou M, Zhang G, Shabala S (2013) Barley responses to combined waterlogging and salinity stress: separating effects of oxygen deprivation and elemental toxicity. Front Plant Sci 4:1–13
Zhang F, Chen G, Huang Q, Orion O, Krugman T, Fahima T, Korol AB, Nevo E, Gutterman Y (2005) Genetic basis of barley caryopsis dormancy and seedling desiccation tolerance at the germination stage. Theor Appl Genet 110(3):445–453. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1851-1
Zhang L-Y, Liu D-C, Guo X-L, Yang W-L, Sun J-Z, Wang D-W, Zhang A (2010) Genomic distribution of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield-related traits in common wheat. J Integr Plant Biol 52(11):996–1007. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00967.x
Zhang X, Shabala S, Koutoulis A, Shabala L, Johnson P, Hayes D, Nichols D, Zhou M (2015) Waterlogging tolerance in barley is associated with faster aerenchyma formation in adventitious roots. Plant Soil 394(1–2):355–372. doi:10.1007/s11104-015-2536-z
Zhang D, Tong J, Xu Z, Wei P, Xu L, Wan Q, Huang Y, He X, Yang J, Shao H, Ma H (2016a) Soybean C2H2-Type zinc finger protein GmZFP3 with conserved QALGGH motif negatively regulates drought responses in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 7:325. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00325
Zhang X, Zhou G, Shabala S, Koutoulis A, Shabala L, Johnson P, Li C, Zhou M (2016b) Identification of aerenchyma formation-related QTL in barley that can be effective in breeding for waterlogging tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 129(6):1167–1177. doi:10.1007/s00122-016-2693-3
Zhou M (2010) Improvement of plant waterlogging tolerance. In: Mancuso S, Shabala S (eds) Waterlogging signalling and tolerance in plants. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 267–285. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-10305-6_13,#Springer-Verlag
Zhou MX (2011) Accurate phenotyping reveals better QTL for waterlogging tolerance in barley. Plant Breed 130(2):203–208. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2010.01792.x
Zhou M, Johnson P, Zhou G, Li C, Lance R (2012) Quantitative trait loci for waterlogging tolerance in a barley cross of Franklin × YuYaoXiangTian Erleng and the relationship between waterlogging and salinity tolerance. Crop Sci 52(5):2082–2088. doi:10.2135/cropsci2012.01.0008
Zhu M, Zhou M, Shabala L, Shabala S (2016) Physiological and molecular mechanisms mediating xylem Na+ loading in barley in the context of salinity stress tolerance. Plant, Cell Environ:n/a-n/a. doi:10.1111/pce.12727
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Australian Research Council Linkage grant (LP120200516) and Grains Research and Development Corporation (GRDC) of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Shabala, S., Koutoulis, A. et al. Meta-analysis of major QTL for abiotic stress tolerance in barley and implications for barley breeding. Planta 245, 283–295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2605-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2605-4