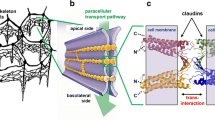
Abstract
Claudins are tight junction membrane proteins and regulate the paracellular passage of ions and water. They can seal the paracellular cleft against solute passage but also form paracellular channels. They are tetraspan proteins with two extracellular segments. Claudin-10 exists in at least two functional isoforms, claudin-10a and claudin-10b, that differ in their first transmembrane segment and first extracellular segment. Both isoforms act as selective paracellular ion channels, either for anions (claudin-10a) or for cations (claudin-10b). Their diverse functions are reflected in completely different expression patterns in the body, especially in the kidney. Their structural and functional similarities and differences make them ideal subjects to study determinants of claudin charge selectivity and pore formation. This review aims to summarise research on permeability properties of the claudin-10 channels and their role in physiology and pathophysiology of the kidney.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, Schoneberg T, Mankertz J, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2002) Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 115:4969–4976
Amasheh S, Schmidt T, Mahn M, Florian P, Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Gitter AH, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2005) Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 321:89–96
Angelow S, El-Husseini R, Kanzawa SA, Yu AS (2007) Renal localization and function of the tight junction protein, claudin-19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F166–F177
Angelow S, Kim KJ, Yu AS (2006) Claudin-8 modulates paracellular permeability to acidic and basic ions in MDCK II cells. J Physiol 571:15–26
Barratt LJ, Rector FC Jr, Kokko JP, Seldin DW (1974) Factors governing the transepithelial potential difference across the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. J Clin Invest 53:454–464
Breiderhoff T, Himmerkus N, Stuiver M, Mutig K, Will C, Meij IC, Bachmann S, Bleich M, Willnow TE, Müller D (2012) Deletion of claudin-10 (Cldn10) in the thick ascending limb impairs paracellular sodium permeability and leads to hypermagnesemia and nephrocalcinosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:14241–14246
Colegio OR, Van Itallie CM, McCrea HJ, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2002) Claudins create charge-selective channels in the paracellular pathway between epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C142–C147
Conrad MP, Piontek J, Gunzel D, Fromm M, Krug SM (2016) Molecular basis of claudin-17 anion selectivity. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:185–200
Eisenman G (1962) Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation. Biophys J 2:259–323
Enck AH, Berger UV, Yu AS (2001) Claudin-2 is selectively expressed in proximal nephron in mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F966–F974
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141:1539–1550
Furuse M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Tsukita S (2001) Conversion of zonulae occludentes from tight to leaky strand type by introducing claudin-2 into Madin-Darby canine kidney I cells. J Cell Biol 153:263–272
Furuse M, Hata M, Furuse K, Yoshida Y, Haratake A, Sugitani Y, Noda T, Kubo A, Tsukita S (2002) Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier: a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 156:1099–1111
Gong Y, Renigunta V, Himmerkus N, Zhang J, Renigunta A, Bleich M, Hou J (2012) Claudin-14 regulates renal Ca(+)(+) transport in response to CaSR signalling via a novel microRNA pathway. EMBO J 31:1999–2012
Günzel D, Stuiver M, Kausalya PJ, Haisch L, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, Meij IC, Hunziker W, Fromm M, Muller D (2009) Claudin-10 exists in six alternatively spliced isoforms that exhibit distinct localization and function. J Cell Sci 122:1507–1517
Hou J, Renigunta A, Gomes AS, Hou M, Paul DL, Waldegger S, Goodenough DA (2009) Claudin-16 and claudin-19 interaction is required for their assembly into tight junctions and for renal reabsorption of magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:15350–15355
Hou J, Shan Q, Wang T, Gomes AS, Yan Q, Paul DL, Bleich M, Goodenough DA (2007) Transgenic RNAi depletion of claudin-16 and the renal handling of magnesium. J Biol Chem 282:17114–17122
Inai T, Kamimura T, Hirose E, Iida H, Shibata Y (2010) The protoplasmic or exoplasmic face association of tight junction particles cannot predict paracellular permeability or heterotypic claudin compatibility. Eur J Cell Biol 89:547–556
Inai T, Sengoku A, Guan X, Hirose E, Iida H, Shibata Y (2005) Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of tight junction proteins, claudin-10 and -15, examined by RT-PCR and immunofluorescence microscopy. Arch Histol Cytol 68:349–360
Kirk A, Campbell S, Bass P, Mason J, Collins J (2010) Differential expression of claudin tight junction proteins in the human cortical nephron. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:2107–2119
Kiuchi-Saishin Y, Gotoh S, Furuse M, Takasuga A, Tano Y, Tsukita S (2002) Differential expression patterns of claudins, tight junction membrane proteins, in mouse nephron segments. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:875–886
Konrad M, Schaller A, Seelow D, Pandey AV, Waldegger S, Lesslauer A, Vitzthum H, Suzuki Y, Luk JM, Becker C, Schlingmann KP, Schmid M, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Ariceta G, Cano F, Enriquez R, Juppner H, Bakkaloglu SA, Hediger MA, Gallati S, Neuhauss SC, Nurnberg P, Weber S (2006) Mutations in the tight-junction gene claudin 19 (CLDN19) are associated with renal magnesium wasting, renal failure, and severe ocular involvement. Am J Hum Genet 79:949–957
Krug SM, Gunzel D, Conrad MP, Rosenthal R, Fromm A, Amasheh S, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2012) Claudin-17 forms tight junction channels with distinct anion selectivity. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:2765–2778
Lee JW, Chou CL, Knepper MA (2015) Deep sequencing in microdissected renal tubules identifies nephron segment-specific transcriptomes. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:2669–2677
Lee NP, Tong MK, Leung PP, Chan VW, Leung S, Tam PC, Chan KW, Lee KF, Yeung WS, Luk JM (2006) Kidney claudin-19: localization in distal tubules and collecting ducts and dysregulation in polycystic renal disease. FEBS Lett 580:923–931
Li J, Angelow S, Linge A, Zhuo M, Yu AS (2013) Claudin-2 pore function requires an intramolecular disulfide bond between two conserved extracellular cysteines. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 305:C190–C196
Milatz S, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, Günzel D, Muller D, Schulzke JD, Amasheh S, Fromm M (2010) Claudin-3 acts as a sealing component of the tight junction for ions of either charge and uncharged solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798:2048–2057
Milatz S, Himmerkus N, Wulfmeyer VC, Drewell H, Mutig K, Hou J, Breiderhoff T, Müller D, Fromm M, Bleich M, Günzel D (2017) Mosaic expression of claudins in thick ascending limbs of Henle results in spatial separation of paracellular Na+ and Mg2+ transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (in press)
Morita K, Furuse M, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1999) Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:511–516
Morita K, Sasaki H, Fujimoto K, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Claudin-11/OSP-based tight junctions of myelin sheaths in brain and Sertoli cells in testis. J Cell Biol 145:579–588
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 161:653–660
Ohta H, Adachi H, Takiguchi M, Inaba M (2006) Restricted localization of claudin-16 at the tight junction in the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop together with claudins 3, 4, and 10 in bovine nephrons. J Vet Med Sci 68:453–463
Plain A, Wulfmeyer VC, Milatz S, Klietz A, Hou J, Bleich M, Himmerkus N (2016) Corticomedullary difference in the effects of dietary Ca(2)(+) on tight junction properties in thick ascending limbs of Henle’s loop. Pflugers Arch 468:293–303
Rosenthal R, Milatz S, Krug SM, Oelrich B, Schulzke JD, Amasheh S, Gunzel D, Fromm M (2010) Claudin-2, a component of the tight junction, forms a paracellular water channel. J Cell Sci 123:1913–1921
Simon DB, Lu Y, Choate KA, Velazquez H, Al-Sabban E, Praga M, Casari G, Bettinelli A, Colussi G, Rodriguez-Soriano J, McCredie D, Milford D, Sanjad S, Lifton RP (1999) Paracellin-1, a renal tight junction protein required for paracellular Mg2+ resorption. Science 285:103–106
Tanaka H, Yamamoto Y, Kashihara H, Yamazaki Y, Tani K, Fujiyoshi Y, Mineta K, Takeuchi K, Tamura A, Tsukita S (2016) Claudin-21 has a paracellular channel role at tight junctions. Mol Cell Biol 36:954–964
Van Itallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2001) Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J Clin Invest 107:1319–1327
Van Itallie CM, Fanning AS, Anderson JM (2003) Reversal of charge selectivity in cation or anion-selective epithelial lines by expression of different claudins. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F1078–F1084
Van Itallie CM, Rogan S, Yu A, Vidal LS, Holmes J, Anderson JM (2006) Two splice variants of claudin-10 in the kidney create paracellular pores with different ion selectivities. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F1288–F1299
Will C, Breiderhoff T, Thumfart J, Stuiver M, Kopplin K, Sommer K, Günzel D, Querfeld U, Meij IC, Shan Q, Bleich M, Willnow TE, Müller D (2010) Targeted deletion of murine Cldn16 identifies extra- and intrarenal compensatory mechanisms of Ca2+ and Mg2+ wasting. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F1152–F1161
Wu J, Helftenbein G, Koslowski M, Sahin U, Tureci O (2006) Identification of new claudin family members by a novel PSI-BLAST based approach with enhanced specificity. Proteins 65:808–815
Yu AS, Cheng MH, Angelow S, Gunzel D, Kanzawa SA, Schneeberger EE, Fromm M, Coalson RD (2009) Molecular basis for cation selectivity in claudin-2-based paracellular pores: identification of an electrostatic interaction site. J Gen Physiol 133:111–127
Yu AS, Enck AH, Lencer WI, Schneeberger EE (2003) Claudin-8 expression in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells augments the paracellular barrier to cation permeation. J Biol Chem 278:17350–17359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on “Claudins – physiology, pathophysiology and clinical relevance”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milatz, S., Breiderhoff, T. One gene, two paracellular ion channels—claudin-10 in the kidney. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 469, 115–121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1921-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1921-7