Abstract
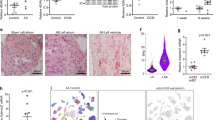
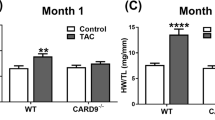
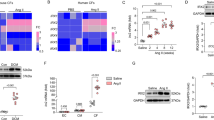
Myocardial fibrosis is an integral component of most cardiac pathologic conditions and contributes to the development of both systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Because of the availability of genetically manipulated animals, mouse models are essential for understanding the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Accordingly, we characterized the inflammatory and fibrotic response in a mouse model of cardiac pressure overload due to transverse aortic constriction (TAC). Following TAC, mouse hearts exhibited induction of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, associated with macrophage, but not neutrophil, infiltration. Induction of inflammatory cytokines was followed by a late upregulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β isoforms, activation of the Smad2/3 and Smad1/5 pathways, induction of matricellular proteins, and deposition of collagen. Inflammatory activity decreased after 28 days of TAC; at this timepoint established fibrosis was noted, accompanied by ventricular dilation and systolic dysfunction. Late induction of inhibitory mediators, such as TGF-β, may play an essential role in the transition from inflammation to fibrosis by suppressing inflammatory gene synthesis while inducing matrix deposition. Our findings identify molecular mediators and pathways with a potential role in cardiac fibrosis laying the foundations for studies exploring the pathogenesis of fibrotic cardiac remodeling using genetically targeted mice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beg AA (2002) Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors: implications for regulating inflammatory and immune responses. Trends Immunol 23:509–512
Berk BC, Fujiwara K, Lehoux S (2007) ECM remodeling in hypertensive heart disease. J Clin Invest 117:568–575
Brown RD, Ambler SK, Mitchell MD, Long CS (2005) The cardiac fibroblast: therapeutic target in myocardial remodeling and failure. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:657–687
Brown RD, Jones GM, Laird RE, Hudson P, Long CS (2007) Cytokines regulate matrix metalloproteinases and migration in cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:200–205
Bryant D, Becker L, Richardson J, Shelton J, Franco F, Peshock R, Thompson M, Giroir B (1998) Cardiac failure in transgenic mice with myocardial expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circulation 97:1375–1381
Bujak M, Dobaczewski M, Chatila K, Mendoza LH, Li N, Reddy A, Frangogiannis NG (2008a) Interleukin-1 receptor type I signaling critically regulates infarct healing and cardiac remodeling. Am J Pathol 173:57–67
Bujak M, Frangogiannis NG (2007) The role of TGF-beta signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc Res 74:184–195
Bujak M, Kweon HJ, Chatila K, Li N, Taffet G, Frangogiannis NG (2008b) Aging-related defects are associated with adverse cardiac remodeling in a mouse model of reperfused myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:1384–1392
Bujak M, Ren G, Kweon HJ, Dobaczewski M, Reddy A, Taffet G, Wang XF, Frangogiannis NG (2007) Essential role of Smad3 in infarct healing and in the pathogenesis of cardiac remodeling. Circulation 116:2127–2138
Cingolani OH, Yang XP, Liu YH, Villanueva M, Rhaleb NE, Carretero OA (2004) Reduction of cardiac fibrosis decreases systolic performance without affecting diastolic function in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 43:1067–1073
Cleutjens JP, Verluyten MJ, Smiths JF, Daemen MJ (1995) Collagen remodeling after myocardial infarction in the rat heart. Am J Pathol 147:325–338
Collins KA, Korcarz CE, Lang RM (2003) Use of echocardiography for the phenotypic assessment of genetically altered mice. Physiol Genomics 13:227–239
Dewald O, Ren G, Duerr GD, Zoerlein M, Klemm C, Gersch C, Tincey S, Michael LH, Entman ML, Frangogiannis NG (2004) Of mice and dogs: species-specific differences in the inflammatory response following myocardial infarction. Am J Pathol 164:665–677
Dewald O, Zymek P, Winkelmann K, Koerting A, Ren G, Abou-Khamis T, Michael LH, Rollins BJ, Entman ML, Frangogiannis NG (2005) CCL2/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulates inflammatory responses critical to healing myocardial infarcts. Circ Res 96:881–889
Frangogiannis NG (2008) The immune system and cardiac repair. Pharmacol Res 58:88–111
Frangogiannis NG (2006a) The mechanistic basis of infarct healing. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1907–1939
Frangogiannis NG (2006b) Targeting the inflammatory response in healing myocardial infarcts. Curr Med Chem 13:1877–1893
Frangogiannis NG, Dewald O, Xia Y, Ren G, Haudek S, Leucker T, Kraemer D, Taffet G, Rollins BJ, Entman ML (2007) Critical role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CC chemokine ligand 2 in the pathogenesis of ischemic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 115:584–592
Frangogiannis NG, Shimoni S, Chang SM, Ren G, Dewald O, Gersch C, Shan K, Aggeli C, Reardon M, Letsou GV, Espada R, Ramchandani M, Entman ML, Zoghbi WA (2002) Active interstitial remodeling: an important process in the hibernating human myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:1468–1474
Gersch C, Dewald O, Zoerlein M, Michael LH, Entman ML, Frangogiannis NG (2002) Mast cells and macrophages in normal C57/BL/6 mice. Histochem Cell Biol 118:41–49
Gharaee-Kermani M, Denholm EM, Phan SH (1996) Costimulation of fibroblast collagen and transforming growth factor beta1 gene expression by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 via specific receptors. J Biol Chem 271:17779–17784
Heymans S, Schroen B, Vermeersch P, Milting H, Gao F, Kassner A, Gillijns H, Herijgers P, Flameng W, Carmeliet P, Van de Werf F, Pinto YM, Janssens S (2005) Increased cardiac expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 is related to cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction in the chronic pressure-overloaded human heart. Circulation 112:1136–1144
Ikeuchi M, Tsutsui H, Shiomi T, Matsusaka H, Matsushima S, Wen J, Kubota T, Takeshita A (2004) Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling exacerbates early cardiac dysfunction but prevents late remodeling after infarction. Cardiovasc Res 64:526–535
Janicki JS, Brower GL (2002) The role of myocardial fibrillar collagen in ventricular remodeling and function. J Card Fail 8:S319–S325
Junqueira LC, Bignolas G, Brentani RR (1979) Picrosirius staining plus polarization microscopy, a specific method for collagen detection in tissue sections. Histochem J 11:447–455
Khan R, Sheppard R (2006) Fibrosis in heart disease: understanding the role of transforming growth factor-beta in cardiomyopathy, valvular disease and arrhythmia. Immunology 118:10–24
Kruglov EA, Nathanson RA, Nguyen T, Dranoff JA (2006) Secretion of MCP-1/CCL2 by bile duct epithelia induces myofibroblastic transdifferentiation of portal fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G765–G771
Kuwahara F, Kai H, Tokuda K, Takeya M, Takeshita A, Egashira K, Imaizumi T (2004) Hypertensive myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction: another model of inflammation? Hypertension 43:739–745
Lee AA, Dillmann WH, McCulloch AD, Villarreal FJ (1995) Angiotensin II stimulates the autocrine production of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in adult rat cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27:2347–2357
Li J, Schwimmbeck PL, Tschope C, Leschka S, Husmann L, Rutschow S, Reichenbach F, Noutsias M, Kobalz U, Poller W, Spillmann F, Zeichhardt H, Schultheiss HP, Pauschinger M (2002) Collagen degradation in a murine myocarditis model: relevance of matrix metalloproteinase in association with inflammatory induction. Cardiovasc Res 56:235–247
Li YY, Feng YQ, Kadokami T, McTiernan CF, Draviam R, Watkins SC, Feldman AM (2000) Myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling in transgenic mice overexpressing tumor necrosis factor alpha can be modulated by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12746–12751
Lutgens E, Gijbels M, Smook M, Heeringa P, Gotwals P, Koteliansky VE, Daemen MJ (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta mediates balance between inflammation and fibrosis during plaque progression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:975–982
McEwan PE, Gray GA, Sherry L, Webb DJ, Kenyon CJ (1998) Differential effects of angiotensin II on cardiac cell proliferation and intramyocardial perivascular fibrosis in vivo. Circulation 98:2765–2773
Muller DN, Dechend R, Mervaala EM, Park JK, Schmidt F, Fiebeler A, Theuer J, Breu V, Ganten D, Haller H, Luft FC (2000) NF-kappaB inhibition ameliorates angiotensin II-induced inflammatory damage in rats. Hypertension 35:193–201
Nielsen LF, Moe D, Kirkeby S, Garbarsch C (1998) Sirius red and acid fuchsin staining mechanisms. Biotech Histochem 73:71–77
Pannu J, Nakerakanti S, Smith E, ten Dijke P, Trojanowska M (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I-dependent fibrogenic gene program is mediated via activation of Smad1 and ERK1/2 pathways. J Biol Chem 282:10405–10413
Quan TE, Cowper S, Wu SP, Bockenstedt LK, Bucala R (2004) Circulating fibrocytes: collagen-secreting cells of the peripheral blood. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:598–606
Sivasubramanian N, Coker ML, Kurrelmeyer KM, MacLellan WR, DeMayo FJ, Spinale FG, Mann DL (2001) Left ventricular remodeling in transgenic mice with cardiac restricted overexpression of tumor necrosis factor. Circulation 104:826–831
Siwik DA, Chang DL, Colucci WS (2000) Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha decrease collagen synthesis and increase matrix metalloproteinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts in vitro. Circ Res 86:1259–1265
Siwik DA, Colucci WS (2004) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases by cytokines and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species in the myocardium. Heart Fail Rev 9:43–51
Strieter RM, Gomperts BN, Keane MP (2007) The role of CXC chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 117:549–556
Sun M, Chen M, Dawood F, Zurawska U, Li JY, Parker T, Kassiri Z, Kirshenbaum LA, Arnold M, Khokha R, Liu PP (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates cardiac remodeling and ventricular dysfunction after pressure overload state. Circulation 115:1398–1407
Sun Y, Zhang J, Lu L, Chen SS, Quinn MT, Weber KT (2002) Aldosterone-induced inflammation in the rat heart: role of oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 161:1773–1781
Wynn TA (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214:199–210
Zymek P, Bujak M, Chatila K, Cieslak A, Thakker G, Entman ML, Frangogiannis NG (2006) The role of platelet-derived growth factor signaling in healing myocardial infarcts. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:2315–2323
Acknowledgments
Supported by NIH R01 HL-76246 and HL-85440.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Y., Lee, K., Li, N. et al. Characterization of the inflammatory and fibrotic response in a mouse model of cardiac pressure overload. Histochem Cell Biol 131, 471–481 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0541-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0541-5