Abstract
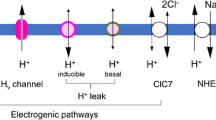
The acid-base status and functional responses of alveolar macrophages (mφ) are influenced by the activity of plasmalemmal V-type H+-pump (V-ATPase), an electrogenic H+ extruder that provides a possible link between intracellular pH (pHi) and plasma membrane potential (Em). This study examined the relationships among Em, pHi, and plasmalemmal V-ATPase activity in resident alveolar mφ from rabbits. Em and pHi were measured using fluorescent probes. Em was −46 mV and pHi was 7.14 at an extracellular pH (pHo) of 7.4. The pHi declined progressively at lower pHo values. Decrements in pHo also caused depolarization of the plasma membrane, independent of V-ATPase activity. The pH effects on Em were sensitive to external K+, and hence, probably involved pH-sensitive K+ conductance. H+ were not distributed at equilibrium across the plasma membrane. V-ATPase activity was a major determinant of the transmembrane H+ disequilibrium. Pump inhibition with bafilomycin A1 caused cytosolic acidification, due most likely to the retention of metabolically generated H+. V-ATPase inhibition also caused depolarization of the plasma membrane, but the effects were mediated indirectly via the accompanying pHi changes. V-ATPase activity was sensitive to Em. Em hyperpolarization (valinomycin-clamp) reduced V-ATPase activity, causing an acidic shift in baseline pHi under steady-state conditions and slowing pHi recovery from NH4Cl prepulse acid-loads. The findings indicate that a complex relationship exists among Em, pHi, and pHo that was partially mediated by plasmalemmal V-ATPase activity. This relationship could have important consequences for the expression of pH- and/or voltage-sensitive functions in alveolar mφ.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Bidani SES Brown TA Heming (1994) ArticleTitlepHi regulation in alveolar macrophages: relative roles of Na+-H+ antiport and H+-ATPase. Am J Physiol 266 L681–L688 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltlaiu7w%3D Occurrence Handle8023957
A Bidani SES Brown TA Heming R Gurich TD DuBose Jr (1989) ArticleTitleCytoplasmic pH in pulmonary macrophages: recovery from acid load is Na+ independent and NEM sensitive. Am J Physiol 257 C65–C76 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaA38%2FmslA%3D Occurrence Handle2526587
A Bidani TA Heming (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of bafilomycin A1 on functional capabilities of LPS-activated alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 57 275–281 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjsFOht7g%3D Occurrence Handle7852842
AR Cameron J Nelson HJ Forman (1983) ArticleTitleDepolarization and increased conductance precede superoxide release by concanavalin A-stimulated rat alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80 3726–3728 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXktlKls7s%3D Occurrence Handle6304734
E Carmeliet (1999) ArticleTitleCardiac ionic currents and acute ischemia: from channels to arrhythmias. Physiol Rev 79 917–1017 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksFemtrg%3D Occurrence Handle10390520
V Castranova L Bowman PR Miles (1979) ArticleTitleTransmembrane potential and ionic content of rat alveolar macrophages. J Cell Physiol 101 471–480 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXls1SqsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle528572
LC Chen QS Qu T Gordon MO Amdur JM Fine (1992) ArticleTitleCharacterization of intracellular pH (pHi) regulation in human, guinea pig, and rabbit alveolar macrophages (Abstract). Am Rev Respir Dis 145 A651
JM Davies I Hunt D Sanders (1994) ArticleTitleVacuolar H+-pumping ATPase variable transport coupling ratio controlled by pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91 8547–8551 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmsVyksbg%3D Occurrence Handle8078920
RM Effros M Dunning R Arndorker E Jacobs J Biller (1996) ArticleTitleSurface pH of the normal and cystic fibrosis nasal mucosa (Abstract). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153 A778
EW Gelfand GB Mills RK Cheung JW Lee S Grinstein (1987) ArticleTitleTransmembrane ion fluxes during activation of human T lymphocytes: role of Ca2+, Na+/H+ exchange and phospholipids turnover. Immunol Rev 95 59–87 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXhvFCitbw%3D Occurrence Handle2437015
SB Gordon RC Read (2002) ArticleTitleMacrophage defences against respiratory tract infections. Br Med Bull 61 45–61 Occurrence Handle10.1093/bmb/61.1.45 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XktlWht7Y%3D Occurrence Handle11997298
WR Harvey (1992) ArticleTitlePhysiology of V-ATPases. J Exp Biol 172 1–17 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhsVait78%3D
TA Heming A Bidani (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of myristate phorbol ester on V-ATPase activity and Na+-H+ exchange in alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 57 600–608 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXltFajs7c%3D Occurrence Handle7722418
TA Heming A Bidani (1995) ArticleTitleNa+-H+ exchange in resident alveolar macrophages: activation by osmotic cell shrinkage. J Leukoc Biol 57 609–616 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXltFajsL4%3D Occurrence Handle7722419
TA Heming DL Traber F Hinder A Bidani (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of bafilomycin A1 on cytosolic pH of sheep alveolar and peritoneal macrophages: evaluation of pH regulatory role of plasma membrane V-ATPase. J Exp Biol 198 1711–1715 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnvFShtLk%3D Occurrence Handle7636444
B Hille (1992) Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Assoc. Inc. Sunderland, MA
JF Hunt K Fang R Malik A Snyder N Malhotra TA Platts-Mills B Gaston (2000) ArticleTitleEndogenous airway acidification. Implications for asthma pathophysiology. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161 694–699 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7nslyrtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10712309
A Kapus R Romanek AY Qu OD Rotstein S Grinstein (1993) ArticleTitleA pH-sensitive and voltage-dependent proton conductance in the plasma membrane of macrophages. J Gen Physiol 102 729–760 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhs1Wmurk%3D Occurrence Handle8270911
F Lang H Oberleithner HA Kolb M Paulmichl H Völkl W Wang (1988) Interaction of intracellular pH and cell membrane potential. D Haussinger (Eds) pH Homeostasis Academic Press New York 27–42
A Lardner (2001) ArticleTitleThe effects of extracellular pH on immune function. J Leukoc Biol 69 522–530 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXivVagurs%3D Occurrence Handle11310837
P Läuger (1991) Electrogenic Ion Pumps. Sinauer Assoc. Inc. Sunderland, MA
MAR Lowry JL Goldberg M Belosevic (1998) ArticleTitleInduction of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis in murine macrophages requires potassium channel activity. Clin Exp Immunol 111 597–603 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00536.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXis1aktbg%3D Occurrence Handle9528905
JK Murphy HJ Forman (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of sodium and proton pump activity on respiratory burst and pH regulation of rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol 264 L523–L532 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlsFyjsb8%3D Occurrence Handle8388649
A Nanda A Gukovskaya J Tseng S Grinstein (1992) ArticleTitleActivation of vacuolar-type proton pumps by protein kinase C. Role in neutrophil pH regulation. J Biol Chem 267 22740–22746 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlvFSjtb0%3D Occurrence Handle1331065
DW Nielson J Goerke JA Clements (1981) ArticleTitleAlveolar subphase pH in the lungs of anesthetized rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78 7119–7123 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2D1c3lvF0%3D Occurrence Handle6947276
JM Novak PM Cala D Ward SS Buys J Kaplan (1988) ArticleTitleRegulatory volume decrease in alveolar macrophages: cation loss is not correlated with changes in membrane recycling. J Cell Physiol 137 243–250 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaD2Mvhtl0%3D Occurrence Handle3192616
CJ Swallow S Grinstein OD Rotstein (1988) ArticleTitleCytoplasmic pH regulation in macrophages by an ATP-dependent and N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive mechanism. Possible involvement of a plasma membrane proton pump. J Biol Chem 263 19558–19563 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXmtVyqtro%3D Occurrence Handle2904439
CJ Swallow S Grinstein OD Rotstein (1990) ArticleTitleA vacuolar type H+-ATPase regulates cytoplasmic pH in murine macrophages. J Biol Chem 265 7645–7654 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXkt1ajsbk%3D Occurrence Handle2139663
H Tapper R Sundler (1992) ArticleTitleCytosolic pH regulation in mouse macrophages. Proton extrusion by plasma-membrane-localized H+-ATPase. Biochem J 281 245–250 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XjvVGrtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1531009
J van Adelsberg Q Al-Awqati (1986) ArticleTitleRegulation of cell pH by Ca2+-mediated exocytotic insertion of H+-ATPases. J Cell Biol 102 1638–1645 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XktVCjt7g%3D Occurrence Handle2871030
AS Waggoner (1979) ArticleTitleThe use of cyanine dyes for the determination of membrane potentials in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol 55 689–695 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXmtVKmsrs%3D Occurrence Handle459861
DA Welsh CM Mason (2001) ArticleTitleHost defense in respiratory infections. Med Clin North Am 85 1329–1347 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnvVCqu7k%3D Occurrence Handle11680105
H Wieczorek D Brown S Grinstein J Ehrenfeld WR Harvey (1999) ArticleTitleAnimal plasma membrane energization by proton-motive V-ATPases. Bioessays 21 637–648 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199908)21:8<637::AID-BIES3>3.3.CO;2-N Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzmvFKhuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10440860
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by the National Institutes of Health grant HL51421 and the Constance Marsili Schafer Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heming, T., Bidani, A. Effects of Plasmalemmal V-ATPase Activity on Plasma Membrane Potential of Resident Alveolar Macrophages . Lung 181, 121–135 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-003-1013-2
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-003-1013-2