Abstract
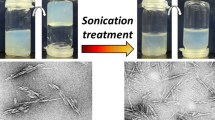
Dynamic light scattering, viscometry, sedimentation, densitometry, refractometry, flow birefringence, and electrically induced dichroism were used in the studies of hydrosols of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Visualization of CNC particles and primary evaluation of their size were performed with the use of atomic force microscopy (AFM). The set of data on hydrodynamic and optical properties of the studied particles in aqueous medium was obtained. The particle size distribution demonstrates wide polydispersity. The values of translational and rotational friction coefficients, intrinsic viscosity, and quantitative data on sedimentation, density, and flow birefringence of CNC sols were obtained. Contributions of particles of various sizes into the phenomena caused by translational and rotational friction of CNC samples were analyzed in detail. It was established that hydrodynamic and optical properties of CNC hydrosols can be described using the model of ellipsoid of revolution with a shape asymmetry parameter (p) equal to 20. According to the data of hydrodynamic studies, the main CNC fraction consists of particles with a length of the order of 300–400 nm. It was demonstrated that optical characteristics of CNC hydrosols are determined by the contribution of large particles (with the characteristic longitudinal size of 1500 nm and above) into flow birefringence and electric dichroism. It was found that the AFM data alone cannot provide insight into morphology of CNC hydrosols.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
George J, Ramana KV, Bawa AS, Siddaramaiah (2011) Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals exhibiting high thermal stability and their polymer nanocomposites. Int J Biol Macromol 48:50–57. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.09.013
Ioelovich M, Leykin A (2006) Formation nano-structure of microcrystalline cellulose. Cellul Chem Technol 40:313–317
Kiziltas EE, Kiziltas A, Nazari B, Gardner DJ, Bousfield DW (2016) Glycerine treated nanofibrillated cellulose composites. J Nanomaterials 2016:7851308. doi:10.1155/2016/7851308
Gindl W, Keckes J (2005) All-cellulose nanocomposite. Polym 46:10221–10225. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.08.040
Karim Z, Claudpierre S, Grahn M, Oksman K, Mathew AP (2016) Nanocellulose based functional membranes for water cleaning: tailoring of mechanical properties, porosity and metal ion capture. J Membr Sci 514:418–428. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2016.05.018
Durán JDG, Arias JL, Gallardo V, Delgado AV (2008) Magnetic colloids as drug vehicles. J Pharm Sci 97:2948–2983. doi:10.1002/jps.21249
Azizi Samir MAS, Alloin F, Dufresne A (2005) Review of recent research into cellulosic whiskers, their properties and their application in nanocomposite field. Biomacromolecules 6:612–626. doi:10.1021/bm0493685
Dufresne A (2006) Comparing the mechanical properties of high performances polymer nanocomposites from biological sources. J Nanosci Nanotech 6:322–330. doi:10.1166/jnn.2006.005
Beck-Candanedo S, Roman M, Gray DG (2005) Effect of reaction conditions on the properties and behavior of wood cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Biomacromolecules 6:1048–1054. doi:10.1021/bm049300p
Lin N, Dufresne A (2014) Nanocellulose in biomedicine: current status and future prospect. Europ Polym J 59:302–325. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.07.025
Zimm BH, Crothers DM (1962) Simplified rotating cylinder viscometer for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 48:905–911
Frisman EV, Shchagina LV, Vorobev VI (1965) A glass rotating viscometer. Biorheology 2:189–194
Schuck P (2000) Size-distribution analysis of macromolecules by sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation and lamm equation modeling. Biophys J 78:1606–1619
Maechtle W (1984) Characterization of dispersions using combined H2O/D2O ultracentrifuge measurements. Makromol Chem 185:1025–1039
Tsvetkov VN (1989) Rigid-chain polymers: hydrodynamic and optical properties in solution. Plenum Press, New York
Tsvetkov VN, Andreeva LN (1981) Flow and electric birefringence in rigid-chain polymer-solutions. Adv Polym Sci 39:95–207. doi:10.1007/3-540-10218-3_3
Vojtylov V, Zernova T, Spartakov A, Trusov A, Voitylov A (2002) Determination of distribution of colloidal particles on their parameters in electro-optical investigation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 209:123–129. doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(02)00173-5
Trusov AA, Vojtylov VV (1993) Electrooptics and conductometry of polydisperse systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Klemeshev VA, Voitylov AV, Klemeshev SA, Petrov MP (2014) Experiment control and data acquisition in electro-optical research. 2014 International Conference on Computer Technologies in Physical and Engineering Applications, ICCTPEA 2014 Proceedings 2014:181–182. doi: 10.1109/ICCTPEA.2014.6893348
Kotelnikov VA (1933) On the carrying capacity of the ether and wire in telecommunications. In material for the first all-union conference on questions of communication. Izd. Red. Upr, Moscow
Perrin F (1936) Brownian motion of an ellipsoid. II. Free rotation and depolarisation of fluorescence: translation and diffusion of ellipsoidal molecules. J Phys Rad 7:1–11. doi:10.1051/jphysrad:01936007010100
Pamies R, Hernández Cifre JG, del Carmen López Martínez M, García de la Torre J (2008) Determination of intrinsic viscosities of macromolecules and nanoparticles. Comparison of single-point and dilution procedures. Colloid Polym Sci 286:1223–1231. doi:10.1007/s00396-008-1902-2
Kuhn W, Kuhn H (1945) Die Abhängigkeit der Viskosität vom Strömungsgefälle bei hochverdünnten Suspensionen und Lösungen. Helv Chim Acta 1:97–127. doi:10.1002/hlca.19450280111
Kuhn W, Kuhn H, Buchner P (1951) Hydrodynamic behavior of macromolecules in solution. Ergeb Exakt Naturwiss 25:1–108
Simha R (1940) The influence of brownian movement on the viscosity of solutions. J Phys Chem 44:25–34. doi:10.1021/j150397a004
Simha R (1945) The influence of molecular flexibility on the intrinsic viscosity, sedimentation, and diffusion of high polymers. J Chem Phys 13:188–195. doi:10.1063/1.1724020
Cummins HZ, Pike ER (eds) (1974) Photon-correlation and light-beating spectroscopy. Plenum Press, New York and London
Ortega A, García de la Torre J (2007) Equivalent radii and ratios of radii from solution properties as indicators of macromolecular conformation, shape, and flexibility. Biomacromolecules 8:2464–2475. doi:10.1021/bm700473f
Tirado MM, Carmen López Martínez M, García de la Torre J (1984) Comparison of theories for the translational and rotational diffusion coefficients of rod-like macromolecules. Application to short DNA fragments. J Chem Phys 81:2047–2052. doi:10.1063/1.447827
García de la Torre J, López Martínez MC, Mercedes Tirado M (1984) Dimensions of short, rodlike macromolecules from translational and rotational diffusion coefficients. Study of the gramicidin dimer. Biopolymers 23:611–615. doi:10.1002/bip.360230402
Tsvetkov VN, Eskin VE, Frenkel SY (1971) Structure of macromolecules in solution. National Lending Library for Science and Technology, Boston
Tsvetkov NV, Bushin SV, Bezrukova MA, Astapenko EP, Mikusheva NG, Lebedeva EV, Podseval’nikova AN, Khripunov AK (2013) Conformational and optical properties of macromolecules of some aliphatic-substituted cellulose esters. Cellulose 20:1057–1071. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-9913-7
Tvetkov VN, Andreeva LN, Tsvetkov NV (1999) Anisotropy of segments and monomer units of polymer molecules. In: Brandrup J, Immergut EH, Grulke E (eds) Polymer handbook, 4th edn. Wiley J & Sons, New York, pp. 745–763
Maxwell J (1873) A treatise on electricity and magnetism. Clarendon Press, Oxford
www.photocor.ru/dynals. Accessed 25 Oct 2006
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (project №16-13-10148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsvetkov, N.V., Lebedeva, E.V., Lezov, A.A. et al. Hydrodynamic and optical characteristics of hydrosols of cellulose nanocrystals. Colloid Polym Sci 295, 13–24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3975-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3975-7