Abstract
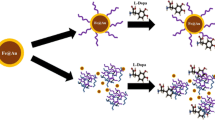
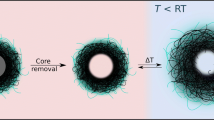
Here, a synthetic method has been optimized for the synthesis of thermoresponsive and pH-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) nanogels which are subsequently loaded with cytochrome C by using a modified breathing-in mechanism. Physico-chemical properties mapped by using dynamic light scattering (DLS) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) confirm the swelling/deswelling kinetics as reversible with a volume phase transition temperature (VPTT) of ~39 °C. Fe@Au nanoparticles were incorporated inside the nanogel networks by using two different methods: coating and in situ growth. The latter bears closer resemblance to the nanogels only, while the former follows the trend of bare Fe@Au nanoparticles. High loading (~96 %) and encapsulation (500 μg/mg of nanogels) of cytochrome C were obtained. Release experiments performed by using a dialysis set-up and monitored by using UV-vis spectroscopy show the highest release at 40 °C and pH 3.2 (high temperature, low pH), with maximum release from the Fe@Au-coated nanogels that also show a reverse swelling-collapse trend. The location of the drug, the incorporation and presence of Fe@Au nanoparticles and the drug incorporation method are found to control both the drug release mechanism and kinetics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du JZ et al. (2010) A tumor-acidity-activated charge-conversional nanogel as an intelligent vehicle for promoted tumoral-cell uptake and drug delivery. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 49(21):3621–3626
Tamura A, Oishi M, Nagasaki Y (2009) Enhanced cytoplasmic delivery of siRNA using a stabilized polyion complex based on PEGylated nanogels with a cross-linked polyamine structure. Biomacromolecules 10(7):1818–1827
Kabanov AV, Vinogradov SV (2009) Nanogels as pharmaceutical carriers: finite networks of infinite capabilities. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 48(30):5418–5429
Otero-Espinar FJ et al. (2010) Cyclodextrins in drug delivery systems. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 20(4):289–301
Matteucci ML, Thrall DE (2000) The role of liposomes in drug delivery and diagnostic imaging: a review. Veterinary Radiology & Ultrasound 41(2):100–107
Torchilin VP (2001) Structure and design of polymeric surfactant-based drug delivery systems. J Control Release 73(2–3):137–172
Chacko RT et al. (2012) Polymer nanogels: a versatile nanoscopic drug delivery platform. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(9):836–851
Nayak S, Lyon LA (2005) Soft nanotechnology with soft nanoparticles. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 44(47):7686–7708
Wang XH, Qiu XP, Wu C (1998) Comparison of the coil-to-globule and the globule-to-coil transitions of a single poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) homopolymer chain in water. Macromolecules 31(9):2972–2976
Constantin M et al. (2011) Lower critical solution temperature versus volume phase transition temperature in thermoresponsive drug delivery systems. Express Polym Lett 5(10):839–848
Bekhradnia S et al. (2014) Structure, swelling, and drug release of thermoresponsive poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. J Mater Sci 49(17):6102–6110
Pelton R (2000) Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 85(1):1–33
Wu X et al. (1994) The kinetics of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex formation. Colloid Polym Sci 272(4):467–477
Chen Y et al. (2014) Near-infrared emitting gold cluster-poly(acrylic acid) hybrid nanogels. ACS Macro Lett 3(1):74–76
Xiong W et al. (2011) Dual temperature/pH-sensitive drug delivery of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) nanogels conjugated with doxorubicin for potential application in tumor hyperthermia therapy. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces 84(2):447–453
Tannock IF, Rotin D, Acid P (1989) In tumors and its potential for therapeutic exploitation. Cancer Res 49(16):4373–4384
Bandyopadhyay S et al. (2014) Synthesis and in vitro cellular interactions of superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles with a crystalline gold shell. Appl Surf Sci 316:171–178
Jafari T, Simchi A, Khakpash N (2010) Synthesis and cytotoxicity assessment of superparamagnetic iron-gold core-shell nanoparticles coated with polyglycerol. J Colloid Interface Sci 345(1):64–71
Zhou T, Wu BY, Xing D (2012) Bio-modified Fe3O4 core/Au shell nanoparticles for targeting and multimodal imaging of cancer cells. J Mater Chem 22(2):470–477
Zhou SQ et al. (1995) Light-scattering-studies of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in tetrahydrofuran and aqueous-solution. Polymer 36(7):1341–1346
Slomkowski S et al. (2011) Terminology of polymers and polymerization processes in dispersed systems (IUPAC recommendations 2011. Pure Appl Chem 83(12):2229–2259
Singh N, Lyon LA (2007) Au nanoparticle templated synthesis of pNIPAm nanogels. Chem Mater 19(4):719–726
Blackburn WH et al. (2009) Peptide-functionalized nanogels for targeted siRNA delivery. Bioconjug Chem 20(5):960–968
Ni HM, Kawaguchi H, Endo T (2007) Characteristics of pH-sensitive hydrogel microsphere of poly(acrylamide-co-meth acrylic acid) with sharp pH-volume transition. Colloid Polym Sci 285(8):873–879
Chen LT, Weiss L (1973) Role of sinus wall in passage of erythrocytes through spleen. Blood 41(4):529–537
Choi HS et al. (2007) Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 25(10):1165–1170
Blackburn WH, Lyon LA (2008) Size-controlled synthesis of monodisperse core/shell nanogels. Colloid Polym Sci 286(5):563–569
Smith MH, Lyon LA (2012) Multifunctional nanogels for siRNA delivery. Acc Chem Res 45(7):985–993
Rahman A, Brown CW (1983) Effect of Ph on the critical micelle concentration of sodium dodecyl-sulfate. J Appl Polym Sci 28(4):1331–1334
Schild HG (1992) Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)—experiment, theory and application. Prog Polym Sci 17(2):163–249
Bromberg LE, Ron ES (1998) Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 31(3):197–221
Siegel RA (1990) Pulsed and self-regulated drug delivery. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Ni H, Kawaguchi H, Endo T (2007) Preparation of pH-sensitive hydrogel microspheres of poly(acrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) with sharp pH-volume transition. Colloid Polym Sci 285(7):819–826
Smith MH, Lyon LA (2011) Tunable encapsulation of proteins within charged microgels. Macromolecules 44(20):8154–8160
Fucinos C et al. (2014) Temperature-and pH-sensitive nanohydrogels of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) for food packaging applications: modelling the swelling-collapse behaviour. PLoS One 9(2)
Dumetz AC et al. (2007) Patterns of protein-protein interactions in salt solutions and implications for protein crystallization. Protein Sci 16(9):1867–1877
Skobeleva VB et al. (2001) Interaction of hydrogels of acrylic acid-acrylamide copolymers with cytochrome c. Polymer Science Series A 43(3):315–322
Siepmann J, Peppas NA (2011) Higuchi equation: derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int J Pharm 418(1):6–12
Brazel CS, Peppas NA (2000) Modeling of drug release from swellable polymers. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 49(1):47–58
Barzegar-Jalali M et al. (2008) Kinetic analysis of drug release from nanoparticles. J Pharm Pharm Sci 11(1):167–177
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank NorFab for financial support in connection to the use of NTNU Nanolab and the Faculty of Natural Sciences and Technology, NTNU for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 959 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandyopadhyay, S., Andersen, M.K., Alvi, M.A.A. et al. Incorporation of Fe@Au nanoparticles into multiresponsive pNIPAM-AAc colloidal gels modulates drug uptake and release. Colloid Polym Sci 294, 1929–1942 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3944-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3944-1