Abstract
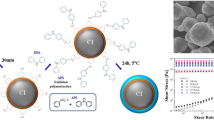
Core-shell structured soft magnetic carbonyl iron (CI) particles coated with poly(glycidyl methacrylate) were fabricated using a dispersion polymerization method. The surface of the CI particles was pretreated with 4-aminobenzoic acid to enhance the affinity between CI and poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA). The synthesized CI/PGMA core-shell particles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometry. The CI/PGMA particles were dispersed into a non-magnetic liquid for applications as a magnetorheological (MR) fluid, in which the rheological properties can be altered significantly by an external magnetic field. The MR suspension was analyzed using a rotational rheometer at various magnetic field strengths. Although the fabricated CI particles exhibited lower MR properties than pure CI particles, they showed improved dispersion stability according to the Turbiscan apparatus.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lopez-Lopez MT, Kuzhir P, Bossis G, Mingalyov P (2008) Preparation of well-dispersed magnetorheological fluids and effect of dispersion on their magnetorheological properties. Rheol Acta 47:787–796
Pu HT, Jiang FJ (2005) Towards high sedimentation stability: magnetorheological fluids based on CNT/Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 16:1486–1489
Claracq J, Sarrazin J, Montfort JP (2004) Viscoelastic properties of magnetorheological fluids. Rheol Acta 43:38–49
Tang X, Zhang X, Tao R, Rong YM (2000) Structure-enhanced yield stress of magnetorheological fluids. J Appl Phys 87:2634–2638
de Vicente J, Lopez-Lopez MT, Duran JDG, Gonzalez-Caballero F (2004) Shear flow behavior of confined magnetorheological fluids at low magnetic field strengths. Rheol Acta 44:94–103
Hagenbuchle M, Liu J (1997) Chain formation and chain dynamics in a dilute magnetorheological fluid. Appl Opt 36:7664–7671
de Vicente J, Klingenberg DJ, Hidalgo-Alvarez R (2011) Magnetorheological fluids: a review. Soft Matter 7:3701–3710
Sung JH, Cho MS, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2004) Electrorheology of semiconducting polymers. J Ind Eng Chem 10:1217–1229
Zhu XC, Jing XJ, Cheng L (2012) Magnetorheological fluid dampers: A review on structure design and analysis. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 23:839–873
Bica I, Liu YD, Choi HJ (2013) Physical characteristics of magnetorheological suspensions and their applications. J Ind Eng Chem 19:394–406
Shorey AB, Jacobs SD, Kordonski WI, Gans RF (2001) Experiments and observations regarding the mechanisms of glass removal in magnetorheological finishing. Appl Opt 40:20–33
Bombard AJF, Knobel M, Alcantara MR, Joekes I (2002) Evaluation of magnetorheological suspensions based on carbonyl iron powders. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 13:471–478
Ko SW, Lim JY, Park BJ, Yang MS, Choi HJ (2009) Magnetorheological carbonyl iron particles doubly wrapped with polymer and carbon nanotube. J Appl Phys 105: art. No. 07E703
Hayashi K, Sakamoto W, Yogo T (2013) One-pot synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles assembled on polysiloxane rod and their response to magnetic field. Colloid Polym Sci 291:2837–2842
Park BJ, Fang FF, Zhang K, Choi HJ (2010) Polymer-coated magnetic carbonyl iron microparticles and their magnetorheological characteristics. Korean J Chem Eng 27:716–722
Jiang WQ, Zhu H, Guo CY, Li JF, Xue Q, Feng JH, Gong XL (2010) Poly(methyl methacrylate)-coated carbonyl iron particles and their magnetorheological characteristics. Polym Int 59:879–883
Fang FF, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2009) Magnetorheology of soft magnetic carbonyl iron suspension with single-walled carbon nanotube additive and its yield stress scaling function. Colloids Surf A 351:46–51
Zhang WL, Choi HJ (2012) Graphene oxide added carbonyl iron microsphere system and its magnetorheology under applied magnetic fields. J Appl Phys 111: art. No. 07E724
de Vicente J, Lopez-Lopez MT, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Duran JDG (2003) Rheological study of the stabilization of magnetizable colloidal suspensions by addition of silica nanoparticles. J Rheol 47:1093–1109
Liu YD, Choi HJ, Choi SB (2012) Controllable fabrication of silica encapsulated soft magnetic microspheres with enhanced oxidation-resistance and their rheology under magnetic field. Colloids Surf A 403:133–138
Bombard AJF, Knobel M, Alcantara MR (2007) Phosphate coating on the surface of carbonyl iron powder and its effect in magnetorheological suspensions. Int J Mod Phys B 21:4858–4867
Mrlik M, Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Bazant P, Saha P, Peer P, Filip P (2013) Synthesis and magnetorheological characteristics of ribbon-like, polypyrrole-coated carbonyl iron suspensions under oscillatory shear. J Appl Polym Sci 128:2977–2982
Kim IG, Kim JE, Liu YD, Choi HJ (2012) Polyamide Coated Soft Magnetic Microspheres and Their Magnetorheology. IEEE Trans Magn 48:3446–3449
Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Saha P, Svrcinova P, Filip P, Stejskal J (2010) Rheological properties of magnetorheological suspensions based on core-shell structured polyaniline-coated carbonyl iron particles. Smart Mater Struct 19: art No. 115008
Fang FF, Choi HJ (2007) Polymeric nanobead coated carbonyl iron particles and their magnetic property. Phys Status Solidi A 204:4190–4193
Kim SY, Kwon SH, Liu YD, Lee JS, You CY, Choi HJ (2014) Core-shell-structured cross-linked poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-coated carbonyl iron microspheres and their magnetorheology. J Mater Sci 49:1345–1352
Fang FF, Liu YD, Choi HJ, Seo Y (2011) Core-Shell Structured Carbonyl Iron Microspheres Prepared via Dual-Step Functionality Coatings and Their Magnetorheological Response. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:3487–3495
Barbey R, Klok HA (2010) Room temperature, aqueous post-polymerization modification of glycidyl methacrylate-containing polymer brushes prepared via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Langmuir 26:18219–18230
Zhou WW, Zhu JX, Cheng CW, Liu JP, Yang HP, Cong CX, Guan C, Jia XT, Fan HJ, Yan QY, Li CM, Yu T (2011) A general strategy toward graphene@metal oxide core-shell nanostructures for high-performance lithium storage. Energ Environ Sci 4:4954–4961
Shanmugharaj AM, Yoon JH, Yang WJ, Ryu SH (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and surface wettability properties of amine functionalized graphene oxide films with varying amine chain lengths. J Colloid Interface Sci 401:148–154
Rahman AU, Iqbal M, Rahman FU, Fu DY, Yaseen M, Lv YQ, Omer M, Garver M, Yang L, Tan TW (2012) Synthesis and characterization of reactive macroporous poly(glycidyl methacrylate-triallyl isocyanurate-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) microspheres by suspension polymerization: Effect of synthesis variables on surface area and porosity. J Appl Polym Sci 124:915–926
Zhang WL, Piao SH, Choi HJ (2013) Facile and fast synthesis of polyaniline-coated poly(glycidyl methacrylate) core-shell microspheres and their electro-responsive characteristics. J Colloid Interface Sci 402:100–106
Shah K, Phu DX, Seong MS, Upadhyay RV, Choi SB (2014) A low sedimentation magnetorheological fluid based on platelike iron particles, and verification using a damper test. Smart Mater Struct 23: art. No. 027001
Chin BD, Park JH, Kwon MH, Park OO (2001) Rheological properties and dispersion stability of magnetorheological (MR) suspensions. Rheol Acta 40:211–219
de Vicente J, Ruiz-Lopez JA, Andablo-Reyes E, Segovia-Gutierrez JP, Hidalgo-Alvarez R (2011) Squeeze flow magnetorheology. J Rheol 55:753–779
Sari B, Yavas N, Makulogullari M, Erol O, Unal HI (2009) Synthesis, electrorheology and creep behavior of polyindole/polyethylene composites. React Funct Polym 69:808–815
Li WH, Du H, Guo NQ (2004) Dynamic behavior of MR suspensions at moderate flux densities. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct 371:9–15
Bell RC, Karli JO, Vavreck AN, Zimmerman DT, Ngatu GT, Wereley NM (2008) Magnetorheology of submicron diameter iron microwires dispersed in silicone oil. Smart Mater Struct 17: art. No. 015028
Hato MJ, Choi HJ, Sim HH, Park BO, Ray SS (2011) Magnetic carbonyl iron suspension with organoclay additive and its magnetorheological properties. Colloids Surf A 377:103–109
Li WH, Chen G, Yeo SH (1999) Viscoelastic properties of MR fluids. Smart Mater Struct 8:460–468
Li WH, Du HJ, Chen G, Yeo SH, Guo NQ (2003) Nonlinear viscoelastic properties of MR fluids under large-amplitude-oscillatory-shear. Rheol Acta 42:280–286
Buron H, Mengual O, Meunier G, Cayre I, Snabre P (2004) Optical characterization of concentrated dispersions: applications to laboratory analyses and on-line process monitoring and control. Polym Int 53:1205–1209
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (C. H. Hong) appreciates the financial support from Inha University, South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, W.J., Jung, H.S., Kwon, S.H. et al. Effect of surface treatment on magnetorheological characteristics of core-shell structured soft magnetic carbonyl iron particles. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 2647–2654 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3669-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3669-6