Abstract
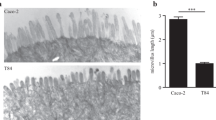
Although the intestinal mucosa forms a crucial barrier between the host and the environment, bacterial translocation (BT) occurs frequently in neonates and may be a source of sepsis. The intestinal mucous gel layer is thought to be a vital component of the gut barrier and is composed, in part, of a family of glycoproteins known as mucins. Our aim was to study the effects of mucin on BT in an enterocyte cell-culture model using a fetal (I-407) and an adult (Caco-2) intestinal cell line. I-407 and Caco-2 cells were grown to confluence on porous filters in a two-chamber Transwell system. The integrity of the monolayers was confirmed by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and permeability using the macromolecule dextran blue. Cells were treated with mucin (40 mg/ml) prior to inoculation of 1 × 106 Escherichia coli C25. The magnitude of BT was determined quantitatively by culturing the samples from the basal chamber of the wells and was expressed as log 10 [Colony Forming Units (CFU)/ml]. Statistical analysis was performed by the Mann-Whitney U test with statistical significance at P < 0.05. Mucin inhibited BT across both fetal and adult cultured enterocyte monolayers; however, the inhibitory effect was less on the fetal cells compared to the adult cells. Dextran-blue studies showed that monolayers were intact throughout the experiments. Despite 98% inhibition of BT, mucin had a statistically significant effect on post-bacterial inoculation TEER in Caco-2 cells and no effect in I-407 cells. The ability of mucin, a mucous-barrier glycoprotein, to inhibit BT across immature intestinal enterocytes, as in the neonate, may be diminished compared to mature adult enterocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gork, A., Usui, N., Ceriati, E. et al. The effect of mucin on bacterial translocation in I-407 fetal and Caco-2 adult enterocyte cultured cell lines. Pediatr Surg Int 15, 155–159 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003830050544
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003830050544