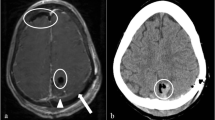
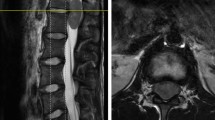
Abstract
Purpose
Craniopharyngioma is a common pediatric brain tumor, with a high rate of recurrence after primary treatment. This retrospective study investigated the effect of various primary treatments on surgical strategies and outcomes for recurrent craniopharyngiomas.
Methods
The study population comprised 35 children (mean age 8.77 years, range 1–16 years) with recurrent craniopharyngioma re-operated from January 1990 to January 2009. The recurrent craniopharyngiomas were excised whenever possible. For analysis, the patients were divided into four groups according to the primary treatment: radical tumor resection (A), incomplete tumor resection (B), radiotherapy + incomplete tumor resection (C), and Ommaya reservoir placement + incomplete tumor resection (D).
Results
Group B had a significantly shorter recurrence-free interval than groups A, C, or D. Outcomes were significantly different among the four groups. The hypothalamic status scores of groups A (2.38 ± 0.27) and C (2.28 ± 0.42) were significantly higher than that of group B (1.64 ± 0.20). There were no statistical differences between any two other groups.
Conclusions
In children, the primary treatments for craniopharyngioma should be considered when choosing the surgical strategy for recurrence. Radiotherapy before repeated surgery can result in a worse functional outcome and hypothalamic-pituitary function.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alen JF, Boto GR, Lagares A, de la Lama A, Gomez PA, Lobato RD (2002) Intratumoural bleomycin as a treatment for recurrent cystic craniopharyngioma. Case report and review of the literature. Neurocirugia (Astur) 13:479–485 discussion 485
Barua KK, Ehara K, Kohmura E, Tamaki N (2003) Treatment of recurrent craniopharyngiomas. Kobe J Med Sci 49:123–132
Caldarelli M, di Rocco C, Papacci F, Colosimo Jr C (1998) Management of recurrent craniopharyngioma. Acta Neurochir 140:447–454
Clark AJ, Cage TA, Aranda D, Parsa AT, Sun PP, Auguste KI, Gupta N (2013) A systematic review of the results of surgery and radiotherapy on tumor control for pediatric craniopharyngioma. Childs Nerv Syst 29:231–238. doi:10.1007/s00381-012-1926-2
De Vile CJ, Grant DB, Kendall BE, Neville BG, Stanhope R, Watkins KE, Hayward RD (1996) Management of childhood craniopharyngioma: can the morbidity of radical surgery be predicted? J Neurosurg 85:73–81. doi:10.3171/jns.1996.85.1.0073
Duff J, Meyer FB, Ilstrup DM, Laws Jr ER, Schleck CD, Scheithauer BW (2000) Long-term outcomes for surgically resected craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 46:291–302 discussion 302-295
Elliott RE, Hsieh K, Hochm T, Belitskaya-Levy I, Wisoff J, Wisoff JH (2010) Efficacy and safety of radical resection of primary and recurrent craniopharyngiomas in 86 children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:30–48. doi:10.3171/2009.7.PEDS09215
Elliott RE, Sands SA, Strom RG, Wisoff JH (2010) Craniopharyngioma clinical status scale: a standardized metric of preoperative function and posttreatment outcome. Neurosurg Focus 28:E2. doi:10.3171/2010.2.FOCUS09304
Fahlbusch R, Honegger J, Paulus W, Huk W, Buchfelder M (1999) Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: experience with 168 patients. J Neurosurg 90:237–250. doi:10.3171/jns.1999.90.2.0237
Fischer EG, Welch K, Shillito Jr J, Winston KR, Tarbell NJ (1990) Craniopharyngiomas in children. Long-term effects of conservative surgical procedures combined with radiation therapy. J Neurosurg 73:534–540. doi:10.3171/jns.1990.73.4.0534
Habrand JL, Ganry O, Couanet D, Rouxel V, Levy-Piedbois C, Pierre-Kahn A, Kalifa C (1999) The role of radiation therapy in the management of craniopharyngioma: a 25-year experience and review of the literature. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 44:255–263. doi:S0360-3016(99)00030–9
Hoffman HJ (1994) Surgical management of craniopharyngioma. Pediatr Neurosurg 21(Suppl 1):44–49
Hoffman HJ, De Silva M, Humphreys RP, Drake JM, Smith ML, Blaser SI (1992) Aggressive surgical management of craniopharyngiomas in children. J Neurosurg 76:47–52. doi:10.3171/jns.1992.76.1.0047
Kalapurakal JA, Goldman S, Hsieh YC, Tomita T, Marymont MH (2000) Clinical outcome in children with recurrent craniopharyngioma after primary surgery. Cancer J 6:388–393
Karavitaki N, Brufani C, Warner JT, Adams CB, Richards P, Ansorge O, Shine B, Turner HE, Wass JA (2005) Craniopharyngiomas in children and adults: systematic analysis of 121 cases with long-term follow-up. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62:397–409. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02231.x
Karavitaki N, Cudlip S, Adams CB, Wass JA (2006) Craniopharyngiomas. Endocr Rev 27:371–397. doi: 10.1210/er.2006-0002
Kim SK, Wang KC, Shin SH, Choe G, Chi JG, Cho BK (2001) Radical excision of pediatric craniopharyngioma: recurrence pattern and prognostic factors. Childs Nerv Syst 17:531–536 discussion 537
Minamida Y, Mikami T, Hashi K, Houkin K (2005) Surgical management of the recurrence and regrowth of craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosurg 103:224–232. doi:10.3171/jns.2005.103.2.0224
Moussa AH, Kerasha AA, Mahmoud ME (2013) Surprising outcome of Ommaya reservoir in treating cystic craniopharyngioma: a retrospective study. Br J Neurosurg 27:370–373. doi:10.3109/02688697.2012.741732
Niranjan A, Kano H, Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2010) Radiosurgery for craniopharyngioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:64–71. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1693
Qi S, Pan J, Lu Y, Gao F, Cao Y, Peng J, Zhang X (2012) The impact of the site of origin and rate of tumour growth on clinical outcome in children with craniopharyngiomas. Clin Endocrinol 76:103–110. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04172.x
Raimondi AJ, Rougerie J (1994) A critical review of personal experiences with craniopharyngioma: clinical history, surgical technique and operative results. 1983. Pediatr Neurosurg 21:134–150 discussion 151-134
Regine WF, Mohiuddin M, Kramer S (1993) Long-term results of pediatric and adult craniopharyngiomas treated with combined surgery and radiation. Radiother Oncol 27:13–21
Sands SA, Milner JS, Goldberg J, Mukhi V, Moliterno JA, Maxfield C, Wisoff JH (2005) Quality of life and behavioral follow-up study of pediatric survivors of craniopharyngioma. J Neurosurg 103:302–311. doi:10.3171/ped.2005.103.4.0302
Scott RM, Hetelekidis S, Barnes PD, Goumnerova L, Tarbell NJ (1994) Surgery, radiation, and combination therapy in the treatment of childhood craniopharyngioma—a 20-year experience. Pediatr Neurosurg 21(Suppl 1):75–81
Shapiro K, Till K, Grant DN (1979) Craniopharyngiomas in childhood. A rational approach to treatment. J Neurosurg 50:617–623. doi:10.3171/jns.1979.50.5.0617
Steno J, Bizik I, Steno A, Matejcik V (2014) Recurrent craniopharyngiomas in children and adults: long-term recurrence rate and management. Acta Neurochir 156:113–122 discussion 122. doi:10.1007/s00701-013-1938-z
Tomita T, McLone DG (1993) Radical resections of childhood craniopharyngiomas. Pediatr Neurosurg 19:6–14
Van Effenterre R, Boch AL (2002) Craniopharyngioma in adults and children: a study of 122 surgical cases. J Neurosurg 97:3–11. doi:10.3171/jns.2002.97.1.0003
Villani RM, Tomei G, Bello L, Sganzerla E, Ambrosi B, Re T, Giovanelli Barilari M (1997) Long-term results of treatment for craniopharyngioma in children. Childs Nerv Syst 13:397–405
Wisoff JH (1994) Surgical management of recurrent craniopharyngiomas. Pediatr Neurosurg 21(Suppl 1):108–113
Yasargil MG, Curcic M, Kis M, Siegenthaler G, Teddy PJ, Roth P (1990) Total removal of craniopharyngiomas. Approaches and long-term results in 144 patients. J Neurosurg 73:3–11. doi:10.3171/jns.1990.73.1.0003
Zuccaro G, Jaimovich R, Mantese B, Monges J (1996) Complications in paediatric craniopharyngioma treatment. Childs Nerv Syst 12:385–390 discussion 390-381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of ethics
The Medical Ethics Committee of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, approved this retrospective study.
Funding
This research was funded by the Guangdong Province Natural Science Funding (No. S2011010003063, S2012020010939), President Foundation of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University (2015C028) and the Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Binghui Qiu is a co-first author of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Y., Qiu, B., Qi, S. et al. Influence of previous treatments on repeat surgery for recurrent craniopharyngiomas in children. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 485–491 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-3003-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-3003-0