Abstract
Objective
Freehand placement of ventricular catheters (VC) is reported to be inaccurate in 10–40 %. Endoscopy, ultrasound, or neuronavigation are used in selected cases with significant technical and time-consuming efforts. We suggest a smartphone-assisted guiding tool for the placement of VC.
Methods
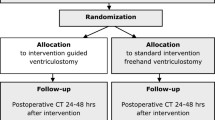
Measurements of relevant parameters in 3D-MRI datasets in a patient cohort with narrow ventricles for a frontal precoronal VC placement were performed. In this context, a guiding tool was developed to apply the respective measures for VC placement. The guiding tool was tested in a phantom followed by CT imaging to quantify placement precision. A smartphone application was designed to assist the relevant measurements. The guide was applied in 35 patients for VC placement.
Results
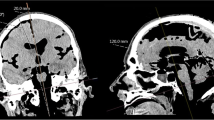
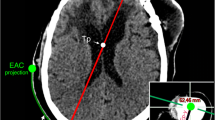
MRI measurements revealed the rectangular approach in the sagittal plane and the individual angle towards the tangent in the coronal section as relevant parameter for a frontal approach. The latter angle ranged from medial (91.96° ± 2.75°) to lateral margins (99.56° ± 4.14°) of the ventricle, which was similar in laterally shifted (±5 mm) entry points. The subsequently developed guiding tool revealed precision measurements in an agarose model with 1.1° ± 0.7° angle deviation. Using the smartphone-assisted guide in patients with narrow ventricles (frontal occipital horn ratio, 0.38 ± 0.05), a primary puncture of the ventricles was possible in all cases. No VC failure was observed during follow-up (9.1 ± 5.3 months).
Conclusions
VC placement in narrow ventricles requires accurate placement with simple means in an every-case routine. The suggested smartphone-assisted guide meets these criteria. Further data are planned to be collected in a prospective randomized study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdoh MG, Bekaert O, Hodel J, Diarra SM, Le Guerinel C, Nseir R, Bastuji-Garin S, Decq P (2012) Accuracy of external ventricular drainage catheter placement. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154(1):153–159
Abu-Serieh B, Ghassempour K, Duprez T, Raftopoulos C (2007) Stereotactic ventriculoperitoneal shunting for refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 60(6):1039–1043
Azeem SS, Origitano TC (2007) Ventricular catheter placement with a frameless neuronavigational system: a 1-year experience. Neurosurgery 60(4 Suppl 2):243–247
Di Rocco C, Marchese E, Velardi F (1994) A survey of the first complication of newly implanted CSF shunt devices for the treatment of nontumoral hydrocephalus. Cooperative survey of the 1991–1992 Education Committee of the ISPN. Childs Nerv Syst 10(5):321–327
Ghajar JB (1985) A guide for ventricular catheter placement. Technical note. J Neurosurg 63(6):985–986
Giese H, Hoffmann KT, Winkelmann A, Stockhammer F, Jallo GI, Thomale UW (2010) Precision of navigated stereotactic probe implantation into the brainstem. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5(4):350–359
Harris CA, McAllister JP 2nd (2012) What we should know about the cellular and tissue response causing catheter obstruction in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery Jun 70(6):1589–1601
Hayhurst C, Beems T, Jenkinson MD, Byrne P, Clark S, Kandasamy J, Goodden J, Nandoe Tewarie RD, Mallucci CL (2010) Effect of electromagnetic-navigated shunt placement on failure rates: a prospective multicenter study. J Neurosurg Dec 113(6):1273–1278
Hermann EJ, Capelle HH, Tschan CA, Krauss JK (2012) Electromagnetic-guided neuronavigation for safe placement of intraventricular catheters in pediatric neurosurgery. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 10:327–333
Hsieh CT, Chen GJ, Ma HI, Chang CF, Cheng CM, Su YH, Ju DT, Hsia CC, Chen YH, Wu HY, Liu MY (2011) The misplacement of external ventricular drain by freehand method in emergent neurosurgery. Acta Neurol Belg 111(1):22–28
Huyette DR, Turnbow BJ, Kaufman C, Vaslow DF, Whiting BB, Oh MY (2008) Accuracy of the freehand pass technique for ventriculostomy catheter placement: retrospective assessment using computed tomography scans. J Neurosurg 108(1):88–91
Kakarla UK, Kim LJ, Chang SW, Theodore N, Spetzler RF (2008) Safety and accuracy of bedside external ventricular drain placement. Neurosurgery 63(1 Suppl 1):ONS162-6
Kandasamy J, Hayhurst C, Clark S, Jenkinson MD, Byrne P, Karabatsou K, Mallucci CL (2011) Electromagnetic stereotactic ventriculoperitoneal csf shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a successful step forward? World Neurosurg 75(1):155–160
Kestle JR, Drake JM, Cochrane DD, Milner R, Walker ML, Abbott R 3rd, Boop FA (2003) Endoscopic Shunt Insertion Trial participants. Lack of benefit of endoscopic ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion: a multicenter randomized trial. J Neurosurg 98(2):284–290
Knaus H, Abbushi A, Hoffmann KT, Schwarz K, Haberl H, Thomale UW (2009) Measurements of burr-hole localization for endoscopic procedures in the third ventricle in children. Childs Nerv Syst 25(3):293–299
Leonardo J, Hanel RA, Grand W (2009) Endoscopic tracking of a ventricular catheter for entry into the lateral ventricle: technical note. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 52(5–6):287–289
Lind CR, Tsai AM, Lind CJ, Law AJ (2009) Ventricular catheter placement accuracy in non-stereotactic shunt surgery for hydrocephalus. J Clin Neurosci 16(7):918–920
Lind CR, Correia JA, Law AJ, Kejriwal R (2008) A survey of surgical techniques for catheterising the cerebral lateral ventricles. J Clin Neurosci 15(8):886–890
Lollis SS, Roberts DW (2008) Robotic catheter ventriculostomy: feasibility, efficacy, and implications. J Neurosurg 108(2):269–274
O'Neill BR, Velez DA, Braxton EE, Whiting D, Oh MY (2008) A survey of ventriculostomy and intracranial pressure monitor placement practices. Surg Neurol 70(3):268–273
Phillips SB, Gates M, Krishnamurthy S (2012) Strategic placement of bedside ventriculostomies using ultrasound image guidance: report of three cases. Neurocrit Care 17(2):255–259
Rehman T, Rehman AU, Rehman A, Bashir HH, Ali R, Bhimani SA, Khan S (2012) A US-based survey on ventriculostomy practices. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114(6):651–654
Reig AS, Stevenson CB, Tulipan NB (2010) CT-based, fiducial-free frameless stereotaxy for difficult ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion: experience in 26 consecutive patients. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 88(2):75–80
Roth J, Constantini S (2012) Selective use of intra-catheter endoscopic-assisted ventricular catheter placement: indications and outcome. Childs Nerv Syst 28(8):1163–1169
Sainte-Rose C, Piatt JH, Renier D, Pierre-Kahn A, Hirsch JF, Hoffman HJ, Humphreys RP, Hendrick EB (1991) Mechanical complications in shunts. Pediatr Neurosurg 17(1):2–9
Saladino A, White JB, Wijdicks EF, Lanzino G (2009) Malplacement of ventricular catheters by neurosurgeons: a single institution experience. Neurocrit Care 10(2):248–252
Sampath R, Wadhwa R, Tawfik T, Nanda A, Guthikonda B (2012) Stereotactic placement of ventricular catheters: does it affect proximal malfunction rates? Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 90(2):97–103
Schulz M, Bohner G, Knaus H, Haberl H, Thomale UW (2010) Navigated endoscopic surgery for multiloculated hydrocephalus in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5(5):434–442
Sekula RF, Cohen DB, Patek PM, Jannetta PJ, Oh MY (2008) Epidemiology of ventriculostomy in the United States from 1997 to 2001. Br J Neurosurg 22(2):213–218
Stieglitz LH, Giordano M, Samii M, Luedemann WO (2010) A new tool for frameless stereotactic placement of ventricular catheters. Neurosurgery 67(3 Suppl Operative):ons131–ons135
Strowitzki M, Komenda Y, Eymann R, Steudel WI (2008) Accuracy of ultrasound-guided puncture of the ventricular system. Childs Nerv Syst 24(1):65–69
Thomale UW, Hosch H, Koch A, Schulz M, Stoltenburg G, Haberl EJ, Sprung C (2010) Perforation holes in ventricular catheters—is less more? Childs Nerv Syst 26(6):781–789
Thomale UW, Schlosser HG, Sprung C (2006) A simple solution for navigated placement of CSF catheters in slit-like or displaced ventricles. GMS CURAC 1:Doc 5, http://www.egms.de/de/journals/curac/2006-1/curac000005.shtml
Toma AK, Camp S, Watkins LD, Grieve J, Kitchen ND (2009) External ventricular drain insertion accuracy: is there a need for change in practice? Neurosurgery 65(6):1197–1200
Wan KR, Toy JA, Wolfe R, Danks A (2011) Factors affecting the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement. J Clin Neurosci 18(4):485–488
Whitehead WE, Jea A, Vachhrajani S, Kulkarni AV, Drake JM (2007) Accurate placement of cerebrospinal fluid shunt ventricular catheters with real-time ultrasound guidance in older children without patent fontanelles. J Neurosurg 107(5 Suppl):406–410
Villavicencio AT, Leveque JC, McGirt MJ, Hopkins JS, Fuchs HE, George TM (2003) Comparison of revision rates following endoscopically versus nonendoscopically placed ventricular shunt catheters. Surg Neurol 59(5):375–379
Vinchon M, Rekate HL, Kulkarni AV (2012) Pediatric hydrocephalus outcomes: a review. Fluids Barriers CNS 9(1):18
Yamada SM, Yamada S, Goto Y, Nakaguchi H, Murakami M, Hoya K, Matsuno A (2012) A simple and consistent technique for ventricular catheter insertion using a tripod. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114(6):622–626
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomale, U.W., Knitter, T., Schaumann, A. et al. Smartphone-assisted guide for the placement of ventricular catheters. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 131–139 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1943-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1943-1