Abstract
Background
External ventricular drainage (EVD) is a freehand neurosurgical procedure performed routinely using the anatomical landmarks.
Objective
The aim of this study was to determine the accuracy of EVD catheter freehand placement.
Materials and methods
Pre-operative and post-operative computed tomography scans for 66 consecutive EVDs performed in 56 adult patients (26 men, 30 women) in 2008 were retrospectively reviewed. Etiologies of acute hydrocephalus were subarachnoid or intraventricular haemorrhage (43 cases) or miscellaneous (13 cases). Pre-operative lateral ventricular volume, position of the burr hole, length of the catheter and its sagittal and coronal angular variations from a theoretical trajectory were measured.
Results
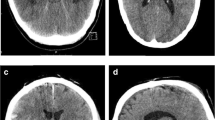
The EVD was placed on the right (53 cases) or left (13 cases) side. The mean pre-operative lateral ventricular volume was 51 cc (10–118 cc). The average distance from the burr hole to the midline was 28 mm (10–49 mm) and to the supra-orbital ridge was 101 mm (75–125 mm). The mean intracranial catheter length was 60 mm (from 39–102 mm). Only 50% of the EVDs in the coronal plane and 40% in the sagittal plane were placed with an angular variation of ±5° to the target. The tip was placed outside of the ventricles in three cases; 13 catheters crossed the midline, and five intracranial minor haemorrhages were detected.
Conclusion
Freehand placement of EVDs does not have sufficient accuracy and may lead to drainage dysfunctions. This data suggests that a guidance system for EVD’s would be required.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RC, Kan P, Klimo P, Brockmeyer DL, Walker ML, Kestle JR (2004) Complications of intracranial pressure monitoring in children with head trauma. J Neurosurg 101:53–58
Bogdahn U, Lau W, Hassel W, Gunreben G, Mertens HG, Brawanski A (1992) Continuous-pressure controlled external ventricular drainage for treatment of acute hydrocephalus: evaluation of risk factors. Neurosurgery 31:898–904
Daniel D, Binz L, Gerard T, Jonathan A, Friedman (2009) Hemorrhagic complications of ventriculostomy placement: a meta-analysis. Neurocrit Care 10(2):253–256
Dunn IF, Fierichs K, Day A, Kim DH (2006) Ventriculostomy. In: Schmidek HH, Robert DW (eds) Schmidek and Sweet, Operative neurosurgical techniques: indications, methods, and results, 5th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 35–36
Ehtisham A, Taylor S, Bayless L, Klein M, Janzen J (2009) Placement of external ventricular drains and intracranial pressure monitors by neurointensivists. Neurocrit Care 10(2):241–247
Hayhurst C, Beems T, Jenkinson MD, Byrne P, Clark S, Samy JK, Goodden J, Tewarie R, Mallucci C (2010) Effect of electromagnetic-navigated shunt placement on failure rates: a prospective multicenter study. J Neurosurg 113(6):1273–1278
Huyette DR, Turnbow BJ, Kaufman C, Vaslow D, Whiting B, Michael Y (2008) Accuracy of the freehand pass technique for ventriculostomy catheter placement: retrospective assessment using computed tomography scans. J Neurosurg 108(1):88–91
Jamshid BG, Ghajar MD (1985) A guide for ventricular catheter placement. J Neurosurg 63:985–986
Kakarla K, Chang W, Theodore N, Spetzler F, Kim J (2008) Safety and accuracy of bedside external ventricular drain placement. Neurosurgery 63(1 Suppl 1):ONS162–ONS167
Khanna RK, Rosenblum ML, Rock JP, Malik GM (1995) Prolonged external ventricular drainage with percutaneous long-tunnel ventriculostomies. J Neurosurg 83:791–794
Krötz M, Linsenmaier U, Kanz KG, Pfeifer KJ, Mutschler W, Reiser M (2004) Evaluation of minimally invasive percutaneous CT-controlled ventriculostomy in patients with severe head trauma. Eur Radiol 14:227–233
O’Hayon BB, Drake JM, Ossip MG, Tuli S, Clarke M (1998) Frontal and occipital horn ratio: a linear estimate of ventricular size for multiple imaging modalities in pediatric hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:245–249
O’Leary ST, Kole MK, Hoover DA, Hysell SE, Thomas A, Shaffrey CI (2000) Efficacy of the Ghajar Guide revisited. J Neurosurg 92:801–803
Saladino A, Bradley W, Eelco F, Wijdicks M, Giuseppe L (2009) Malplacement of ventricular catheters by neurosurgeons. Neurocrit Care 10(2):155–156
Scheithauer S, Burgel U, Ryang Y-M, Koch S, Schiefer J, Hafner H, Haase G, Lemmen S (2009) Prospective surveillance of drain-associated meningitis/ventriculitis in a neurosurgery and a neurologic intensive care unit. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1381–1385
Stangl AP, Meyer B, Zentner J, Schramm J (1998) Continuous external CSF drainage: a perpetual problem in neurosurgery. Surg Neurol 50:77–82
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdoh, M.G., Bekaert, O., Hodel, J. et al. Accuracy of external ventricular drainage catheter placement. Acta Neurochir 154, 153–159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1136-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1136-9