Abstract
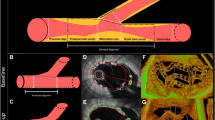
Overlapping implantation of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds is frequently necessary, but its influence on vessel and scaffold structure has not been thoroughly analyzed previously. The aim of this study was to analyze the acute effects of overlapping implantation on BRS as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT). A total of 38 patients with de novo coronary artery stenoses who underwent OCT in the context of implantation of novolimus-eluting BRS (DESolve, Elixir Medical Corporation, Sunnyvale, California, USA) were investigated. In 15 patients, overlapping implantation of two BRS was performed, while 23 patients with implantation of one single BRS served as the control group. OCT data were retrospectively analyzed regarding acute scaffold implantation results. There were no significant differences between the overlap and control group in terms of residual in-scaffold area stenosis, scaffold area, mean or minimal lumen area, eccentricity index, incomplete scaffold apposition area or malapposition. While strut fracture was slightly more frequent in BRS with overlap its incidence was low overall. In patients with overlapping BRS, overlap segments did not display smaller lumen areas than segments without overlap (mean lumen area overlap: 8.16 ± 2.97 mm2 vs. no overlap: 7.70 ± 2.55 mm2; p = 0.71; minimal lumen area overlap: 6.83 ± 2.71 mm2 vs. no overlap: 6.17 ± 2.58 mm2; p = 0.37). Acute mechanical performance of novolimus-eluting BRS is not impaired by overlapping implantation. It can be assumed that vessel expansion compensates for the double scaffold layer in the overlap area resulting in a similar lumen area in overlap areas and in those with a single strut layer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kereiakes DJ, Wang H, Popma JJ, Kuntz RE, Donohoe DJ, Schofer J, Schampaert E, Meier B, Leon MB, Moses JW (2006) Periprocedural and late consequences of overlapping Cypher sirolimus-eluting stents: pooled analysis of five clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:21–31
O’Sullivan CJ, Stefanini GG, Räber L, Heg D, Taniwaki M, Kalesan B, Pilgrim T, Zanchin T, Moschovitis A, Büllesfeld L, Khattab AA, Meier B, Wenaweser P, Jüni P, Windecker S (2014) Impact of stent overlap on long-term clinical outcomes in patients treated with newer-generation drug-eluting stents. EuroIntervention 9:1076–1084
Räber L, Jüni P, Löffel L, Wandel S, Cook S, Wenaweser P, Togni M, Vogel R, Seiler C, Eberli F, Lüscher T, Meier B, Windecker S (2010) Impact of stent overlap on angiographic and long-term clinical outcome in patients undergoing drug-eluting stent implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1178–1188
Farooq V, Vranckx P, Mauri L, Cutlip DE, Belardi J, Silber S, Widimsky P, Leon M, Windecker S, Meredith I, Negoita M, van Leeuwen F, Neumann FJ, Yeung AC, Garcia-Garcia HM, Serruys PW (2013) Impact of overlapping newer generation drug-eluting stents on clinical and angiographic outcomes: pooled analysis of five trials from the international Global RESOLUTE Program. Heart 99:626–633
Kimura T, Kozuma K, Tanabe K, Nakamura S, Yamane M, Muramatsu T, Saito S, Yajima J, Hagiwara N, Mitsudo K, Popma JJ, Serruys PW, Onuma Y, Ying S, Cao S, Staehr P, Cheong WF, Kusano H, Stone GW, Japan Investigators ABSORB (2015) A randomized trial evaluating everolimus-eluting Absorb bioresorbable scaffolds vs. everolimus-eluting metallic stents in patients with coronary artery disease: ABSORB Japan. Eur Heart J 36:3332–3342
Serruys PW, Chevalier B, Dudek D, Cequier A, Carrié D, Iniguez A, Dominici M, van der Schaaf RJ, Haude M, Wasungu L, Veldhof S, Peng L, Staehr P, Grundeken MJ, Ishibashi Y, Garcia-Garcia HM, Onuma Y (2015) A bioresorbable everolimus-eluting scaffold versus a metallic everolimus-eluting stent for ischaemic heart disease caused by de-novo native coronary artery lesions (ABSORB II): an interim 1-year analysis of clinical and procedural secondary outcomes from a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 385:43–54
Sabaté M, Windecker S, Iñiguez A, Okkels-Jensen L, Cequier A, Brugaletta S, Hofma SH, Räber L, Christiansen EH, Suttorp M, Pilgrim T, Anne van Es G, Sotomi Y, García-García HM, Onuma Y, Serruys PW (2016) Everolimus-eluting bioresorbable stent vs. durable polymer everolimus-eluting metallic stent in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: results of the randomized ABSORB ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction-TROFI II trial. Eur Heart J 37:229–240
Dörr O, Liebetrau C, Wiebe J, Hecker F, Rixe J, Möllmann H, Hamm C, Nef H (2015) Bioresorbable scaffolds for the treatment of in-stent restenosis. Heart Vessels 30:265–269
Toušek P, Kočka V, Malý M, Lisa L, Buděšínský T, Widimský P (2016) Neointimal coverage and late apposition of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable scaffolds implanted in the acute phase of myocardial infarction: OCT data from the PRAGUE-19 study. Heart Vessels 31:841–845
Ishibashi Y, Nakatani S, Sotomi Y, Suwannasom P, Grundeken MJ, Garcia-Garcia HM, Bartorelli AL, Whitbourn R, Chevalier B, Abizaid A, Ormiston JA, Rapoza RJ, Veldhof S, Onuma Y, Serruys PW (2015) Relation between bioresorbable scaffold sizing using QCA-Dmax and clinical outcomes at 1 year in 1,232 patients from 3 study cohorts (ABSORB Cohort B, ABSORB EXTEND, and ABSORB II). JACC Cardiovasc Interv 8:1715–1726
Serruys PW, Onuma Y, Ormiston JA, de Bruyne B, Regar E, Dudek D, Thuesen L, Smits PC, Chevalier B, McClean D, Koolen J, Windecker S, Whitbourn R, Meredith I, Dorange C, Veldhof S, Miquel-Hebert K, Rapoza R, García-García HM (2010) Evaluation of the second generation of a bioresorbable everolimus drug-eluting vascular scaffold for treatment of de novo coronary artery stenosis: six-month clinical and imaging outcomes. Circulation 122:2301–2312
Mattesini A, Boeder N, Löblich K, Valente S, Foin N, Caiazzo G, Ghione M, Gensini GF, Italo P, Di Mario C, Nef H (2016) Absorb Vs DESolve: an optical coherence tomography comparison of acute mechanical performances. EuroIntervention 12:566–573
Mattesini A, Secco GG, Dall’Ara G, Ghione M, Rama-Merchan JC, Lupi A, Viceconte N, Lindsay AC, De Silva R, Foin N, Naganuma T, Valente S, Colombo A, Di Mario C (2014) ABSORB biodegradable stents versus second-generation metal stents: a comparison study of 100 complex lesions treated under OCT guidance. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 7:741–750
Farooq V, Serruys PW, Heo JH, Gogas BD, Onuma Y, Perkins LE, Diletti R, Radu MD, Räber L, Bourantas CV, Zhang Y, van Remortel E, Pawar R, Rapoza RJ, Powers JC, van Beusekom HM, Garcìa-Garcìa HM, Virmani R (2013) Intracoronary optical coherence tomography and histology of overlapping everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in a porcine coronary artery model: the potential implications for clinical practice. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 6:523–532
Verheye S, Ormiston JA, Stewart J, Webster M, Sanidas E, Costa R, Costa JR Jr, Chamie D, Abizaid AS, Pinto I, Morrison L, Toyloy S, Bhat V, Yan J, Abizaid A (2014) A next-generation bioresorbable coronary scaffold system: from bench to first clinical evaluation: 6- and 12-month clinical and multimodality imaging results. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 7:89–99
Everaert B, Felix C, Koolen J, den Heijer P, Henriques J, Wykrzykowska J, van der Schaaf R, de Smet B, Hofma S, Diletti R, Van Mieghem N, Regar E, Smits P, van Geuns RJ (2015) Appropriate use of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in percutaneous coronary interventions: a recommendation from experienced users: a position statement on the use of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in the Netherlands. Neth Heart J 23:161–165
Tamburino C, Latib A, van Geuns RJ, Sabate M, Mehilli J, Gori T, Achenbach S, Alvarez MP, Nef H, Lesiak M, Di Mario C, Colombo A, Naber CK, Caramanno G, Capranzano P, Brugaletta S, Geraci S, Araszkiewicz A, Mattesini A, Pyxaras SA, Rzeszutko L, Depukat R, Diletti R, Boone E, Capodanno D, Dudek D (2015) Contemporary practice and technical aspects in coronary intervention with bioresorbable scaffolds: a European perspective. EuroIntervention 11:45–52
Wiebe J, Nef HM, Hamm CW (2014) Current status of bioresorbable scaffolds in the treatment of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:2541–2551B
Biscaglia S, Secco GG, Tumscitz C, Di Mario C, Campo G (2015) Optical coherence tomography evaluation of overlapping everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold implantation guided by enhanced stent visualization system. Int J Cardiol 182:1–3
Biscaglia S, Campo G, Tebaldi M, Tumscitz C, Pavasini R, Fileti L, Secco GG, Di Mario C, Ferrari R (2016) Bioresorbable vascular scaffold overlap evaluation with optical coherence tomography after implantation with or without enhanced stent visualization system (WOLFIE study): a two-centre prospective comparison. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32:211–223
Ishibashi Y, Muramatsu T, Nakatani S, Sotomi Y, Suwannasom P, Grundeken MJ, Cho YK, Garcia-Garcia HM, van Boven AJ, Piek JJ, Sabaté M, Helqvist S, Baumbach A, McClean D, de Sousa Almeida M, Wasungu L, Miquel-Hebert K, Dudek D, Chevalier B, Onuma Y, Serruys PW (2015) Incidence and potential mechanism(s) of post-procedural rise of cardiac biomarker in patients with coronary artery narrowing after implantation of an everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold or everolimus-eluting metallic stent. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 8:1053–1063
Ortega-Paz L, Capodanno D, Giacchi G, Gori T, Nef H, Latib A, Caramanno G, Di Mario C, Naber C, Lesiak M, Capranzano P, Wiebe J, Mehilli J, Araszkiewicz A, Pyxaras S, Mattesini A, Geraci S, Naganuma T, Colombo A, Münzel T, Sabaté M, Tamburino C, Brugaletta S (2016) Impact of overlapping on 1-year clinical outcomes in patients undergoing everolimus-eluting bioresorbable scaffolds implantation in routine clinical practice: Insights from the European multicenter GHOST-EU registry. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. doi:10.1002/ccd.26674. [Epub ahead of print]
Bourantas CV, Papafaklis MI, Kotsia A, Farooq V, Muramatsu T, Gomez-Lara J, Zhang YJ, Iqbal J, Kalatzis FG, Naka KK, Fotiadis DI, Dorange C, Wang J, Rapoza R, Garcia-Garcia HM, Onuma Y, Michalis LK, Serruys PW (2014) Effect of the endothelial shear stress patterns on neointimal proliferation following drug-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold implantation: an optical coherence tomography study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 7:315–324
Bourantas CV, Papafaklis MI, Lakkas L, Sakellarios A, Onuma Y, Zhang YJ, Muramatsu T, Diletti R, Bizopoulos P, Kalatzis F, Naka KK, Fotiadis DI, Wang J, Garcia Garcia HM, Kimura T, Michalis LK, Serruys PW (2014) Fusion of optical coherence tomographic and angiographic data for more accurate evaluation of the endothelial shear stress patterns and neointimal distribution after bioresorbable scaffold implantation: comparison with intravascular ultrasound-derived reconstructions. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 30:485–494
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Holger Nef received speaking honoraria and a research grant (to institution) from Elixir Medical. All other authors have no potential conflict of interest. There are no relationships with industry regarding this study.
Additional information
F. Blachutzik and N. Boeder contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blachutzik, F., Boeder, N., Wiebe, J. et al. Overlapping implantation of bioresorbable novolimus-eluting scaffolds: an observational optical coherence tomography study. Heart Vessels 32, 781–789 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0932-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0932-9