Abstract
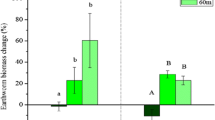
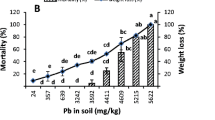
The survival and cast production of the tropical endogeic earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus and the changes in chemical and physical characteristics induced by gut passage were studied over an 80-day period in soils contaminated with different levels of Pb. The soils were from a Pb mining area in the state of Paraná, SE Brazil, and ranged from clayey to sandy texture and total Pb contents from 52 to 9,716 mg kg−1. In soils with the highest total Pb contents, earthworms showed lower survival rates, reduced biomass, high Pb uptake, and negligible cast production. In soils with low to intermediate total Pb (maximum 4,278 mg kg−1), earthworm survival and cast production were higher, biomass loss was lower, and gut passage increased pH, CEC, P, K+, and Mg2+ concentrations in the casts compared to the control soil. In the sandy soil (clay <176 g kg−1), worms preferentially ingested finer soil particles, increasing organic C and silt contents in casts. However, this selective feeding also resulted in higher Pb accumulation in worm tissues. Gut passage also increased water-dispersible clay and reduced flocculation in the casts, increasing the susceptibility of the soil to erosion. Lead contamination and uptake into the tissues did not limit the ability of earthworms to select finer soil particles and to transform soil chemical and physical properties, although it affected cast production rates and survival (especially at high Pb concentrations).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barois I, Lavelle P (1986) Changes in respiration rate and some physicochemical properties of a tropical soil during transit through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae, Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 18:539–541
Barois I, Verdier B, Kaiser P, Mariotti A, Rangel P, Lavelle P (1987) Influence of the tropical earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae) on the fixation and mineralization of nitrogen. In: Pagliai AMB, Omodeo P (eds) On earthworms. Mucchi Editore, Modena, pp 151–158
Barois I, Villemin G, Lavelle P, Toutain F (1993) Transformation of the soil structure through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Oligochaeta) intestinal tract. Geoderma 56:57–66
Barois I, Lavelle P, Brossard M, Tondoh J, Martinez M, Rossi J, Senapati B, Angeles A, Fragoso C, Jimenez J, Decaëns T, Lattaud C, Kanonyo J, Blanchart E, Chapuis L, Brown GG, Moreno AG (1999) Ecology of earthworm species with large environmental tolerance and or extended distributions. In: Lavelle P, Brussaard L, Hendrix P (eds) Earthworms management in tropical agroecosystems. CABI International, Wallingford, pp 57–85
Bartz MLC, Costa ACS, Tormena CA, Souza IG Jr, Brown GG (2010) Sobrevivência, produção e atributos químicos de coprólitos de minhocas em um Latossolo vermelho distroférrico (Oxisol) sob diferentes sistemas de manejo. Acta Zool Mex 26:261–280
Blanchart E, Albrecht A, Brown GG, Decäens T, Duboisset A, Lavelle P, Mariani L, Roose E (2004) Effects of tropical endogeic earthworms on soil erosion: a review. Agric Ecosyst Environ 104:303–315
Brown GG, James SW, Pasini A, Nunes DH, Benito N, Martins PT, Sautter KD (2006) Exotic, peregrine, and invasive earthworms in Brazil: diversity, distribution, and effects on soils and plants. Carib J Sci 42:339–358
Buch AC, Brown GG, Niva CC, Sautter KD, Lourençato LF (2011) Life cycle of Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae) in tropical artificial soil. Pedobiologia 53S:19–25
Caro G, Abourachid A, Decaëns T, Buono L, Mathieu J (2012) Is earthworms’ dispersal facilitated by the ecosystem engineering activities of conspecifics? Biol Fertil Soils 48:961–965
Chapuis L, Brossard M (1995) Modifications et stabilité du phosphore échangeable d’un ferralsol ingéré par un ver géophage. CR Acad Sci Paris 320:587–592
Chapuis-Lardy L, Brossard M, Lavelle P, Schouller E (1998) Phosphorus transformations in a ferralsol through ingestion by Pontoscolex corethrurus, a geophagous earthworm. Eur J Soil Biol 34:61–67
Chauvel A, Grimaldi M, Barros E, Blanchart E, Sarrazin M, Lavelle P (1999) Pasture degradation by an Amazonian earthworm. Nature 389:32–33
Davies NA, Hodson ME, Black S (2003) The influence of time on lead toxicity and bioaccumulation determined by the OECD earthworm toxicity test. Environ Pollut 121:55–61
Depkat-Jakob PS, Hunger S, Schulz K, Brown GG, Tsai SM, Drake HL (2012) Emission of methane by Eudrilus eugeniae and other earthworms from Brazil. Appl Environ Microbiol 7949:1–6
Duarte AP, Melo VF, Brown GG, Pauletti V (2012) Changes in the forms of lead and manganese in soils by passage through the gut of the tropical endogeic earthworm (Pontoscolex corethrurus). Eur J Soil Biol 53:32–39
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996) Biology and ecology of earthworms, 3rd edn. Chapman & Hall, London
Emerson WW, Chi CL (1977) Exchangeable calcium, magnesium and sodium and the dispersion of illites in water. II. Dispersion of illites in water. Aust J Soil Res 15:255–262
Ernst G, Zimmermann S, Christie P, Frey B (2008) Mercury, cadmium and lead concentrations in different ecophysiological groups of earthworms in forest soils. Environ Pollut 156:1304–1313
Gates GE (1973) Contributions to North American earthworms (Annelida), no. 6. Contributions to a revision of the earthworm family Glossoscolecidae I. Pontoscolex corethrurus (Müller, 1857). Bull Tall Timbers Res Station 14:1–12
Gee G, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis: part 1—physical and mineralogical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 383–411
Hobbelen PHF, Koolhaas JE, van Gestel CAM (2006) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa in relation to total and available metal concentrations in field soils. Environ Pollut 144:639–646
Hue NV, Evans CE (1986) Procedures used for soil and plant analysis by the Auburn University soil testing laboratory no. 106. Department of Agronomy and Soils, Auburn
Huerta EL, Fragoso C, Barois I, Lavelle P (2005) Enhancement of growth and reproduction of the tropical earthworm Polypheretima elongata (Megascolecidae) by addition of Zea mays and Mucuna pruriens var. utilis litter to the soil. Eur J Soil Biol 41:45–53
Jusselme MD, Poly F, Miambi E, Mora P, Blouin M, Pando A, Rouland-Lefèvre C (2012) Effect of earthworms on plant Lantana camara Pb-uptake and on bacterial communities in root-adhering soil. Sci Total Environ 416:200–207
Kale RD, Krishnamoorthy RV (1980) The calcium content of the body tissues and castings of earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus. Pedobiologia 20:309–315
Kizilkaya R (2004) Cu and Zn accumulation in earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. in sewage sludge amended soil and fractions of Cu and Zn in casts and surrounding soil. Ecol Eng 22:141–151
Lattaud C, Locati S, Mora P, Rouland C, Lavelle P (1998) The diversity of digestive systems in tropical geophagous earthworms. Appl Soil Ecol 9:189–195
Lavelle P, Rangel P, Kanyonyo J (1983) Intestinal mucus production by two species of tropical earthworms: Millsonia lamtoiana (Megascolecidae) and Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae). In: Lebrun P, Medts A, Grégoire-Wibo C, Wauthy G (eds) New trends in soil biology. Louvain la Neuve, Dieu-Brichart, pp 405–410
Lavelle P, Barois I, Cruz I, Fragoso C, Hernandez A, Pineda A, Rangel P (1987) Adaptive estrategies of Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolicidae, Oligochaeta), a peregrine geophagous earthworm of the humid tropics. Biol Fertil Soils 5:188–194
Lee KE (1985) Earthworms: their ecology and relationships with soils and land use. Academic Press, Sydney
Leveque T, Capowiez Y, Schreck E, Mazzia C, Auffan M, Foucault Y, Austruy A, Dumat C (2013) Assessing ecotoxicity and uptake of metals and metalloids in relation to two different earthworm species (Eiseina hortensis and Lumbricus terrestris). Environ Pollut 179:232–241
Li L, Wu J, Tian G, Xu Z (2009) Effect of the transit through the gut of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) on fractionation of Cu and Zn in pig manure. J Hazard Mater 167:634–640
Li H, Wang C, Li X, Christie P, Dou Z, Zhang J, Xiang D (2013) Impact of the earthworm Aporrectodea trapezoides and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices on 15N uptake by maize from wheat straw. Biol Fertil Soils 49:263–271
Lim CH, Jackson ML (1986) Dissolution for total elemental analysis. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1–12
López-Hernández D, Lavelle P, Fardeau JC, Niño M (1993) Phosphorous transformations in two P-sorption contrasting tropical soils during transit through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae, Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 25:789–792
Lukkari T, Teno S, Väisänen A, Haimi J (2006) Effects of earthworms on decomposition and metal availability in contaminated soil: microcosm studies of populations with different exposure histories. Soil Biol Biochem 38:359–370
Marhan S, Scheu S (2005) Effects of sand and litter availability on organic matter decomposition in soil and in casts of Lumbricus terrestris L. Geoderma 128:155–166
Marichal R, Martinez AF, Praxedes C, Ruiz D, Carvajal AF, Oszwald J, Pilar Hurtado M, Brown GG, Grimaldi M, Desjardins T, Sarrazin M, Decaëns T, Velázquez E, Lavelle P (2010) Invasion of Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae, Oligochaeta) in landscapes of the Amazonian deforestation. Appl Soil Ecol 46:443–449
Marichal R, Grimaldi M, Mathieu J, Brown GG, Desjardins T, Silva ML Jr, Praxedes C, Martins M, Velázquez E, Lavelle P (2012) Is invasion of deforested Amazonia by the earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus driven by soil properties? Pedobiologia 55:233–240
Morgan JE, Morgan AJ (1998) The distribution and intracellular compartmentation of metals in the endogeic earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa sampled from an unpolluted and metal-contaminated site. Environ Pollut 99:167–175
Müller F (1857) Lumbricus corethrurus, Burstenschwanz. Archiv fur Naturg 23:6–113
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) Effects of metals on life cycle parameters of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to field-contaminated, metal-polluted soils. Environ Pollut 149:44–58
Nannoni F, Protano G, Riccobono F (2011) Uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy elements by two earthworm species from a smelter contaminated area in northern Kosovo. Soil Biol Biochem 43:2359–2367
Righi G (1984) Pontoscolex (Oligochaeta, Glossoscolecidae) a new evaluation. Stud Neotropical Fauna Environ 19:159–177
Sanderson P (2008) Ecotoxicological testing of lead contaminated soil using a multispecies soil system. Division of Information Technology, Engineering and the Environment, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes Campus (Bachelors of Applied Science Honours)
Sizmur T, Hodson ME (2009) Do earthworms impact metal mobility and availability in soil?—A review. Environ Pollut 157:1981–1989
Sizmur T, Palumbo-Roe B, Watts MJ, Hodson ME (2011) Impact of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (L.) on As, Cu, Pb and Zn mobility and speciation in contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159:742–748
Soil Taxonomy (1999) A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. United States Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No 436, Washington
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1996) Effects of variations of the organic matter content and pH of soils on the availability and toxicity of zinc on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Pedobiologia 40:80–96
Suzuki Y, Matsubara T, Hoshino M (2003) Breakdown of mineral grains by earthworms and beetle larvae. Geoderma 112:131–142
Trigo D, Barois I, Garvin MH, Huerta E, Irisson S, Lavelle P (1999) Mutualism between earthworms and soil microflora. Pedobiologia 43:866–873
Udovic M, Lestan D (2007) The effect of earthworms on the fractionation and bioavailability of heavy metals before and after soil remediation. Environ Pollut 148:663–668
Udovic M, Plavc Z, Lestan D (2007) The effect of earthworms on the fractionation, mobility and bioavailability of Pb, Zn and Cd before and after soil leaching with EDTA. Chemosphere 70:126–134
Wu B, Liu Z, Xu Y, Li D, Li M (2012) Combined toxicity of cadmium and lead on the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 81:122–126
Zorn MI, van Gestel CAM, Eijsackers H (2005) The effect of two endogeic earthworm species on zinc distribution and availability in artificial soil columns. Soil Biol Biochem 37:917–925
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, A.P., Melo, V.F., Brown, G.G. et al. Earthworm (Pontoscolex corethrurus) survival and impacts on properties of soils from a lead mining site in Southern Brazil. Biol Fertil Soils 50, 851–860 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0906-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0906-y