Abstract
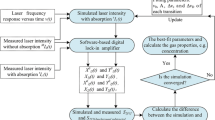
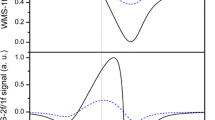
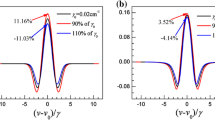
We introduce the basics of an apodized 2f/1f wavelength modulation method for the spectroscopy of the R(9) transition line in the first overtone band of carbon monoxide (12C16O) in near-infrared (NIR) region around 2.33 μm. Performance of the method is investigated for high gas concentrations beyond the optically thin limit to generalize common 2f/1f wavelength modulation spectroscopy (WMS) reported by Rieker et al. (Appl Opt 48:5546, [28]). Numerical simulations are performed based on real experimental parameters associated with a NIR spectrometer designed in our laboratory. The results primarily show a more linear response and less error than occurred in the common WMS-2f/1f method for an optically thick sample. It is also theoretically shown that the apodized method enables sharpening the spectrum without peak displacement compared to the common WMS-2f/1f method. The validity of the method is verified experimentally by the trace detection of an air-broadened R(9) CO absorption line centered at 4,294.637 cm−1 at atmospheric pressure and room temperature. The effect of a so-called scaling k-factor on the sharpening of WMS-2f/1f signal is investigated through trace simulation and detection of CO and methane (CH4) lines in the scanning range of a distributed feedback laser. The obtained results show very good agreement between simulation and experiment.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.S. Rothman, D. Jacquemart, A. Barbe, D. Chris Benner, M. Birk, L. Brown, M. Carleer, C. Chackerian Jr, K. Chance, L.H. Coudert, The HITRAN2004 molecular spectroscopic database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 96, 139–204 (2005)
H.W. Siesler, Y. Ozaki, S. Kawata, H.M. Heise, Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: Principles, Instruments, Applications (Wiley, New York, 2008)
X. Zhou, X. Liu, J.B. Jeffries, R. Hanson, Development of a sensor for temperature and water concentration in combustion gases using a single tunable diode laser. Meas. Sci. Technol. 14, 1459 (2003)
M. Gondal, A. Dastageer, M. Shwehdi, Photoacoustic spectrometry for trace gas analysis and leak detection using different cell geometries. Talanta 62, 131–141 (2004)
E.L. Izake, Forensic and homeland security applications of modern portable Raman spectroscopy. Forensic Sci. Int. 202, 1–8 (2010)
J. Wiss, C. Fleury, U. Onken, Safety improvement of chemical processes involving azides by online monitoring of the hydrazoic acid concentration. Org. Process Res. Dev. 10, 349–353 (2006)
S. Colak, M. Van der Mark, G. t Hooft, J. Hoogenraad, E. Van der Linden, F. Kuijpers, Clinical optical tomography and NIR spectroscopy for breast cancer detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 5, 1143–1158 (1999)
D.I. Ellis, R. Goodacre, Metabolic fingerprinting in disease diagnosis: biomedical applications of infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 131, 875–885 (2006)
D. Sands, Diode Lasers (Taylor & Francis, New York, 2010)
E. Zucker, in LEOS’99. IEEE Lasers and Electro-Optics Society 1999 12th Annual Meeting. High power diode lasers (IEEE, 1999), pp 72–73
Y. Li, W. Yuen, G. Li, C. Chang-Hasnain, Top-emitting micromechanical VCSEL with a 31.6-nm tuning range. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 10, 18–20 (1998)
J. Faist, F. Capasso, D.L. Sivco, C. Sirtori, A.L. Hutchinson, A.Y. Cho, Quantum cascade laser. Science 264, 553–556 (1994)
J. Faist, Quantum Cascade Lasers (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2013)
S. Wang, Principles of distributed feedback and distributed Bragg-reflector lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 10, 413–427 (1974)
M.G. Allen, Diode laser absorption sensors for gas-dynamic and combustion flows. Meas. Sci. Technol. 9, 545 (1998)
S. Babin, D. Churkin, A. Ismagulov, S. Kablukov, M. Nikulin, Single frequency single polarization DFB fiber laser. Laser Phys. Lett. 4, 428 (2007)
T. Cai, G. Wang, H. Jia, W. Chen, X. Gao, Temperature and water concentration measurements in combustion gases using a DFB diode laser at 1.4 μm. Laser Phys. 18, 1133–1142 (2008)
M. Andersson, L. Persson, T. Svensson, S. Svanberg, Flexible lock-in detection system based on synchronized computer plug-in boards applied in sensitive gas spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 113107 (2007)
G.B. Rieker, Wavelength-Modulation Spectroscopy for Measurements of Gas Temperature and Concentration in Harsh Environments (BiblioBazaar, 2011)
S. Schilt, L. Thevenaz, P. Robert, Wavelength modulation spectroscopy: combined frequency and intensity laser modulation. Appl. Opt. 42, 6728–6738 (2003)
H. Li, G.B. Rieker, X. Liu, J.B. Jeffries, R.K. Hanson, Extension of wavelength-modulation spectroscopy to large modulation depth for diode laser absorption measurements in high-pressure gases. Appl. Opt. 45, 1052–1061 (2006)
B.D. Cannon, Reducing of Residual Amplitude Modulation in Frequency-Modulated Signals, U.S. Patent 7,230,712, 2007
D.T. Cassidy, J. Reid, Atmospheric pressure monitoring of trace gases using tunable diode lasers. Appl. Opt. 21, 1185–1190 (1982)
L.S. Chang, J.B. Jeffries, R.K. Hanson, Mass flux sensing via tunable diode laser absorption of water vapor. AIAA J. 48, 2687–2693 (2010)
K. Duffin, A.J. McGettrick, W. Johnstone, G. Stewart, D.G. Moodie, Tunable diode-laser spectroscopy with wavelength modulation: a calibration-free approach to the recovery of absolute gas absorption line shapes. J. Lightwave Technol. 25, 3114–3125 (2007)
A.J. McGettrick, K. Duffin, W. Johnstone, G. Stewart, D.G. Moodie, Tunable diode laser spectroscopy with wavelength modulation: a phasor decomposition method for calibration-free measurements of gas concentration and pressure. J. Lightwave Technol. 26, 432–440 (2008)
L.S. Chang, C.L. Strand, J.B. Jeffries, R.K. Hanson, G.S. Diskin, R.L. Gaffney, D.P. Capriotti, Supersonic mass-flux measurements via tunable diode laser absorption and nonuniform flow modeling. AIAA J. 49, 2783–2791 (2011)
G.B. Rieker, J.B. Jeffries, R.K. Hanson, “Calibration-free wavelength-modulation spectroscopy for measurements of gas temperature and concentration in harsh environments. Appl. Opt. 48, 5546–5560 (2009)
P. Kluczynski, O. Axner, Theoretical description based on Fourier analysis of wavelength-modulation spectrometry in terms of analytical and background signals. Appl. Opt. 38, 5803–5815 (1999)
L. Jiang, J. Sislian, Velocity and density measurements in supersonic high-temperature exhaust plumes. AIAA J. 36, 1216–1222 (1998)
J.F. Becker, T.B. Sauke, M. Loewenstein, Stable isotope analysis using tunable diode laser spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 31, 1921–1927 (1992)
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge partial supports by the Mobarakeh Steel Company through grant 48222675 and the Shahid Montazeri power plant through grant 880/3050/110. We also wish to acknowledge the office of graduate studies at the university of Isfahan for their support and research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinzadeh Salati, S., Khorsandi, A. Apodized 2f/1f wavelength modulation spectroscopy method for calibration-free trace detection of carbon monoxide in the near-infrared region: theory and experiment. Appl. Phys. B 116, 521–531 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5728-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5728-3