Abstract
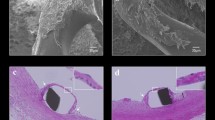
Although metallic stents are effective in preventing acute occlusion and reducing late restenosis after coronary angioplasty, many concerns still remain. In this report, short-term effects of fully bioabsorbable sirolimus-loaded poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA) stents (Xinsorb) were evaluated in a porcine coronary model. Commercially available PLLA-coated sirolimus-eluting stents (Excel) were used as controls. The purpose of this study was to assess technical feasibility, biocompatibility, and impact on coronary stenosis of fully bioabsorbable PLLA stents. Our preliminary experience suggested that Xinsorb stents have succeeded in preventing elastic recoil and suppressing neointimal formation for the first 90 days and only mildly delayed the endothelialisation process of the stented blood vessel. Coronary stenosis following Xinsorb and Excel stent implantations after 30 and 90 days was 18.6 ± 5.2% versus 21.4 ± 7.2% and 24.5 ± 4.7% versus 27.7 ± 5.6%, respectively (p > 0.05). Both Xinsorb and Excel stents required approximately 1–3 months for re-endothelialization of the inner wall of stented blood vessels. These data provided additional insights into the mechanism and efficacy of fully bioabsorbable PLLA stents in normal porcine coronary arteries while raising questions regarding the potential durability of this novel medical device. Long-term follow-up will be required to validate the long-term efficacy of fully bioabsorbable PLLA stents.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sousa JE, Costa MA, Sousa AGMR (2003) Two-year angiographic and intravascular ultrasound follow-up after implantation of sirolimus-eluting stents in human coronary arteries. Circulation 107:381–383
Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA (2004) A polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting stent inpatients with coronary arteries diseases. New Eng J Med 350:221–231
Serruys PW, Kutryk KJ, Ong AT (2006) Coronary-artery stents. N Engl J Med 354:483–495
Tamai H, Igaki K, Kyo E et al (2000) Initial and 6-month results of biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents in humans. Circulation 102:399–404
Serruys PW, Ormiston JA, Onuma Y et al (2009) A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system (ABSORB): 2-year outcomes and results from multiple imaging methods. Lancet 373:897–910
Mintz GS, Popma JJ, Pichard AD et al (1996) Arterial remodeling after coronary angioplasty: a serial intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation 94:35–43
Joner M, Finn AV, Farb A et al (2006) Pathology of drug-eluting stents in humans: delayed healing and late thrombotic risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:193–202
Luscher TF, Steffel J, Eberli FR et al (2007) Drug-eluting stent and coronary thrombosis: biologicalmechanisms and clinical implications. Circulation 115:1051–1058
Kotani J, Awata M, Nanto S et al (2006) Incomplete neointimal coverage of sirolimus-eluting stents: angioscopic findings. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:2108–2111
Hofma SH, van der Giessen WJ, van Dalen BM et al (2006) Indication of long-term endothelial dysfunction after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Eur Heart J 27:166–170
Ako J, Morino Y, Honda Y et al (2005) Late incomplete stent apposition after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: a serial intravascular ultrasound analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:1002–1005
Wilson GJ, Nakazawa G, Schwartz RS et al (2009) Comparison of inflammatory response after implantation of sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents in porcine coronary arteries. Circulation 120:141–149
Balla S, Aggarwall K, Nistala R (2010) Bioabsorbable coronary stents—are these the next big thing in coronary angioplasty? Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov 5:86–90
Kimura T, Yokoi H, Nakagawa Y et al (1996) Three-year follow-up after implantation of metallic coronary-artery stents. N Engl J Med 334:561–566
Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Regar E et al (2008) A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): a prospective open-label trial. Lancet 371:899–907
Ormiston JA, Webster MWI, Armstrong G (2007) First-in-human implantation of a fully bioabsorbable drug-eluting stent: the BVS poly-l-lactic acid everolimus-eluting coronary stent. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 69:128–131
Bünger CM, Grabow N, Christina Kröger C et al (2006) Iliac anastomotic stenting with a sirolimus-eluting biodegradable poly-l-lactide stent: a preliminary study after 6 weeks. J Endovasc Ther 13:630–639
Onuma Y, Serruys PW, Perkins LEL et al (2010) Intracoronary optical coherence tomography and histology at 1 month and 2, 3, and 4 years after implantation of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in a porcine coronary artery model an attempt to decipher the human optical coherence tomography images in the ABSORB trial. Circulation 122:2288–2300
Bünger CM, Grabow N, Sternberg K (2007) Sirolimus-eluting biodegradable poly-l-lactide stent for peripheral vascular application: a preliminary study in porcine carotid arteries. J Surg Res 139:77–82
Marx SO, Jayaraman T, Go LO et al (1995) Rapamycin-FKBP inhibits cell cycle regulators of proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 76:412–417
Huang YY, Venkatraman SS, Boey FYC et al (2010) In vitro and in vivo performance of a dual drug-eluting stent (DDES). Biomaterials 31:4382–4391
Schwartz RS, Huber KC, Murphy JG et al (1991) Restenosis and the proportional neointimal response to coronary artery injury: results in a porcine model. J Am Coll Cardiol 19:267–274
Cartera AJ, Aggarwalb M, Kopiac GA et al (2004) Long-term effects of polymer-based, slow-release, sirolimus-eluting stents in a porcine coronary model. Cardiovasc Res 63:617–624
Gong FR, Cheng XY, Wang SF et al (2009) Biodegradable comb-dendritic tri-block copolymers consisting of poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(l-lactide): synthesis, characterizations, and regulation of surface morphology and cell responses. Polymer 50:2775–2785
Joner M, Nakazawa G, Finn AV et al (2008) Endothelial cell recovery between comparator polymer-based drug-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:333–342
Finn AV, Kolodgie FD, Harnek J et al (2005) Differential response of delayed healing and persistent inflammation at sites of overlapping sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation 112:270–278
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB503905), The Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China (11441900300, 11441900900), and funded by Shandong Huaan Biotechnology Co., Ltd, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Shen and Qibing Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Wang, Q., Wu, Y. et al. Short-term effects of fully bioabsorbable PLLA coronary stents in a porcine model. Polym. Bull. 68, 1171–1181 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0682-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0682-x