Abstract
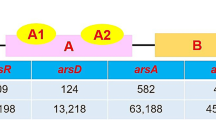
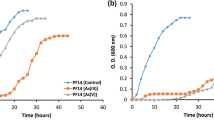
Nutrient availability in nature influenced the microbial ecology and behavior present in existing environment. In this study, we have focused on isolation of arsenic-oxidizing cultures from arsenic devoid environment and studied effect of carbon starvation on rate of arsenite oxidation. In spite of the absence of arsenic, a total of 40 heterotrophic, aerobic, arsenic-transforming bacterial strains representing 18 different genera were identified. Nineteen bacterial species were isolated from tannery effluent and twenty-one from tannery soil. A strong co-relation between the carbon starvation and arsenic oxidation potential of the isolates obtained from the said niche was observed. Interestingly, low carbon content enhanced the arsenic oxidation ability of the strains across different genera in Proteobacteria obtained. This represents the impact of physiological response of carbon metabolism under metal stress conditions. Enhanced arsenic-oxidizing ability of the strains was validated by the presence of aio gene and RT-PCR, where 0.5- to 26-fold up-regulation of arsenite oxidase gene in different genera was observed. The cultures isolated from tannery environment in this study show predominantly arsenic oxidation ability. This detoxification of arsenic in lack of carbon content can aid in effective in situ arsenic bioremediation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achour AR, Bauda P, Billard P (2007) Diversity of arsenite transporter genes from arsenic-resistant soil bacteria. Res Microbiol 158:128–137
Ackermann J, Vetterlein D, Tanneberg H, Neue HU, Mattusch J, Jahn R (2008) Speciation of arsenic under dynamic conditions. Eng Life Sci 8:589–597
Amy PS, Morita RY (1983) Protein patterns of growing and starved cells of a marine Vibrio sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1748–1752
Anderson CR, Cook GM (2004) Isolation and characterization of arsenate-reducing bacteria from arsenic-contaminated sites in New Zealand. Curr Microbiol 48:341–347
Bachate SP, Khapare RM, Kodam KM (2012) Oxidation of arsenite by two beta-proteobacteria isolated from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:2135–2145
Cai L, Liu G, Rensing C, Wang G (2009) Genes involved in arsenic transformation and resistance associated with different levels of arsenic-contaminated soils. BMC Microbiol 9:4
Codispoti L (1989) Phosphorous vs. nitrogen limitation of new and export production. In: Berger W, Smetacek V, Wefer G (eds) Productivity of the ocean: present and past. Wiley, Chichester, pp 377–394
Cullen WR, Reimer KJ (1989) Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem Rev 89:713–764
Duquesne K, Lieutaud A, Ratouchniak J, Muller D, Lett MC, Bonnefoy V (2008) Arsenite oxidation by a chemoautotrophic moderately acidophilic Thiomonas sp.: from the strain isolation to the gene study. Environ Microbiol 10:228–237
Ehrlich HL (2002) Bacterial oxidation of As(III) compounds. In: Frankenberger Jr. WT (ed) Environmental chemistry of arsenic. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, pp 313–328
Gihring TM, Bond PL, Peters SC, Banfield JF (2003) Arsenic resistance in the archaeon “Ferroplasma acidarmanus”: new insights into the structure and evolution of the ars genes. Extremophiles 7:123–130
Herman D, Costerton J (1993) Starvation-survival of p-nitrophenol degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:340–343
Hood MA, Guckert JB, White DC, Deck F (1986) Effect of nutrient deprivation on lipid, carbohydrate, DNA, RNA and protein levels in Vibrio cholera. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:788–793
Hsieh CY, Tsai MH, Ryan DK, Pancorbo OC (2004) Toxicity of the 13 priority pollutant metals to Vibrio fisheri in the Microtox chronic toxicity test. Sci Total Environ 320:37–50
Inskeep WP, Macur RE, Hamamura N, Warelow TP, Ward SA, Santini JM (2007) Detection, diversity and expression of aerobic bacterial arsenite oxidase genes. Environ Microbiol 9:934–943
Jackson CR, Dugas SL, Harrison KG (2005) Enumeration and characterization of arsenate-resistant bacteria in arsenic free soils. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2319–2322
Jackson CR, Harrison KG, Dugas SL (2005) Enumeration and characterization of culturable arsenate resistant bacteria in a large estuary. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:727–734
Jenkins DE, Chaisson SA, Matin A (1990) Starvation induce cross protection against osmotic challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 172:2779–2781
Jenkins DE, Schultz JE, Matin A (1988) Starvation induced cross protection against heat or H2O2 challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:3910–3914
Johnson DR, Park J, Kokor JJ, Abriola LM (2006) Effect of carbon starvation on toluene degradation activity by toluene monooxygenase-expressing bacteria. Biodegradation 17:437–445
Koechler S, Cleiss-Arnold J, Proux C, Sismeiro O, Dillies MA, Goulhen-Chollet F, Hommais F, Lièvremont D, Arsène-Ploetze F, Coppée JY, Bertin PN (2010) Multiple controls affect arsenite oxidase gene expression in Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans. BMC Microbiol 10:53
Leung KT, Moore M, Lee H, Trevors JT (2005) Effect of carbon starvation on p-nitrophenol degradation by a Moraxella strain in buffer and river water. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51:237–245
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Macur RE, Jackson CR, Botero LM, McDermott TR, Inskeep WP (2004) Bacterial populations associated with the oxidation and reduction of arsenic in an unsaturated soil. Environ Sci Technol 38:104–111
Macur RE, Wheeler JT, McDermott TR, Inskeep WP (2001) Microbial populations associated with the reduction and enhanced mobilization of arsenic in mine tailings. Environ Sci Technol 35:3676–3682
Morita RY (1993) Bioavailability of energy and the starvation state. In: Kjelleberg S (ed) Starvation in bacteria. Springer, New York, pp 1–18
Novitsky JA, Morita RY (1976) Morphological characterization of small cells resulting from nutrient starvation of a psychrophilic marine Vibrio. Appl Environ Microbiol 32:617–622
Oremland RS, Hoeft SE, Santini JM, Bano N, Hollibaugh RA, Hollibaugh JT (2002) Anaerobic oxidation of arsenite in Mono Lake water and by a facultative, arsenite-oxidizing chemoautotroph, strain MLHE-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4795–4802
Pepi M, Volterrani M, Renzi M, Marvasi M, Gasperini S, Franchi E (2007) Arsenic-resistant bacteria isolated from contaminated sediments of the Orbetello Lagoon, Italy, and their characterization. J Appl Microbiol 103:2299–2308
Quemeneur M, Heinrich-Salmeron A, Muller D, Lievremont D, Jauzein M, Bertin PN, Garrido F, Joulian C (2008) Diversity surveys and evolutionary relationships of aoxB genes in aerobic arsenite-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4567–4573
Sahu RK, Katiyar S, Tiwari J, Kisku GC (2007) Assessment of drain water receiving effluent from tanneries and its impact on soil and plants with particular emphasis on bioaccumulation of heavy metals. J Environ Biol 28:685–690
Salmassi TM, Venkateswaren K, Satomi M, Newman DK, Hering JG (2002) Oxidation of arsenite by Agrobacterium albertimagni, AOL15, sp. nov., isolated from Hot Creek, California. Geomicrobiol J 19:53–66
Santini JM, Sly LI, Schnagl RD, Macy JM (2000) A new chemolithoautotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a gold mine: phylogenetic, physiological and preliminary biochemical studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:92–97
Schmidt TM (2006) The maturing of microbial ecology. Int Microbiol 9:217–223
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Villegas-Torres MF, Bedoya-Reina OC, Salazar C, Vives-Florez MJ, Dussan J (2011) Horizontal arsC gene transfer among microorganisms isolated from arsenic polluted soil. Int Biodeter Biodegr 65: 147–152
Watson SP, Clements MO, Foster SJ (1998) Characterization of the starvation-survival response of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 180:1750–1758
Acknowledgements
The authors VSN and SPB would like to thank University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for Senior Research Fellowship and D. S. Kothari postdoctoral fellowship, respectively. We also thank Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility, Indian Institute of Technology-Bombay (SAIF, IIT-B) for elemental analysis. This work at Savitribai Phule Pune University was supported by University Grants Commission, New Delhi, and University with Potential for Excellence (UPE-II).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandre, V.S., Bachate, S.P., Salunkhe, R.C. et al. Enhanced Detoxification of Arsenic Under Carbon Starvation: A New Insight into Microbial Arsenic Physiology. Curr Microbiol 74, 614–622 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1203-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1203-4