Abstract
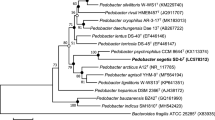
A Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped, motile, non-spore-forming bacterial strain, designated 13-QT, was isolated from seaside soil under the stacks of the red algae in Hainan province in China. Identification was carried out on the basis of polyphasic taxonomy. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain 13-QT belonged to the genus Pedobacter, and the highest similarity was 94.4 % with Pedobacter terricola KCTC 12876T. Strain 13-QT was able to grow at 10–40 °C, in pH 5.0–10.0, in the presence of 0–2.0 % NaCl. The major fatty acids were iso-C15:0 (40.4 %), summed feature 3 (comprising iso-C15:0 2-OH and/or C16:1 ω7c) (18.9 %) and iso-C17:0 3-OH (18.4 %). The predominant menaquinone was MK-7. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 42.7 mol%. Strain 13-QT could be distinguished from the nearest phylogenetic neighbors by various chemotaxonomic and phenotypic properties. The results of the polyphasic analyses suggested that strain 13-QT should be considered to represent a novel species of the genus Pedobacter, for which the name Pedobacter hainanensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is 13-QT (=CCTCC AB 2012076T = NRRL B-59850T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LB:
-
Luria-Bertani agar
- MA:
-
Marine agar 2216
- NA:
-
Nutrient agar
- TSA:
-
Trypticase soy agar
- TSB:
-
Trypticase soy broth
References
Steyn PL, Segers P, Vancanneyt M, Sandra P, Kersters K, Joubert JJ (1998) Classification of heparinolytic bacteria into a new genus, Pedobacter, comprising four species: Pedobacter heparinus comb, nov., Pedobacter piscium comb. nov., Pedobacter africanus sp. nov. and Pedobacter saltans sp. nov. Proposal of the family Sphingobacteriaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 48:165–177
Kim MK, Na JR, Cho DH, Soung NK, Yang DC (2007) Pedobacter koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1336–1341
Yoon JH, Lee MH, Kang SJ, Park SY (2006) Pedobacter sandarakinus sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1273–1277
Gordon NS, Valenzuela A, Adams SM, Ramsey PW, Pollock JL, Holben WE, Gannon JE (2009) Pedobacter nyackensis sp. nov., Pedobacter alluvionis sp. nov. and Pedobacter borealis sp. nov., isolated from Montana flood-plain sediment and forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1720–1726
Jeon Y, Kim JM, Park JH, Lee SH, Seong CH, Lee SS, Jeon CO (2009) Pedobacter oryzae sp. nov., isolated from rice paddy soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2491–2495
Kwon SW, Kim BY, Lee KH, Jang KY, Seok SJ, Kwon JS, Kim WG, Weon HY (2007) Pedobacter suwonensis sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:480–484
Kwon SW, Son JA, Kim SJ, Kim YS, Park IC, Bok JI, Weon HY (2011) Pedobacter rhizosphaerae sp. nov. and Pedobacter soli sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2874–2879
Margesin R, SprÖer C, Schumann P, Schinner F (2003) Pedobacter cryoconitis sp. nov., a facultative psychrophile from alpine glacier cryoconite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1291–1296
Shivaji S, Chaturvedi P, Reddy DS, Suresh K (2005) Pedobacter himalayensis sp. nov., from the Hamta glacier located in the Himalayan mountain ranges of India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1083–1088
Luo XS, Wang Z, Dai J et al (2010) Pedobacter glucosidilyticus sp. nov, isolated from dry riverbed soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:229–233
Michel G, Pojasek K, Li YG, Sulea T, Linhardt RJ, Raman R, Prabhakar V, Sasisekharan R, Cygler M (2004) The structure of chondroitin B lyase complexed with glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides unravels a calcium-dependent catalytic machinery. J Biol Chem 31:32882–32896
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York
Dojka MA, Hugenholtz P, Haack SK, Pace NR (1998) Microbial diversity in a hydrocarbon and chlorinated-solvent-contaminated aquifer undergoing intrinsic bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3869–3877
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stercher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Buck JD (1982) Non-staining (KOH) method for determination of Gram reactions of marine-bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:992–993
Carson LA, Favero MS, Bond WW, Petersen NJ (1973) Morphological, biochemical, and growth characteristics of Pseudomonas cepacia from distilled water. Appl Microbiol 25:476–483
Lee HG, Kim SG, Im WT, Oh HM, Lee ST (2009) Pedobacter composti sp. nov., isolated from compost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:345–349
Barrow GI, Feltham RKA (1993) Cowan and Steel’s manual for the identification of medical bacteria, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fautz E, Reichenbach H (1980) A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 8:87–91
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Collins MD (1985) Analysis of isoprenoid quinones. Methods Microbiol 18:329–366
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc., Newark
Ntougias S, Fasseas C, Fasseas C, Zervakis GI (2007) Olivibacter sitiensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from alkaline olive-oil mill wastes in the region of Sitia, Crete. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:398–404
Gallego V, Garcia MT, Ventosa A (2006) Pedobacter aquatilis sp. nov., isolated from drinking water, and emended description of the genus Pedobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1853–1858
Hwang CY, Choi DH, Cho BC (2006) Pedobacter roseus sp. nov., isolated from a hypertrophic pond, and emended description of the genus Pedobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1831–1836
Tang YL, Wang Y, Ji SM, Zhang KD et al (2010) Pedobacter xinjiangensis sp. nov., from the Desert, Xinjiang. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:397–402
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Park S, Oh TK (2007) Pedobacter lentus sp. nov. and Pedobacter terricola sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2089–2095
An DS, Kim SG, Ten LN, Cho CH (2009) Pedobacter daechungensis sp. nov., from freshwater lake sediment in South Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:69–72
Roh SW, Quan ZX, Nam YD, Chang HW, Kim K, Kim MY, Im WT, Jing L, Kim SH, Lee ST, Bae JW (2008) Pedobacter agri sp. nov., from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1640–1643
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2011AA090704, No. 2011AA10A205), National Department Public Benefit Research Foundation of China (Grant No. 200903052), and National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2011CB200906).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain 13-QT is JQ 083404.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Yy., Fu, Yb., Wang, My. et al. Pedobacter hainanensis sp. nov., Isolated from Seaside Soil. Curr Microbiol 66, 487–492 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0305-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0305-x