Abstract
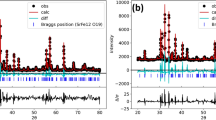
Sphene (CaTiSiO5), a calcium titanosilicate ceramic has been prepared from a powder mixture of CaCO3, TiO2 and SiO2 using vibro-milling for homogenization and activation of precursors. During the high-pressure and high-temperature synthesis (HPS) process at 4 GPa and 1,200 °C, sphene undergoes into phase transition, from room-temperature phase P21 /a to high-temperature phase A2/a. Evidence of that structural phase transition is given in this paper using infrared, Raman spectroscopy and X-ray powder diffraction. Rietveld refinement was employed to get the structural information of the synthesized powder. The most important structural change due to phase transition, the disappearance of the characteristic out-of-center distortion of the Ti atom and moving to the center of octahedra, was confirmed. HPS is an effective method for producing full-dense ceramics without any additives. Reduction of particle size occurred during high-pressure compaction. Microstructure and particle size of both phases were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angel RJ, Kunz M, Miletich R, Woodland AB, Koch M, Xirouchakis D (1999) High pressure phase transition in CaTiOSiO4 titanite. Phase Trans 68:533–543
Avvakumov E (1986) Mekhanicheskiye metody aktivatsii khimicheskikh protsessov. Nauka, Novosibirsk
Beirau T, Mihailova B, Matveeva G, Kolb U, Malcherek T, Groat LA, Bismayer U (2012) Structural anisotropy and annealing-induced nanoscale atomic rearrangements in metamict titanite. Am Miner 97:1354–1365
Benjamin JS (1992) Fundamentals of mechanical alloying. Mater Sci Forum 1:88–90
Bismayer U, Schmahl W, Schmidt C, Groat LA (1992) Linear birefringence and X-ray diffraction studies of the structural phase transition in titanite CaTiSiO5. Phys Chem Miner 19:260–266
Dana ES (1922) A text-book of mineralogy: with an extended treatise on crystallography and physical mineralogy, vol 316. Wiley, Chapman Hall, New York, London, pp 195–200
Dana ES (1959) Manual of mineralogy, 17th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 412–413
Downs RT, Hall-Wallace M (2003) The American Mineralogist Crystal Structure Database. Am Mineral 88:247–250
Dowty E (1987) Vibrational interactions of tetrahedra in silicate glasses and crystals: I. Calculations on ideal silicate–aluminate–germanate structural units. Phys Chem Miner 14:80–93
Gadsden JA (1975) Infrared spectra of minerals and related inorganic compounds, Butterworth, Group addresses, England, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, USA
Ghose S, Ito Y, Hatch DM (1991) Paraelectric–antiferroelectric phase transition in titanite, CaTiSiO5: a high temperature X-ray diffraction study of the order parameter and transition mechanism. Phys Chem Miner 17:591–603
Heyns AM, Harden PM, Prinsloo LC (2000) Resonance Raman study of the high-pressure phase transition in chromium-doped titanite, CaTiOSiO4. J Raman Spectrosc 31:837–841
Higgins B, Ribbe PH (1976) The crystal chemistry and space groups of natural and synthetic titanites. Am Miner 61:878–888
Kostov-Kytin V, Mihailova B, Kalvachev Y, Tarassov M (2005) Atomic arrangements in amorphous sodium titanosilicate precursor powders. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 86:223–230
Kunz M, Xirouchakis D, Lindsley DH, Hauserman D (1996) High-pressure phase transition in titanite (CaTiOSiO4). Am Miner 81:1527–1530
Kunz M, Arlt T, Stolz J (2000) In situ powder diffraction study of titanite (CaTiOSiO4) at high pressure and high temperature. Am Miner 85:1465–1473
LeBail A (1992) Extracting structure factors from powder diffraction data by iterating full pattern profile fitting. In: Prince E, Stalick JK (eds) Accuracy in powder diffraction II, special publication, vol 846. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, p 213
Mazurenko AM, Urbanovich VS, Kuchinski VM (1994) High pressure apparatus for sintering ceramics based on high-melting point compounds. News of the Academy of Science, ser. Phys Tech Sci 1:42–46 (in Russian)
Moenke H (1962) Mineralspectren. Deutsche Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, Berlin
Oberti R, Smith DC, Rossi G, Caucia F (1991) The crystal chemistry of high-aluminum titanites. Eur J Miner 3:777–792
Pantić J, Kahlenberg V, Poharc-Logar V, Kremenović A (2011) Natural CaO–TiO2–SiO2 based ceramics. Process Appl Ceram 5:79–84
Pantić J, Kremenović A, Došen A, Prekajski M, Stanković N, Baščarević Z, Matović B (2013) Influence of mechanical activation on sphene based ceramic material synthesis. Ceram Int 39:483–488
Ribbe PH (1982) Titanite. In: Ribbe PH (ed) Orthosilicates, Mineralogical Society of America. Rev Miner 5:137–155
Rodriguez-Carvajal J (1993) Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys B 192:55–69
Rodriguez-Carvajal J (1998) FullProf computer program. ftp://charybde.saclay.cea.fr/pub/divers/fullprof.98/windows/winfp98.zip
Rodríguez-Carvajal J (2001) Recent developments of the program FULLPROF. In: Commission on Powder Diffraction (IUCr). Newsletter 26:12-19. http://journals.iucr.org/iucr-top/comm/cpd/Newsletters/
Salje EKH, Bismayer U (1997) Hard mode spectroscopy: the concept and applications. Phase Trans 63:1–75
Speer JA, Gibbs GV (1976) The crystal structure of synthetic titanite, CaTiOSiO4 and the domain textures of natural titanites. Am Miner 1976(61):238–247
Su Y, Balmer ML, Bunker BC (2000) Raman spectroscopic studies of silicotitanates. J Phys Chem B 104:8160–8169
Taylor M, Brown GE (1976) High-temperature structural study of the P21 /a ↔A2/a phase transition in synthetic titanite, CaTiSiO5. Am Miner 61:435–447
Urbanovich VS (1996) Sintering at high pressures and properties of aluminum nitride ceramics. In: Trzeciakowski WA (ed) High pressure science and technology. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, pp 112–114
Urbanovich VS, Shkatulo GG (2003) Computerized system for the sintering of nanoceramics at high pressures. Powder Metall Met Ceram 42:19–23
Zachariasen WHZ (1930) The crystal structure of titanite. Krystallography 73:7–16
Zhang M, Salje E, Bismayer U, Unruh H, Wruck B, Schmidt C (1995) Phase transition(s) in titanite CaTiSiO5: an infrared spectroscopy, dielectric response and heat capacity study. Phys Chem Miner 22:41–49
Zhang M, Salje EKH, Bismayer U (1997) Structural phase transition near 825 K in titanite: evidence from infrared spectroscopic observations. Am Miner 82:30–35
Zhang M, Salje EKH, Capitani GC, Leroux H, Clark AM, Schluter J, Ewing RC (2000a) Annealing of α-decay damage in zircon: a Raman spectroscopic study. J Phys: Condens Matter 12:3131–3148
Zhang M, Salje EKH, Farnan I, Graem-Barber A, Danial P, Ewing RC, Clark AM, Leroux H (2000b) Metamictisation of circon: Raman spectroscopic study. J Phys: Condens Matter 12:1915–1925
Zhang M, Boatner L, Salje EKH, Ewing RC, Daniel P, Weber WJ, Zhang Y, Farnan I (2008) Micro-Raman and micro-infrared spectroscopic studies of Pb- and Au-irradiated ZrSiO4: optical properties, structural damage and amorpization. Phys Rev B 77:144110–1444113
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Serbian Education and Science Ministry in the Framework of Projects No. 45012 and 176016 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pantić, J., Urbanovich, V., Poharc-Logar, V. et al. Synthesis and characterization of high-pressure and high-temperature sphene (CaTiSiO5). Phys Chem Minerals 41, 775–782 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-014-0693-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-014-0693-x