Abstract
Background
Surgical radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with superior oncological outcome in comparison with percutaneous RFA. The present study aimed to retrospectively evaluate the relative perioperative safety and postoperative outcome of the laparoscopic or thoracoscopic approach versus the open approach to RFA for small HCC.
Methods
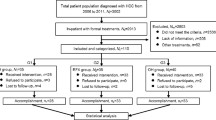
A retrospective analysis was performed in 55 consecutive patients who underwent open (n = 32) or laparoscopic/thoracoscopic (LTS) RFA (n = 23) for primary unresectable HCC between January 2005 and December 2010. Baseline characteristics, survival/recurrence rates, and complications after treatment were compared between the two groups.
Results
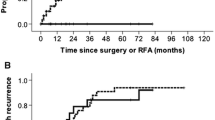
There was a trend showing that LTS RFA was performed for tumors located in the anterior segment (e.g., segments III, V, VIII). The LTS RFA group had a significantly lower intraoperative blood loss, shorter operative time, and shorter postoperative hospital stay, compared with the open RFA group. No major postoperative complications occurred in patients who underwent LTS RFA. No significant differences in overall survival, recurrence-free survival and local recurrence rates were observed between the two groups.
Conclusions
In consideration of operative invasiveness and postoperative recovery, LTS RFA is superior to the open approach in patients with small HCC. Moreover, the surgical outcome did not differ between the two approaches. Laparoscopic/thorascopic RFA can be considered to be a useful procedure for ablation therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Imamura H et al (2005) Prognostic impact of anatomic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 242:252–259
Fan ST, Ng IO, Poon RT et al (1999) Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: the surgeon’s role in long-term survival. Arch Surg 134:1124–1130
Regimbeau JM, Kianmanesh R, Farges O et al (2002) Extent of liver resection influences the outcome in patients with cirrhosis and small hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery 131:311–317
Livraghi T, Giorgio A, Marin G et al (1995) Hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis in 746 patients: long-term results of percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 197:101–108
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC et al (2004) Radiofrequency ablation improves prognosis compared with ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma ≤4 cm. Gastroenterology 127:1714–1723
Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S et al (2005) A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 129:122–130
Aramaki M, Kawano K, Ohno T et al (2004) Microwave coagulation therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 51:1784–1787
Teratani T, Yoshida H, Shiina S et al (2006) Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology 43:1101–1108
Huang JW, Hernandez-Alejandro R, Croome KP et al (2011) Surgical vs percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in dangerous locations. World J Gastroenterol 17:123–129
Komorizono Y, Oketani M, Sako K et al (2003) Risk factors for local recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma tumors after a single session, single application of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Cancer 97:1253–1262
Hori T, Nagata K, Hasuike S et al (2003) Risk factors for the local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a single session of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J Gastroenterol 38:977–981
Ueno S, Sakoda M, Kubo F et al (2009) Surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16:359–366
Yokoyama T, Egami K, Miyamoto M et al (2003) Percutaneous and laparoscopic approaches of radiofrequency ablation treatment for liver cancer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 10:425–427
Ballem N, Berber E, Pitt T et al (2008) Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term follow-up. HPB 10:315–320
Cassera MA, Potter KW, Ujiki MB et al (2011) Computed tomography (CT)-guided versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: a single-institution comparison of morbidity rates and hospital costs. Surg Endosc 25:1088–1095
Minami Y, Kudo M (2010) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: current status. World J Radiol 2:417–424
Izumi N (2011) Recent advances of radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:115–122
Machi J, Uchida S, Sumida K et al (2001) Ultrasound-guided radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver tumors: percutaneous, laparoscopic, and open surgical approaches. J Gastrointest Surg 5:477–489
Topal B, Hompes D, Aerts R et al (2007) Morbidity and mortality of laparoscopic vs. open radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. Eur J Surg Oncol 33:603–607
Tanaka S, Shimada M, Shirabe K et al (2009) Surgical radiofrequency ablation for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: an endoscopic or open approach. Hepatogastroenterology 56:1169–1173
Kim YS, Lee WJ, Rhim H et al (2010) The minimal ablative margin of radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma (>2 and <5 cm) needed to prevent local tumor progression: 3D quantitative assessment using CT image fusion. Am J Roentgenol 195:758–765
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Ohmori S et al (2002) Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment response based on tumor size and morphology. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:1225–1232
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H et al (2008) Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization versus hepatectomy. Radiology 247:260–266
Wong SN, Lin CJ, Lin CC et al (2008) Combined percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma in high-risk locations. Am J Roentgenol 190:187–195
Zhang YJ, Liang HH, Chen MS et al (2007) Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radiofrequency ablation with or without ethanol injection: a prospective randomized trial. Radiology 244:599–607
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakoda, M., Ueno, S., Iino, S. et al. Endoscopic versus Open Radiofrequency Ablation for Treatment of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J Surg 37, 597–601 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1868-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1868-6