Abstract
Purpose
Revision surgery for component malrotation in the painful TKA is a relatively novel indication. The purpose of this study was to assess the benefit of revision TKA for component malrotation with regard to the clinical and functional outcomes.
Methods
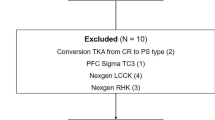
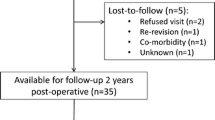
Our retrospective case–control study included 51 patients who underwent revision surgery for malrotation with mean follow up of 42 months. They were equally matched to patients who had surgery for aseptic loosening.
Results
Knee society scores improved from 44/49 to 75/60 (p < 0.001) for the study group and 44/47 to 76/57 (p < 0.001) for the control group. There was no statistical difference between the groups, including for VAS scores, narcotic reduction or patient satisfaction. Our study showed that revision surgery for malrotation is as beneficial as surgery for aseptic loosening with regard to clinical and functional outcome.
Conclusions
We recommend CT in painful TKA to assess component malrotation for which revision TKA is beneficial.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2011) Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry Annual Report for 2011. Australian Orthopaedic Association, Sydney
Mortazavi SM, Molligan J, Austin MS, Purtill JJ, Hozack WJ, Parvizi J (2011) Failure following revision total knee arthroplasty: infection is the major cause. Int Orthop 35:1157–1164. doi:10.1007/s00264-010-1134-1
Bourne RB, Chesworth BM, Davis AM, Mahomed NN, Charron KD (2010) Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:57–63. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-1119-9
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Eckhoff DG, Metzger RG, Vandewalle MV (1995) Malrotation associated with implant alignment technique in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 321:28–31
Hofmann S, Romero J, Roth-Schiffl E, Albrecht T (2003) Rotational malalignment of the components may cause chronic pain or early failure in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopade 32:469–476. doi:10.1007/s00132-003-0503-5
Incavo SJ, Wild JJ, Coughlin KM, Beynnon BD (2007) Early revision for component malrotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 458:131–136. doi:10.1097/BLO.0b013e3180332d97
Lakstein D, Zarrabian M, Kosashvili Y, Safir O, Gross AE, Backstein D (2010) Revision total knee arthroplasty for component malrotation is highly beneficial: a case control study. J Arthroplast 25:1047–1052. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.07.004
Pietsch M, Hofmann S (2012) Early revision for isolated internal malrotation of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(6):1057–1063. doi:10.1007/s00167-011-1637-3
Keating EM, Meding JB, Faris PM, Ritter MA (2002) Long-term followup of nonmodular total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:34–39
Jazrawi LM, Birdzell L, Kummer FJ, Di Cesare PE (2000) The accuracy of computed tomography for determining femoral and tibial total knee arthroplasty component rotation. J Arthroplast 15:761–766. doi:10.1054/arth.2000.8193
van der Linden-van der Zwaag HM, Bos J, van der Heide HJ, Nelissen RG (2011) A computed tomography based study on rotational alignment accuracy of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery. Int Orthop 35:845–850. doi:10.1007/s00264-010-1082-9
Rienmuller A, Guggi T, Gruber G, Preiss S, Drobny T (2012) The effect of femoral component rotation on the five-year outcome of cemented mobile bearing total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1628-0
Thompson JA, Hast MW, Granger JF, Piazza SJ, Siston RA (2011) Biomechanical effects of total knee arthroplasty component malrotation: a computational simulation. J Orthop Res 29:969–975. doi:10.1002/jor.21344
Colwell CW Jr, Chen PC, D’Lima D (2011) Extensor malalignment arising from femoral component malrotation in knee arthroplasty: effect of rotating-bearing. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 26:52–57. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2010.08.009
Vanbiervliet J, Bellemans J, Verlinden C, Vandenneucker H, Luyckx JP, Labey L, Innocenti B (2011) The influence of malrotation and femoral component material on patellofemoral wear during gait. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:1348–1354. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.93B10.26831
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the help of Leslie Stover who assisted in patient evaluation of functional outcome and Mathew MacDonald who assisted in collection of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sternheim, A., Lochab, J., Drexler, M. et al. The benefit of revision knee arthroplasty for component malrotation after primary total knee replacement. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 2473–2478 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1675-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1675-6