Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the relationships among cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of t-Tau, p-Tau and Aβ1-42 amyloid peptide and 123I-FP-CIT uptake.
Methods
The study included 58 subjects (31 men and 27 women, age 67 ± 9 years) with a clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease diagnosed according to the United Kingdom Parkinson Disease Society Brain Bank criteria. All subjects underwent a CSF assay 28 ± 3 days before 123I-FP-CIT SPECT scanning. The relationships were evaluated by means of linear regression analysis and Pearson correlation.
Results
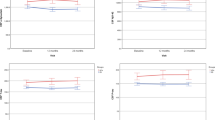
Striatal 123I-FP-CIT was positively related to both t-Tau and p-Tau CSF values with low levels of t-Tau and p-Tau being related to a low uptake of 123I-FP-CIT. In particular, differences with higher statistical significance were found for the striatum between the contralateral side and the side mainly affected on clinical examination (P < 0.001). No significant relationships were found between Aβ1-42 amyloid peptide and 123I-FP-CIT binding.
Conclusion
The results of our study suggest that the presynaptic dopaminergic system is more involved in Parkinson disease patients with lower t-Tau and p-Tau CSF values while values of Aβ1-42 amyloid peptide seems not to be related to nigrostriatal degeneration in our series.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schillaci O, Chiaravalloti A, Pierantozzi M, Di Pietro B, Koch G, Bruni C, et al. Different patterns of nigrostriatal degeneration in tremor type versus the akinetic-rigid and mixed types of Parkinson’s disease at the early stages: molecular imaging with 123I-FP-CIT SPECT. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28:881–6.
Del Tredici K, Braak H. Dysfunction of the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system and related circuitry in Parkinson’s disease-related dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84:774–83.
Chiaravalloti A, Stefani A, Di Biagio D, Pierantozzi M, Tavolozza M, Di Pietro B, et al. Cardiac sympathetic denervation is not related to nigrostriatal degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Nucl Med. 2013;27:444–51.
Halliday G, Lees A, Stern M. Milestones in Parkinson’s disease – clinical and pathologic features. Mov Disord. 2011;26:1015–21.
Playford ED, Brooks DJ. In vivo and in vitro studies of the dopaminergic system in movement disorders. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1992;4:144–71.
Treglia G, Cason E, Cortelli P, Gabellini A, Liguori R, Bagnato A, et al. Iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy and iodine-123 ioflupane single photon emission computed tomography in Lewy body diseases: complementary or alternative techniques? J Neuroimaging. 2014;24:149–54.
Blennow K, Dubois B, Fagan AM, Lewczuk P, de Leon MJ, Hampel H. Clinical utility of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2014.02.004.
Tamaoka A, Sawamura N, Odaka A, Suzuki N, Mizusawa H, Shoji S, et al. Amyloid beta protein 1-42/43 (A beta 1-42/43) in cerebellar diffuse plaques: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunocytochemical study. Brain Res. 1995;679:151–6.
Lei P, Ayton S, Finkelstein DI, Adlard PA, Masters CL, Bush AI. Tau protein: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:1775–8.
Medina M, Avila J. The role of extracellular Tau in the spreading of neurofibrillary pathology. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:113.
Consensus report of the Working Group on: “Molecular and Biochemical Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease”. The Ronald and Nancy Reagan Research Institute of the Alzheimer’s Association and the National Institute on Aging Working Group. Neurobiol Aging. 1998;19:109–16.
Kang JH, Irwin DJ, Chen-Plotkin AS, Siderowf A, Caspell C, Coffey CS, et al. Association of cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 1-42, T-tau, P-tau181, and α-synuclein levels with clinical features of drug-naive patients with early Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70:1277–87.
Attems J, Quass M, Jellinger KA. Tau and alpha-synuclein brainstem pathology in Alzheimer disease: relation with extrapyramidal signs. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113:53–62.
Hughes A, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992;66:181–4.
Fahn S, Elton RL, Committee motUD. Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale. Florhan Park HJ: Macmillan Healthcare Information; 1987
Teunissen CE, Tumani H, Bennett JL, Berven FS, Brundin L, Comabella M, et al. Consensus guidelines for CSF and blood biobanking for CNS biomarker studies. Mult Scler Int. 2011;2011:246412.
Dickson JC, Tossici-Bolt L, Sera T, de Nijs R, Booij J, Bagnara MC, et al. Proposal for the standardisation of multi-centre trials in nuclear medicine imaging: prerequisites for a European 123I-FP-CIT SPECT database. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:188–97.
Tatsch K, Asenbaum S, Bartenstein P, Catafau A, Halldin C, Pilowsky LS, et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine procedure guidelines for brain neurotransmission SPET using 123I-labelled dopamine transporter ligands. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:BP30–5.
Chang LT. A method for attenuation correction in radionuclide computed tomography. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1978:25:638–43.
Schillaci O, Chiaravalloti A, Travascio L, Floris R, Simonetti G. F-FDG PET/MR in herpes simplex virus encephalitis: A case study. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.remn.2013.10.002.
Schillaci O, Pierantozzi M, Filippi L, Manni C, Brusa L, Danieli R, et al. The effect of levodopa therapy on dopamine transporter SPECT imaging with (123)I-FP-CIT in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:1452–6.
Chiaravalloti A, Danieli R, Abbatiello P, Di Pietro B, Travascio L, Cantonetti M, et al. Factors affecting intrapatient liver and mediastinal blood pool 18F-FDG standardized uptake value changes during ABVD chemotherapy in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:1123–32.
Nakagawa S, Cuthill IC. Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2007;82:591–605.
Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988.
Abdo WF, Bloem BR, Van Geel WJ, Esselink RA, Verbeek MM. CSF neurofilament light chain and tau differentiate multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:742–7.
Montine TJ, Shi M, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Craft S, Ginghina C, et al. CSF Abeta(42) and tau in Parkinson’s disease with cognitive impairment. Mov Disord. 2010;25:2682–5.
Shi M, Bradner J, Hancock AM, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson disease diagnosis and progression. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:570–80.
Arima K, Hirai S, Sunohara N, Aoto K, Izumiyama Y, Ueda K, et al. Cellular co-localization of phosphorylated tau- and NACP/alpha-synuclein-epitopes in Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson’s disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res. 1999;843:53–61.
Muntane G, Dalfo E, Martinez A, Ferrer I. Phosphorylation of tau and alpha-synuclein in synaptic-enriched fractions of the frontal cortex in Alzheimer’s disease, and in Parkinson’s disease and related alpha-synucleinopathies. Neuroscience. 2008;152:913–23.
Blennow K, Hampel H, Weiner M, Zetterberg H. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:131–44.
Bajaj N, Hauser RA, Grachev ID. Clinical utility of dopamine transporter single photon emission CT (DaT-SPECT) with (123I) ioflupane in diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84:1288–95.
Hong Z, Shi M, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, et al. DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2010;133:713–26.
Zhang J, Sokal I, Peskind ER, Quinn JF, Jankovic J, Kenney C, et al. CSF multianalyte profile distinguishes Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:526–9.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiaravalloti, A., Stefani, A., Fiorentini, A. et al. Do CSF levels of t-Tau, p-Tau and β1-42 amyloid correlate with dopaminergic system impairment in patients with a clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease? A 123I-FP-CIT study in the early stages of the disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41, 2137–2143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2841-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2841-4