Abstract
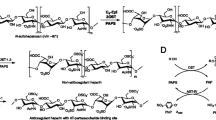
A bioengineered heparin, as a replacement for animal-derived heparin, is under development that relies on the fermentative production of heparosan by Escherichia coli K5 and its subsequent chemoenzymatic modification using biosynthetic enzymes. A critical enzyme in this pathway is the mammalian 6-O-sulfotransferase (6-OST-1) which specifically sulfonates the glucosamine residue in a heparin precursor. This mammalian enzyme, previously cloned and expressed in E. coli, is required in kilogram amounts if an industrial process for bioengineered heparin is to be established. In this study, high cell density cultivation techniques were exploited to obtain recombinant 6-OST-1. Physiological studies were performed in shake flasks to establish optimized growth and production conditions. Induction strategies were tested in fed-batch experiments to improve yield and productivity. High cell density cultivation in 7-l culture, together with a coupled inducer strategy using isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside and galactose, afforded 482 mg l−1 of enzyme with a biomass yield of 16.2 mg gcdw −1 and a productivity of 10.5 mg l−1 h−1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhaskar U, Sterner E, Hickey AM, Onishi A, Zhang F, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2012) Engineering of routes to heparin and related polysaccharides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1–16
Carvalho RJ, Cabrera-Crespo J, Tanizaki MM, Gonçalves VM (2012) Development of production and purification processes of recombinant fragment of Pneumococcal surface protein A in Escherichia coli using different carbon sources and chromatography sequences. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(3):683–694
Chen J, Avci FY, Munoz EM, McDowell LM, Chen M, Pedersen LC, Zhang L, Linhardt RJ, Liu J (2005) Enzymatic redesigning of biologically active heparan sulfate. J Biol Chem 280:42817–42825
De Mey M, De Maeseneire S, Soetaert W, Vandamme E (2007) Minimizing acetate formation in E. coli fermentation. J Ind Biotechnol 34:689–700
Donovan RS, Robinson CW, Glick BR (1996) Optimizing inducer and culture conditions for expression of foreign proteins under the control of the lac promoter. J Ind Microb 16:145–154
Guerrini M, Beccati D, Shriver Z, Naggi AM, Bisio A, Capila I, Lansing J, Guglieri S, Fraser B, Al-Hakim A, Gunay S, Viswanathan K, Zhang Z, Robinson L, Venkataraman G, Buhse L, Nasr M, Woodcock J, Langer R, Linhardt RJ, Casu B, Torri G, Sasisekharan R (2008) Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate is a major contaminant in heparin associated with adverse clinical events. Nat Biotechnol 26:669–775
Lee SY (1996) High cell-density culture of Escherichia coli. Tibtech 14:98–105
Lindahl U, Li JP, Kusche-Gullberg M, Salmivirta M, Alaranta S, Veromaa T, Emeis J, Roberts I, Taylor C, Oreste P, Zoppetti G, Naggi A, Torri G, Casu B (2005) Generation of “neoheparin” from E. coli K5 capsular polysaccharide. J Med Chem 48:349–352
Linhardt RJ (2003) Heparin: Structure and Activity. J Med Chem 46:2551–2554
Linhardt RJ, Liu J (2012) Synthetic heparin. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12:217–219
Liu H, Zhang Z, Linhardt RJ (2009) Lessons learned from the contamination of heparin. Nat Prod Rep 26:313–321
Paul P, Suwan J, Liu J, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2012) Recent advances in sulfotransferase enzyme activity assays. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:1491–1500
Restaino OF, Cimini D, De Rosa M, Catapano A, De Rosa M, Schiraldi C (2011) High cell density cultivation of Escherichia coli K4 in a microfiltration bioreactor: a step towards improvement of chondroitin precursor production. Microb Cell Factories 10:10
Shiloach J, Fass R (2005) Growing E. coli to high cell density—a historical perspective on method development. Biotechnol Adv 23(5):345–357
Wang Z, Ly M, Zhang F, Zhong W, Suen A, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2010) E. coli K5 fermentation and the preparation of heparosan, a bioengineered heparin precursor. Biotechnol Bioengineer 107:964–973
Wang Z, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2011a) E. coli K5 heparosan fermentation and improvement by genetic engineering. Bioengineered Bugs 2:1–15
Wang Z, Li J, Cheong S, Bhaskar U, Akihiro O, Zhang F, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2011b) Response surface optimization of the heparosan N-deacetylation in producing bioengineered heparin. J Biotechnol 156:188–196
Wang Z, Yang B, Zhang Z, Ly M, Takieddin M, Mousa S, Liu J, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2011c) Control of the heparosan N-deacetylation leads to an improved bioengineered heparin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:91–99
Weng YP, Hsu FC, Yang WS, Chen HP (2006) Optimization of the overexpression of glutamate mutase S component under the control of T7 system by using lactose and IPTG as the inducers. Enzym Microb Technol 38:465–469
Zhang Z, McCallum SA, Xie J, Nieto L, Corzana F, Jiménez-Barbero J, Chen M, Liu J, Linhardt RJ (2008) Solution structures of chemoenzymatically synthesized heparin and its precursors. J Am Chem Soc 130:12998–13007
Zhang F, Yang B, Ly M, Solakyildirim K, Xiao Z, Wang Z, Beaudet JM, Torelli AY, Dordick JS, Linhardt RJ (2011) Structural characterization of heparins from different commercial sources. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:2793–2803
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the USA–Italy Fulbright Commission to have selected Dr. Restaino as Fulbright Visiting Scientist and to have supported her during this work. This research was supported by grant HL096972 from the National Institutes of Health and by the Bioengineered Heparin Consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paper prepared for Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, November 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Restaino, O.F., Bhaskar, U., Paul, P. et al. High cell density cultivation of a recombinant E. coli strain expressing a key enzyme in bioengineered heparin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 3893–3900 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4682-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4682-z