Abstract
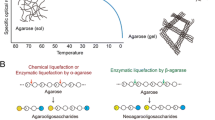
3,6-Anhydro-l-galactose (L-AHG) constitutes 50 % of agarose, which is the main component of red macroalgae. No information is currently available on the mass production, metabolic fate, or physiological effects of L-AHG. Here, agarose was converted to L-AHG in the following three steps: pre-hydrolysis of agarose into agaro-oligosaccharides by using acetic acid, hydrolysis of the agaro-oligosaccharides into neoagarobiose by an exo-agarase, and hydrolysis of neoagarobiose into L-AHG and galactose by a neoagarobiose hydrolase. After these three steps, L-AHG was purified by adsorption and gel permeation chromatographies. The final product obtained was 95.6 % pure L-AHG at a final yield of 4.0 % based on the initial agarose. In a cell proliferation assay, L-AHG at a concentration of 100 or 200 μg/ mL did not exhibit any significant cytotoxicity. In a skin whitening assay, 100 μg/ mL of L-AHG showed significantly lower melanin production compared to arbutin. L-AHG at 100 and 200 μg/ mL showed strong anti-inflammatory activity, indicating the significant suppression of nitrite production. This is the first report on the production of high-purity L-AHG and its physiological activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki C, Hirase S (1953) Studies on the chemical constitution of agar-agar. XV. Exhaustive mercaptolyses of agar-agar. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 26:463–467
Chen H-M, Zheng L, Yan X-J (2005) The preparation and bioactivity research of agaro-oligosaccharides. Food Technol Biotechnol 43:29–36
Chen H, Yan X, Zhu P, Lin J (2006) Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of agaro-oligosaccharides in vitro and in vivo. Nutr J 5:1–12
Day DF, Yaphe W (1975) Enzymatic hydrolysis of agar: purification and charaterization of neoagarobiose hyrolase and ρ-nitrophenyl α-galactoside hydrolase. Can J Microbiol 21:1512–1518
Ding AH, Nathan CF, Stuehr DJ (1988) Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages: comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol 141:2407–2412
Dooley TP (1997) Topical skin depigmentation agents: current products and discovery of novel inhibitors of melanogenesis. J Dermatol Treat 8:275–279
Ducatti DRB, Colodi FG, Goncalves AG, Duarte MER, Noseda MD (2011) Production of agaro- and carra-oligosaccharides by partial acid hydrolysis of galactans. Bras J Pharmacogn 21:296–304
Ekborg NA, Taylor LE, Longmire AG, Henrissat B, Weiner RM, Hutcheson SW (2006) Genomic and proteomic analyses of the agarolytic system expressed by Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3396–3405
Fu XT, Kim SM (2010) Agarase: review of major sources, categories, purification method, enzyme characteristics and applications. Mar Drugs 8:200–218
Ha SC, Lee S, Lee J, Kim HT, Ko H-J, Kim KH, Choi I-G (2011) Crystal structure of a key enzyme in the agarolytic pathway, α-neoagarobiose hydrolase from Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412:238–244
Hassairi I, Amar RB, Nonus M, Gupta BB (2001) Production and separation of α-agarase from Altermonas agarlyticus strain GJ1B. Bioresour Technol 79:47–51
Jol CN, Neiss TG, Penninkhof B, Rudolph B, De Ruiter GA (1999) A novel high-performance anion-exchange chromatographic method for the analysis of carrageenans and agars containing 3,6-anhydrogalactose. Anal Biochem 268:213–222
Kim C, Ryu HJ, Kim SH, Yoon J-J, Kim HS, Kim YJ (2010a) Acidity tunable ionic liquids as catalysts for conversion of agar into mixed sugars. Bull Korean Chem Soc 31:511–514
Kim HT, Lee S, Lee D, Kim H-S, Bang W-G, Kim KH, Choi I-G (2010b) Overexpression and molecular characterization of Aga50D from Saccharophagus degradans 2-40: an exo-type β-agarase producing neoagarobiose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:227–234
Kitamura Y, Abe Y, Yasui T (1991) Metabolism of levoglucosan (1,6-anhydro-β-d-glucopyranose) in microorganisms. Agric Biol Chem 55:515–521
Kobayashi R, Takisada M, Suzuki T, Kirimura K, Usami S (1997) Neoagarobiose as a novel moisturizer with whitening effect. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:162–163
Kuhn A, Yu S, Giffhorn F (2006) Catabolism of 1,5-anhydro-d-fructose in Sinorhizobium morelense S-30.7.5: discovery, characterization, and overexpression of a new 1,5-anhydro-d-fructose reductase and its application in sugar analysis and rare sugar synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1248–1257
Lee AK, Sung SH, Kim YC, Kim SG (2003) Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-α and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on I-κBα phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br J Pharmacol 139:11–20
Lee S, Lee JY, Ha SC, Jung J, Shin DH, Kim KH, Choi I-G (2009) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of neoagarobiose hydrolase from Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. Acta Crystallogr Sect F-Struct Biolo Cryst Commun 65:1299–1301
Maeda K, Fukuda M (1996) Arbutin: mechanism of its depigmenting action in human melanocyte culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:765–769
Miller IJ, Wong H, Newman RH (1982) A 13C N.M.R. study of some disaccharides from algal polysaccharides. Aust J Chem 35:853–856
Penney KB, Smith CJ, Allen JC (1984) Depigmenting action of hydroquinone depends on disruption of fundamental cell processes. J Investig Dermatol 82:308–310
Quemener B, Lahaye M, Metro F (1995) Assessment of methanolysis for the determination of composite sugars of gelling carageenans and agarose by HPLC. Carbohydr Res 266:53–64
Rees DA (1961) Enzymic synthesis of 3:6-anhydro-l-galactose within porphyran from l-galactose 6-sulphate units. Biochem J 81:347–352
Sekkal M, Huvenne J-P, Legrand P, Sombret B, Mollet J-C, Mouradi-Givernaud A, Verdus M-C (1993) Direct structural identification of polysaccharides from red algae by FTIR microspectrometry. I: localization of agar in Gracilaria verrucosa sections. Mikrochim Acta 112:1–10
Shin MH, Lee DY, Wohlgemuth G, Choi I-G, Fiehn O, Kim KH (2010) Global metabolite profiling of agarose degradation by Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. New Biotechnol 27:156–168
Stevenson TT, Furneaux RH (1991) Chemical methods for the analysis of sulfated galactans from red algae. Carbohydr Res 210:277–298
Su J-C, Hassid WZ (1962) Carbohydrates and nucleotides in the red algal Porphyra perforata. I. Isolation and identification of carbohydrates. Biochem 3:468–474
Sugano Y, Kodama H, Terada I, Yamazaki Y, Noma M (1994) Purification and characterization of a novel enzyme, α-neoagarooligosaccharide hydrolase (α-NAOS hydrolase), from a marine bacterium, Vibrio sp. strain JT0107. J Bacteriol 176:6812–6818
Tomono J, Sagawa H, Kato I (2009) Agarase and gene thereof. US Patent 7622291 B2
Tsuboi T, Kondoh H, Hiratsuka J, Mishima Y (1998) Enhanced melanogenesis induced by tyrosinase gene-transfer increases boron-uptake and killing effect of boron neutron capture therapy for amelanotic melanoma. Pigment Cell Res 11:275–282
Urabe K, Nakayama J, Hori Y (1998) Mixed epidermal and dermal hypermelanoses. In: Norlund JJ, Boissy RE, Hearing VJ (eds) The pigmentary system: physiology and pathophysiology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 909–911
Van Der Meulen HJ, Harder W (1976) Characterization of neoagarotetra-ase and neoagarobiase of Cytophaga flevensis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 42:81–94
Vera J, Alvarez R, Murano E, Slebe JC, Leon O (1998) Identification of a marine agarolytic Pseudoalteromonas isolate and characterization of its extracellular agarase. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4378–4383
Yamaji K, Sarker KP, Maruyama I, Hizukuri S (2002) Antioxidant effects of 1,5-anhydro-d-fructose, a new natural sugar, in vitro. Planta Med 68:16–19
Yang B, Yu G, Zhao X, Jiao G, Ren S, Chai W (2009) Mechanism of mild acid hydrolysis of galactan polysaccharides with highly ordered disaccharide repeats leading to a complete series of exclusively odd-numbered oligosaccharides. FEBS J 276:2125–2137
Yun EJ, Shin MH, Yoon J-J, Kim YJ, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2011) Production of 3,6-anhydro-l-galactose from agarose by agarolytic enzymes of Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. Process Biochem 46:88–93
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Grant (2011-0015629) funded by the Korean Government (MEST) and the Korea University Grant. Facility support at Korea University Food Safety Hall for the Institute of Biomedical Science and Food Safety is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, E.J., Lee, S., Kim, J.H. et al. Enzymatic production of 3,6-anhydro-l-galactose from agarose and its purification and in vitro skin whitening and anti-inflammatory activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 2961–2970 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4184-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4184-z