Abstract
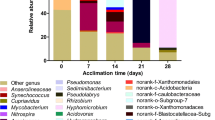
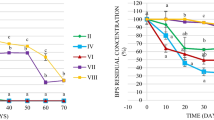
Bisphenol A (BPA) is one of the endocrine-disrupting chemicals that are ubiquitous in aquatic environments. Biodegradation is a major way to clean up the BPA pollution in sediments. However, information on the effective BPA biodegradation in anaerobic sediments is still lacking. The present study investigated the biodegradation potential of BPA in river sediment under nitrate- or sulfate-reducing conditions. After 120-day incubation, a high removal of BPA (93 or 89 %) was found in sediment microcosms (amended with 50 mg kg−1 BPA) under these two anaerobic conditions. Illumina MiSeq sequencing analysis indicated that Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Chloroflexi, Firmicutes, Gemmatimonadetes, and Actinobacteria were the major bacterial groups in BPA-degrading sediments. The shift in bacterial community structure could occur with BPA biodegradation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M, Gormley N, Gilbert JA, Smith G, Knight R (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624
Cha IT, Roh S, Kim SJ, Hong HJ, Lee HW, Lim WT, Rhee SK (2013) Desulfotomaculum tongense sp nov., a moderately thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a hydrothermal vent sediment collected from the Tofua Arc in the Tonga Trench. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:1185–1192
Chang BV, Chang IT, Yuan SY (2008) Anaerobic degradation of phenanthrene and pyrene in mangrove sediment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:145–149
Chang BV, Liu JH, Liao CS (2014) Aerobic degradation of bisphenol-A and its derivatives in river sediment. Environ Technol 35:416–424
Chang BV, Lu ZJ, Yuan SY (2009) Anaerobic degradation of nonylphenol in subtropical mangrove sediments. J Hazard Mater 165:162–167
Chang BV, Yuan SY, Chiou CC (2011) Biodegradation of bisphenol-A in river sediment. J Environ Sci Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 46:931–937
Chouhan S, Yadav SK, Prakash J, Swati, Singh SP (2014) Effect of Bisphenol A on human health and its degradation by microorganisms: a review. Ann Microbiol 2014(64):13–21
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Esteban S, Gorga M, Gonzalez-Alonso S, Petrovic M, Barcelo D, Valcarcel Y (2014) Monitoring endocrine disrupting compounds and estrogenic activity in tap water from Central Spain. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9297–9310
Esteban S, Gorga M, Petrovic M, Gonzalez-Alonso S, Barcelo D, Valcarcel Y (2014) Analysis and occurrence of endocrine-disrupting compounds and estrogenic activity in the surface waters of Central Spain. Sci Total Environ 466:939–951
Fuentes S, Mendez V, Aguila P, Seeger M (2014) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons: catabolic genes, microbial communities, and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4781–4794
Ike M, Jin CS, Fujita M (2000) Biodegradation of bisphenol A in the aquatic environment. Water Sci Technol 42:31–39
Ju F, Zhang T (2014) Novel microbial populations in ambient and mesophilic biogas-producing and phenol-degrading consortia unraveled by high-throughput sequencing. Microb Ecol 68:235–246
Kaksonen AH, Spring S, Schumann P, Kroppenstedt RM, Puhakka JA (2007) Desulfurispora thermophila gen. nov., sp nov., a thermophilic, spore-forming sulfate-reducer isolated from a sulfidogenic fluidized-bed reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1089–1094
Kamaraj M, Sivaraj R, Venckatesh R (2014) Biodegradation of Bisphenol A by the tolerant bacterial species isolated from coastal regions of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 93:216–222
Kang JH, Kondo F (2002) Bisphenol A degradation by bacteria isolated from river water. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 43:265–269
Kang JH, Kondo F (2005) BPA degradation in river water is different from that in seawater. Chemosphere 60:1288–1292
Kang JH, Ri N, Kondo F (2004) Streptomyces sp strain isolated from river water has high bisphenol A degradability. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:178–180
Kotowska U, Kapelewska J, Sturgulewska J (2014) Determination of phenols and pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewaters from Polish treatment plants by ultrasound-assisted emulsification-microextraction followed by GC-MS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:660–673
Li GY, Zu L, Wong PK, Hui XP, Lu Y, Xiong JK, An TC (2012) Biodegradation and detoxification of bisphenol A with one newly-isolated strain Bacillus sp GZB: kinetics, mechanism and estrogenic transition. Bioresour Technol 114:224–230
Liao XB, Chen C, Zhang JX, Dai Y, Zhang XJ, Xie SG (2014) Operational performance, biomass and microbial community structure: impacts of backwashing on drinking water biofilter. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3393-7
Luo YL, Guo WS, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD, Hai FI, Zhang J, Liang S, Wang XCC (2014) A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 473:619–641
Matsumura Y, Hosokawa C, Sasaki-Mori M, Akahira A, Fukunaga K, Ikeuchi T, Oshiman KI, Tsuchido T (2009) Isolation and characterization of novel bisphenol- A-degrading bacteria from soils. Biocontrol Sci 14:161–169
Ojha A, Mishra AK, Vashisht AK (2013) Isolation of phenol degrading bacteria from industrial waste water and their growth kinetic assay. J Pure Appl Microbiol 7:683–690
Sakai K, Yamanaka H, Moriyoshi K, Ohmoto T, Ohe T (2007) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and related compounds by Sphingomonas sp strain BP-7 isolated from seawater. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:51–57
Samaras VG, Stasinakis AS, Thomaidis NS, Mamais D, Lekkas TD (2014) Fate of selected emerging micropollutants during mesophilic, thermophilic and temperature co-phased anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 162:365–372
Selvaraj KK, Shanmugam G, Sampath S, Larsson DGJ, Ramaswamy BR (2014) GC-MS determination of bisphenol A and alkylphenol ethoxylates in river water from India and their ecotoxicological risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 99:13–20
Shi JH, Liu XW, Chen QC, Zhang H (2014) Spatial and seasonal distributions of estrogens and bisphenol A in the Yangtze River Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea. Chemosphere 111:336–343
Tan B, Dong XL, Sensen CW, Foght J (2013) Metagenomic analysis of an anaerobic alkane-degrading microbial culture: potential hydrocarbon-activating pathways and inferred roles of community members. Genome 56:599–611
Toyama T, Kainuma Y, Kikuchi S, Mori K (2012) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and 4-alkylphenols by Novosphingobium sp strain TYA-1 and its potential for treatment of polluted water. Water Sci Technol 66:2202–2208
Voordeckers JW, Fennell DE, Jones K, Haggblom MM (2002) Anaerobic biotransformation of tetrabromobisphenol A, tetrachlorobisphenol A, and bisphenol A in estuarine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 36:696–701
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang B, Huang B, Jin W, Wang Y, Zhao SM, Li FR, Hu P, Pan XJ (2012) Seasonal distribution, source investigation and vertical profile of phenolic endocrine disrupting compounds in Dianchi Lake, China. J Environ Monit 14:1275–1282
Wang B, Huang B, Jin W, Zhao SM, Li FR, Hu P, Pan XJ (2013) Occurrence, distribution, and sources of six phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in the 22 river estuaries around Dianchi Lake in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3185–3194
Wang Z, Yang Y, Sun W, Xie S, Liu Y (2014) Nonylphenol biodegradation in river sediment and associated shifts in community structures of bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 106:1–5
Wang L, Zhao JM, Li YM (2014) Removal of bisphenol A and 4-n-nonylphenol coupled to nitrate reduction using acclimated activated sludge under anaerobic conditions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:391–400
Watanabe M, Kojima H, Fukui M (2013) Desulfotomaculum intricatum sp nov., a sulfate reducer isolated from freshwater lake sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3574–3578
Winderl C, Penning H, von Netzer F, Meckenstock RU, Lueders T (2010) DNA-SIP identifies sulfate-reducing Clostridia as important toluene degraders in tar-oil-contaminated aquifer sediment. ISME J 4:1314–1325
Yang YY, Wang Z, Xie SG (2014) Aerobic biodegradation of bisphenol A in river sediment and associated bacterial community change. Sci Total Environ 470–471:1184–1188
Yuan HY, Yao J, Masakorala K, Wang F, Cai MM, Yu C (2014) Isolation and characterization of a newly isolated pyrene-degrading Acinetobacter strain USTB-X. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:2724–2732
Zhang WW, Yin K, Chen LX (2013) Bacteria-mediated bisphenol A degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5681–5689
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by special fund of the State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control (No. 14Y02ESPCP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yuyin Yang and Zhao Wang contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
(DOCX 94 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wang, Z., He, T. et al. Sediment Bacterial Communities Associated with Anaerobic Biodegradation of Bisphenol A. Microb Ecol 70, 97–104 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0551-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0551-x