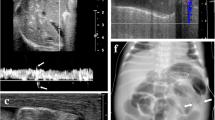
Abstract
Background
Abdominal radiography is the reference standard in imaging neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC); however, ultrasound of the abdomen including bowel may be of value in this setting.
Objective
To correlate sonographic and radiographic findings with patient outcomes in NEC.
Materials and methods
We reviewed sonographic and radiographic exams, as well as clinical, pathological and laboratory records. Ultrasound images were reviewed for free intraperitoneal gas, peritoneal fluid, pneumatosis intestinalis, portal gas, bowel vascularity, bowel wall thickness and echogenicity, peristalsis and the presence of dilated bowel with anechoic contents. Contemporaneously acquired radiographs were reviewed for intraperitoneal gas, pneumatosis intestinalis, portal gas, the sentinel loop sign and gas pattern. Patients were categorized into two groups based on clinical outcome.
Results
Forty-four neonates receiving 55 sonograms were included. Focal fluid collections, echogenic free fluid, increased bowel wall echogenicity and increased bowel wall thickness were statistically significant in predicting an unfavorable outcome. Other features approached significance in predicting poor outcomes: free peritoneal gas, pneumatosis intestinalis, aperistalsis, bowel wall thinning and absent bowel perfusion. Anechoic free peritoneal fluid predicted a good outcome. The sentinel loop sign on radiographs predicted an unfavorable outcome.
Conclusions
Abdominal sonography and radiography in patients with NEC can help prognosticate the outcome.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdon WE, Grossman H, Baker DH et al (1964) Necrotizing enterocolitis in the premature infant. Radiology 83:879–887
Buonomo C (1999) The radiology of necrotizing enterocolitis. Radiol Clin N Am 37:1187–1198, vii
Epelman M, Daneman A, Navarro OM et al (2007) Necrotizing enterocolitis: review of state-of-the-art imaging findings with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 27:285–305
Siegle RL, Rabinowitz JG, Korones SB et al (1976) Early diagnosis of necrotizing enterocolitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 127:629–632
Rabinowitz JG, Siegle RL (1976) Changing clinical and roentgenographic patterns of necrotizing enterocolitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 126:560–566
Daneman A, Woodward S, de Silva M (1978) The radiology of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). A review of 47 cases and the literature. Pediatr Radiol 7:70–77
Coursey CA, Hollingsworth CL, Wriston C et al (2009) Radiographic predictors of disease severity in neonates and infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:1408–1413
Silva CT, Daneman A, Navarro OM et al (2007) Correlation of sonographic findings and outcome in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Radiol 37:274–282
Faingold R, Daneman A, Tomlinson G et al (2005) Necrotizing enterocolitis: assessment of bowel viability with color Doppler US. Radiology 235:587–594
Dilli D, Suna Oguz S, Erol R et al (2011) Does abdominal sonography provide additional information over abdominal plain radiography for diagnosis of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates? Pediatr Surg Int 27:321–327
Miller SF, Seibert JJ, Kinder DL et al (1993) Use of ultrasound in the detection of occult bowel perforation in neonates. J Ultrasound Med 12:531–535
Kim WY, Kim WS, Kim IO et al (2005) Sonographic evaluation of neonates with early-stage necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Radiol 35:1056–1061
Bomelburg T, von Lengerke HJ (1992) Sonographic findings in infants with suspected necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur J Radiol 15:149–153
Azarow K, Connolly B, Babyn P et al (1998) Multidisciplinary evaluation of the distended abdomen in critically ill infants and children: the role of bedside sonography. Pediatr Surg Int 13:355–359
Goske MJ, Goldblum JR, Applegate KE et al (1999) The “circle sign”: a new sonographic sign of pneumatosis intestinalis—clinical, pathologic and experimental findings. Pediatr Radiol 29:530–535
Ein SH, Marshall DG, Girvan D (1977) Peritoneal drainage under local anesthesia for perforations from necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 12:963–967
Thyoka M, Eaton S, Kiely EM et al (2011) Outcomes of diverting jejunostomy for severe necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 46:1041–1044
Pierro A, Hall N, Ade-Ajayi A et al (2004) Laparoscopy assists surgical decision making in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 39:902–906, discussion 902–906
Wexler HA (1978) The persistent loop sign in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: a new indication for surgical intervention? Radiology 126:201–204
Leonard T Jr, Johnson JF, Pettett PG (1982) Critical evaluation of the persistent loop sign in necrotizing enterocolitis. Radiology 142:385–386
Weinstein MM (1986) The persistent loop sign in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: a new cause. Pediatr Radiol 16:71–72
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. J. Christopher Edgar for his assistance with the statistical calculations for this study. We are also grateful to Dr. Alan Daneman for his insight and guidance in preparing this manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muchantef, K., Epelman, M., Darge, K. et al. Sonographic and radiographic imaging features of the neonate with necrotizing enterocolitis: correlating findings with outcomes. Pediatr Radiol 43, 1444–1452 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2725-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2725-y