Abstract
Introduction
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) and extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM) are rare neurological disorders characterized by demyelination in and/or outside the pons. Whether diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) might facilitate an earlier diagnosis has not yet been studied systematically.
Methods
We describe demographics, clinical presentation, and early magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings with special emphasis on the relevance for diagnosis of CPM and/or EPM in eight patients.
Results
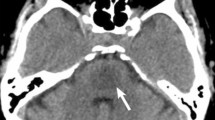
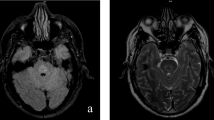
Of the analysed eight patients (aged 37–70 years; two men, six women), CPM was diagnosed in three, EPM in one, and a combination of CPM and EPM in four patients. Aetiology was rapid correction of sodium in two patients; a combination of hyponatremia, alcoholism and alcohol withdrawal in five patients and unclear in one patient. Seven patients suffered from chronic alcoholism and four from malnutrition. Demyelinating lesions were found in the pons, thalamus, caudate nucleus, putamen and midbrain. While the lesions could be clearly delineated on T2- and T1-weighted images, DWI demonstrated a strong signal in only six patients. Furthermore, DWI demonstrated lesions only to some extent in two patients and was completely negative in two patients on initial MRI. In none of the patients did the demonstration of hyperintense lesions on DWI precede detection on conventional MRI sequences. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values were heterogenous with a decrease in two cases and an increase in the remainder.
Conclusions
We conclude that early DWI changes are a common finding in CPM/EPM but do not regularly precede tissue changes detectable on conventional MRI sequences. Heterogenous ADC values possibly represent different stages of disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin RJ (2004) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: the osmotic demyelination syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(Suppl 3):iii22–iii28
Lohr JW (1994) Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia: association with hypokalemia. Am J Med 96:408–413
Tomlinson BE, Pierides AM, Bradley WG (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. Two cases with associated electrolyte disturbance. Q J Med 45:373–386
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Norenberg MD (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination: relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science 211:1068–1070
Gocht A, Colmant HJ (1987) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: a report of 58 cases. Clin Neuropathol 6:262–270
Pfister HW, Einhäupl KM, Brandt T (1985) Mild central pontine myelinolysis: a frequently undetected syndrome. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 235:134–139
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry 81:154–172
Laubenberger J, Schneider B, Ansorge O, Gotz F, Haussinger D, Volk B, Langer M (1996) Central pontine myelinolysis: clinical presentation and radiologic findings. Eur Radiol 6:177–183
Menger H, Jorg J (1999) Outcome of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis (n = 44). J Neurol 246:700–705
Cramer SC, Stegbauer KC, Schneider A, Mukai J, Maravilla KR (2001) Decreased diffusion in central pontine myelinolysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1476–1479
Chu K, Kang DW, Ko SB, Kim M (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR findings of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Acta Neurol Scand 104:385–388
Ruzek KA, Campeau NG, Miller GM (2004) Early diagnosis of central pontine myelinolysis with diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:210–213
van Everdingen KJ, van der Grond J, Kappelle LJ, Ramos LM, Mali WP (1998) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in acute stroke. Stroke 29:1783–1790
Kim JA, Chung JI, Yoon PH, Kim DI, Chung TS, Kim EJ, Jeong EK (2001) Transient MR signal changes in patients with generalized tonicoclonic seizure or status epilepticus: periictal diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1149–1160
Di Bonaventura C, Bonini F, Fattouch J, Mari F, Petrucci S, Carni M, Tinelli E, Pantano P, Bastianello S, Maraviglia B, Manfredi M, Prencipe M, Giallonardo AT (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in patients with partial status epilepticus. Epilepsia 50(Suppl 1):45–52
Sedlaczek O, Hirsch JG, Grips E, Peters CN, Gass A, Wohrle J, Hennerici M (2004) Detection of delayed focal MR changes in the lateral hippocampus in transient global amnesia. Neurology 62:2165–2170
Provenzale JM, Mukundan S, Barboriak DP (2006) Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MR imaging for brain tumor characterization and assessment of treatment response. Radiology 239:632–649
Kang EG, Jeon SJ, Choi SS, Song CJ, Yu IK (2010) Diffusion MR imaging of hypoglycemic encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:559–564
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345
Castriota-Scanderbeg A, Sabatini U, Fasano F, Floris R, Fraracci L, Mario MD, Nocentini U, Caltagirone C (2002) Diffusion of water in large demyelinating lesions: a follow-up study. Neuroradiology 44:764–767
Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Rocca MA, Comi G, Horsfield MA, Filippi M (2000) Pathologic damage in MS assessed by diffusion-weighted and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology 54:1139–1144
Chua GC, Sitoh YY, Lim CC, Chua HC, Ng PY (2002) MRI findings in osmotic myelinolysis. Clin Radiol 57:800–806
Graff-Radford J, Fugate JE, Kaufmann TJ, Mandrekar JN, Rabinstein AA (2011) Clinical and radiologic correlations of central pontine myelinolysis syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc 86:1063–1067
Kallakatta RN, Radhakrishnan A, Fayaz RK, Unnikrishnan JP, Kesavadas C, Sarma SP (2011) Clinical and functional outcome and factors predicting prognosis in osmotic demyelination syndrome (central pontine and/or extrapontine myelinolysis) in 25 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:326–331
King JD, Rosner MH (2010) Osmotic demyelination syndrome. Am J Med Sci 339:561–567
Eisele P, Szabo K, Griebe M, Roßmanith C, Förster A, Hennerici M, Gass A (2012) Reduced diffusion in a subset of acute ms lesions—a serial multiparametric MRI study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol (in press)
Shin HW, Song D, Sohn YH (2009) Normal diffusion-weighted MR imaging predicts a good prognosis in extrapontine myelinolysis-induced parkinsonism. Mov Disord 24:1701–1703
Dervisoglu E, Yegenaga I, Anik Y, Sengul E, Turgut T (2006) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging may provide prognostic information in osmotic demyelination syndrome: report of a case. Acta Radiol 47:208–212
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Förster, A., Nölte, I., Wenz, H. et al. Value of diffusion-weighted imaging in central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Neuroradiology 55, 49–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1083-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1083-z