Abstract
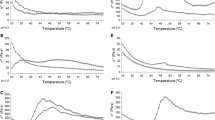
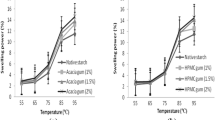
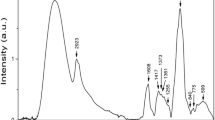
The rheological properties and microstructure of imitation cheeses containing 3%, w/w, pre-gelatinised maize, waxy-maize, wheat, potato or rice starches were compared to a control (0%, w/w, starch). Dispersions of pre-gelatinised rice or waxy-maize starches with casein had the highest viscosities following heating at 80 °C compared to casein heated alone or in mixtures with the other starches. Imitation cheese products containing pre-gelatinised starches had larger fat globule size distributions (especially rice or waxy-maize starch) and less homogeneous background protein matrices than the control as evidenced by scanning electron microscopy, which indicated poorer fat emulsification. The resultant imitation cheeses were softer, less cohesive and had reduced melting properties compared to the control. During processing, the pre-gelatinised starch competed with the rennet casein for water and impaired the caseins hydration as evidenced visually by delayed emulsification of free oil. Differences in levels of amylose retrogradation may have been responsible for variances in functionality between starches of different origins.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guinee TP, Caric M, Kalab M (2004) In cheese: chemistry, physics and microbiology, 3rd edn, vol 2. Major Cheese Groups. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 349–394
Mounsey JS, O’Riordan ED (2001) J Food Sci 66:586–591
Mounsey JS, O’Riordan ED (1999) J Food Sci 64:701–703
Ennis MP, Mulvihill DM (1999) Food Hydrocoll 13:325–337
Montesinos-Herrero C, Cottell DC, O’Riordan ED, O’Sullivan M (2006) Int Dairy J 16:910–919
Wu MC, Lanier TC, Hamann DD (1985) J Food Sci 50:20–25
Kong CS, Ogawa H, Iso N (1999) J Food Sci 64:283–286
Pellegrino L, Resmini P, De Noni I, Masotti F (1996) J Dairy Sci 79:725–734
IDF (1989) Bull IDF 239:1–20
Zwiercan GA, Lacrourse NL, Lenchin JM (1987) US Patent 4,695,475
IDF (1958) International Dairy Federation, Brussels (Standard FIL-IDF 4)
NSAI (1955) National Standards Authority of Ireland, Dublin (IS 69)
IDF (1993) International Dairy Federation, Brussels (Standard FIL-IDF 20B)
Olson NF, Price WV (1958) J Dairy Sci 41:999–1000
Szczesniak AS (1963) J Food Sci 28:385–389
Swinkels JJM (1985) Starch/Stärke 37:1–5
Hennelly PJ, Dunne PG, O’Sullivan M, O’Riordan ED (2005a) Eur Food Res Technol 220:415–420
Hennelly PJ, Dunne PG, O’Sullivan M, O’Riordan ED (2005b) J Food Eng 75:388–395
Carpenter RN, Finnie KJ, Olsen RL (1998) US Patent 5,807,601
Davies L (1995) Food Technology Europe June/July, pp 44–52
Morris ER (1991) In: Harris P (ed) Food gels. Elsevier Applied Science, London, UK, pp 291–359
Tolstoguzov VB (1991) Food Hydrocoll 4:429–468
Kim JM (1986) PhD Thesis, Department of Food Science and Nutrition, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI
Zobel HF (1988) Starch/Stärke 40:44–50
Conde-Petit B, Escher F (1994) Starch/Stärke 46:172–177
Stampanoni CR, Noble AC (1991) J Texture Stud 22:381–392
Guinee TP, Auty MAE, Mullins C (1999) Aust J Dairy Technol 54:84–89
Zhou N, Mulvaney SJ (1998) J Dairy Sci 81:2561–2571
Paulson BM, McMahon DJ, Oberg CJ (1998) J Dairy Sci 81:2053–2064
Biliaderis CG, Page CM, Slade L, Sirett RR (1985) Carbohydr Polym 5:367–389
Ring SC, Colonna P, I’Anson J, Kalichvesky MT, Miles MJ, Morris VJ, Orford PD (1987) Carbohydr Res 162:277–293
Eliasson AC, Gudmunson M (1996) In: Eliasson AC (ed) Carbohydrates in food. 1, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 431–503
Acknowledgments
This research has been funded by the Irish Department of Agriculture and Food under the Food Institutional Research Measure (National Development Plan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mounsey, J.S., O’Riordan, E.D. Modification of imitation cheese structure and rheology using pre-gelatinised starches. Eur Food Res Technol 226, 1039–1046 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0629-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0629-5