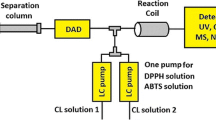
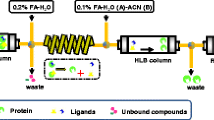
Abstract
Screening and analysis of bioactive compounds from natural products is challenging work due to their complexity. This study presents the first report on hyphenation of solid-phase ligand-fishing using immobilized xanthine oxidase microcolumn (IXOM) and high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detector–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–DAD–MS/MS) for screening and identification of XO inhibitors from complex mixtures. Solid-phase ligand-fishing system was hyphenated with the HPLC system via four-port switching valve and a six-port injection valve as an interface for transferring effluents from IXOM to HPLC, and collecting chromatograms from LFMC (ligand-fishing microextraction column) and C18 column in a run by only one DAD. Mixtures containing allopurinol (positive control) and tryptophane (negative control) were analyzed in order to verify the specificity and reproducibility of the approach. Subsequently, the newly developed system was applied to screening and identification of XO inhibitors from L. macranthoides and its human microsomal metabolites. Six prototype compounds (3-caffeoylquinic acid, 5-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid) and three metabolites (3-caffeoyl-epi-quinic acid, 5-caffeoyl-epi-quinic acid, 4-caffeoyl-epi-quinic acid) with XO binding affinities were identified. The XO inhibition activities of six prototype compounds were evaluated and confirmed using in vitro enzymatic assay. With the online system developed here, we present a feasible, selective, and effective strategy for rapid screening and identification of enzyme inhibitors from complex mixtures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang ZF, Leung ELH, Liu L, Jiang ZH, Zhong NS. Developing influenza treatments using traditional Chinese medicine. Science. 2015;347:S35–7.
Xu J, Xu QS, Chan CO, Mok DK, Yi LZ, Chau FT. Identifying bioactive components in natural products through chromatographic fingerprint. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;870:45–55.
Zhao HD, Hu X, Chen XQ, Shi SY, Jiang XY, Liang XJ, et al. Analysis and improved characterization of minor antioxidants from leaves of Malus doumeri using a combination of major constituents’ knockout with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1398:57–65.
Wang BC, Deng J, Gao YM, Zhu LC, He R, Xu YQ. The screening toolbox of bioactive substances from natural products: a review. Fitoterapia. 2011;82:1141–51.
Shi SY, Zhou HH, Zhang YP, Jiang XY, Chen XQ, Huang KL. Coupling HPLC to on-line, post-column (bio)chemical assays for high-resolution screening of bioactive compounds from complex mixtures. Trend Anal Chem. 2009;28:865–77.
Zhang YP, Shi SY, Xiong X, Chen XQ, Peng MJ. Comparative evaluation of three methods based on high-performance liquid chromatography analysis combined with a 2,2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl assay for the rapid screening of antioxidants from Pueraria lobata flowers. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402:2965–76.
Song HP, Chen J, Hong JY, Hao HP, Qi LW, Lu J, et al. A strategy for screening of high-quality enzyme inhibitors from herbal medicines based on ultrafiltration LC-MS and in silico molecular docking. Chem Commun. 2015;51:1494–7.
Mirzaei M, Mirdamadi S, Ehsani MR, Aminlari M, Hosseini E. Purification and identification of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptide from Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein hydrolysate. J Funct Foods. 2015;19:259–68.
Zhao HD, Zhang YP, Guo Y, Shi SY. Indentification of α-glucosidase inhibitors in Radix Astragali and its human microsomal metabolites using ultrafiltration HPLC–DAD–MSn. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015;104:31–7.
Wu L, Zhang QL, Zhang XY, Lv C, Li J, Yuan Y, et al. Pharmacokinetics and blood-brain barrier penetration of (+)-catechin and (−)-epicatechin in rats by microdialysis sampling coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:9377–83.
Li DQ, Zhao J, Li SP, Zhang QW. Discovery of xanthine oxidase inhibitors from a complex mixture using an online, restricted-access material coupled with column-switching liquid chromatography with a diode-array detection system. Anal Biochem Chem. 2014;406:1975–84.
Singh N, Ravichandran S, Spelman K, Fugmann SD, Moaddel R. The identification of a novel SIRT6 modulator from Trigonella foenum-graecum using ligand fishing with protein coated magnetic beads. J Chromatogr B. 2014;968:105–11.
Qing LS, Xue Y, Zheng Y, Xiong J, Liao X, Ding LS, et al. Ligand fishing from Dioscorea nipponica extract using human serum albumin functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217:4663–8.
Deng X, Shi SY, Li SM, Yang TL. Magnetic ligand fishing combination with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-mass spectrometry to screen and characterize cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors from green tea. J Chromatogr B. 2014;973:55–60.
An YX, Li X, Sun HM, Bian WH, Li ZJ, Zhang YY, et al. Target-directed screening of the bioactive compounds specifically binding to (2)-adrenoceptor in Semen brassicae by high-performance affinity chromatography. J Mol Recognit. 2015;28:628–34.
Wang SX, Zhao K, Zang WJ, Zhang Q, Zhao XF, Zhao M, et al. Highly selective screening of the bioactive compounds in Huoxue capsule using immobilized beta(2)-adrenoceptor affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 2014;457:1–7.
Zhang YP, Shi SY, Guo JF, You QP, Feng DS. On-line surface plasmon resonance-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of human serum albumin binders from Radix Astragali. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1293:92–9.
Marchesini GR, Buijs J, Haasnoot W, Hooijerink D, Jansson O, Nielen MWF. Nanoscale affinity chip interface for coupling inhibition SPR immunosensor screening with nano-LC TOF MS. Anal Chem. 2008;80:1159–68.
Wang SW, Wang C, Zhao X, Mao SL, Wu YT, Fan GR. Comprehensive two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography system with immobilized liposome chromatography column and monolithic column for separation of the traditional Chinese medicine Schisandra chinensis. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;713:121–9.
Wang Y, Kong L, Lei XY, Hu LH, Zou HF, Welbeck E, et al. Comprehensive two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography system with immobilized liposome chromatography column and reverse-phase column for separation of complex traditional Chinese medicine Longdan Xiegan Decoction. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216:2185–91.
Turiel E, Díaz-Álvarez M, Martín-Esteban A. Supported liquid membrane-protected molecularly imprinted beads for the solid phase micro-extraction of triazines from environmental waters. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1432:1–6.
Lashgari M, Lee HK. Micro-solid phase extraction of perfluorinated carboxylic acids from human plasma. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1432:7–16.
Schwarz LJ, Danylec B, Harris SJ, Boysen RI, Hearn MTW. Sequential molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction methods for the analysis of resveratrol and other polyphenols. J Chromatogr A. 2015;1438:22–30.
Liu J, Zhang J, Wang F, Zou YF, Chen XF. Isolation and characterization of new minor triterpenoid saponins from the buds of Lonicera macranthoides. Carbohydr Res. 2013;370:76–81.
Chen CY, Qi LW, Li HJ, Li P, Yi L, Ma HL, et al. Simultaneous determination of iridoids, phenolic acids, flavonoids, and saponins in Flos Lonicerae and Flos Lonicerae Japonicae by HPLC-DAD-ELSD coupled with principle component analysis. J Sep Sci. 2007;30:3181–92.
Li YJ, Chen J, Li Y, Li P. Identification and quantification of free radical scavengers in the flower buds of Lonicera species by online HPLC-DPPH assay coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr. 2012;26:449–57.
Ren MT, Chen J, Song Y, Sheng LS, Li P, Qi LW. Identification and quantification of 32 bioactive compounds in Lonicera species by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;48:1351–60.
Tang D, Li HJ, Chen J, Guo CW, Li P. Rapid and simple method for screening of natural antioxidants from Chinese herb Flos Lonicerae Japonicae by DPPH-HPLC-DAD-TOF/MS. J Sep Sci. 2008;31:3519–26.
Liu LL, Shi SY, Zhao HD, Yu JG, Jiang XY, Chen XQ. Selective fishing and analysis of xanthine oxidase binders from two Fabaceae species by coupling enzyme functionalized core-shell magnetic nanoparticles with HPLC-MS. J Chromatogr B. 2014;945–946:163–70.
Zhang SH, Hu X, Shi SY, Huang LQ, Chen W, Chen L, et al. Typical ultraviolet spectra in combination with diagnostic mass fragmentation analysis for the rapid and comprehensive profiling chlorogenic acids in the buds of Lonicera macranthoides. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:3659–72.
Hu X, Zhao HD, Shi SY, Li H, Zhou XL, Jiao FP, et al. Sensitive characterization of polyphenolic antioxidants in Polygonatum odoratum by selective solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography–diode array detector–quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015;112:15–22.
Okamoto K, Nishino T. Mechanism of inhibition of xanthine oxidase with a new tight binding inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7816–21.
Clifford MN, Johnston KL, Knight S, Kuhnert N. Hierarchical scheme for LC–MSn identification of chlorogenic acids. J Agric Food Chem. 2003;51:2900–11.
Moridani MY, Scobie H, Jamshizadeh A, Salehi P, O’Brien PJ. Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and dihydrocaffeic acid metabolism: glutathione conjugate formation. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001;29:1432–9.
dos Santos MD, Martins PR, dos Santos PA, Bortocan R, Iamamoto Y, Lopes NP. Oxidative metabolism of 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid), a bioactive natural product, by metalloporphyrin and rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26:62–70.
Jang DS, Yoo NH, Kim NH, Lee YM, Kim CS, Kim J, et al. 3,5-Di-O-caffeoyl-epi-quinic acid from the leaves and stems of Erigeron annuus inhibits protein glycation, aldose reductase, and cataractogenesis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33:329–33.
Ling X, Bochu W. A review of phytotherapy of gout: perspective of new pharmacological treatments. Pharmazie. 2014;69:243–56.
Hu X, Chen L, Shi SY, Cai P, Liang XJ, Zhang SH. Antioxidant capacity and phenolic compounds of Lonicerae macranthoides by HPLC–DAD–OTOF–MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016;124:254–60.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21275163), the Science and Technology Program of Hunan Province, China (2015NK3037), and the Shenghua Yuying project of Central South University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, MJ., Shi, SY., Chen, L. et al. Online coupling solid-phase ligand-fishing with high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detector–tandem mass spectrometry for rapid screening and identification of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in natural products. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 6693–6701 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9784-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9784-5